What Is Zero Trust Architecture In Cybersecurity?
Let’s keep it simple: Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a cybersecurity approach that assumes no one is trustworthy—not even your coworkers or devices inside your network. Every user, every device, every time—it all needs to be verified before access is granted.
In simple terms, Zero Trust means: “Never trust, always verify.”
You could think of it as a high-tech “show me your ID” system. Even if someone’s already in the building, they still need to prove they belong in every room they enter. This extra layer of security helps stop threats like data breaches, phishing attacks, or insider risks.
Understanding the Need for Zero Trust Architecture
Cyber threats are evolving daily, and traditional security models are struggling to keep up. In fact, according to a 2023 study, 81% of data breaches involve weak or stolen passwords. Shocking, right?
Now, let’s do a reality check. In today’s world, cyber threats are skyrocketing. Did you know:
- 81% of data breaches involve weak or stolen passwords.
- Cyberattacks cost businesses $4.45 million on average per breach.
Of course, once a hacker gets inside a traditional network, it’s game over. The “castle and moat” approach assumes everything inside is safe, but that’s no longer true. Cybercriminals are smarter, and insider threats are rising. This is where Zero Trust Architecture steps in to save the day.
Why Zero Trust Is Critical Today?
- Rise of Cyber Threats—Attackers are getting smarter, and insider threats are on the rise.
- Remote Work Explosion—With more employees working from home, securing devices and networks is a bigger challenge.
- Cloud Dependence—Companies store critical data in the cloud, which requires stronger protection.
Therefore, with Zero Trust in Action, you can achieve:
- Continuous Verification: Every user, device, and access request is verified.
- Access Segmentation: Users only get access to the resources they need—nothing more.
- Reduced Cyber Risks: Companies using Zero Trust report up to a 50% drop in security incidents.
In short, Zero Trust is your defensive system against modern cyber threats. Without it, you’re leaving your data vulnerable to breaches.
What are the 5 Core Principles of Zero Trust?
Let’s break down the 5 core principles of Zero Trust. These principles, coined by Gartner, form the backbone of this modern security model:
1. Zero Trust Is a Paradigm
Zero Trust isn’t just a set of rules; it’s a shift in how we approach security. The main idea is simple: don’t trust anything by default. No device, user, or network segment gets automatic trust. This approach makes everything more secure by default.
2. Assume the Presence of Hostile Actors
With zero trust mindset, we assume there are bad actors inside the system already. Cyber threats don’t just come from outside—they can come from within. So, by acting on the assumption that there is always a risk, you’re in a better position to stop any breaches before they escalate.
3. Establish Strong Identity
Every access request needs to be backed by strong identity verification. This basically implies that users, devices, and apps need to prove who they are before accessing anything. It’s all about ensuring that the person or device requesting access is who they say they are, often through multifactor authentication.
4. Limit Access to What’s Necessary
People don’t need access to everything. Zero Trust follows the principle of least privilege, meaning users only get access to what’s absolutely essential for their role. This minimizes the damage if a threat actor gets in.
5. Risk-Based Adaptive Access
Not every access request is equal. With risk-based adaptive access, the system evaluates the risk level of each request in real time. For example:
- Logging in from a trusted device? Lower risk.
- Accessing from an unknown location? Higher risk = more verification steps.
These principles are critical to implementing Zero Trust. By following them, organizations can make their systems more secure and reduce the chances of a serious breach. Zero Trust is about staying ahead of the threats and being prepared for anything.
5 Pillars of Zero Trust Architecture?
Zero Trust is becoming a standard in cybersecurity. The 5 pillars were introduced by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) to help organizations build an effective Zero Trust strategy. These pillars guide the key aspects of how you should secure your systems.
1. Identity
The first step is verifying who’s trying to access your system. Identity is the foundation of Zero Trust. You can’t just assume someone is trustworthy because they’re inside your network. You use methods like multi-factor authentication (MFA) to make sure the person asking for access is who they say they are.
2. Devices
The next step is ensuring the devices being used to access your network are secure. You can’t allow just any device into your systems. Devices need to meet specific security standards before they’re granted access. If a device is compromised or doesn’t meet security standards, it doesn’t get in.
3. Networks
With Zero Trust, the network is no longer trusted by default. Instead, network segmentation is used to separate different parts of the system. This means only the necessary resources are accessible, and access is granted based on user needs. If a breach happens in one part of the network, it doesn’t spread to others. Each access request is carefully reviewed.
4. Applications and Workloads
You also need to make sure your applications and workloads are protected. Access to these is based on the identity of the user and the security of the device they’re using. Every request for access is evaluated before being allowed to proceed. Only authorized users on secure devices are granted access to applications and workloads.
5. Data
Finally, Zero Trust puts a strong emphasis on data protection. Instead of just securing your network, it focuses on securing your data itself. This means identifying what data is critical, categorizing it, and ensuring only authorized individuals have access to sensitive information.
Each of these pillars work together and create a security model where you constantly verify and reassess who is accessing what. It’s not about trusting your network, it’s about verifying every access request. This approach helps protect systems by making sure you’re constantly evaluating risks.
How does Zero Trust Architecture Work?
As we already discussed, ZTA has cemented this strong principle, “Trust no one, verify everyone and everything.” It doesn’t trust anyone connected to the network, not even the company’s C-level executives.
Before granting a user access to the system, it verifies the person, and the device used to log in, and imposes privilege restrictions to limit access to data they do not need.
Before accessing the application, each user has to go through three steps of the architecture’s process.
Step 1: Identity Verification
When someone or something wants to connect to your system, Zero Trust doesn’t just assume they are legitimate. It checks for:
- Who is asking for access?
- What they’re trying to do, and
- Where they’re coming from.
This verification ensures that only authorized users, devices, and applications are given access.
Step 2: Evaluating The Risk
Once the identity is verified, the system evaluates the potential risk associated with the request. It looks at the context of the request, ensuring that there’s no suspicious activity or threats. This is done by checking traffic for signs of cyberattacks or the presence of sensitive data that shouldn’t be exposed.
Step 3: Implementing Policies
Finally, based on the risk assessment, Zero Trust calculates a risk score. If everything is secure, access is granted. If there’s any potential danger, access is restricted or blocked. This ensures that every connection is treated carefully and securely before it’s allowed to proceed.
Zero Trust requires full visibility into all traffic and users—nothing gets in without being verified. The architecture also works by segregating access based on a user’s needs, ensuring that someone only has access to what they need and nothing more.
At its core, Zero Trust forces constant verification, ensuring that even trusted users or systems can’t be relied upon without proper checks. It’s about securing access before the connection happens, making it much harder for threats to slip through unnoticed.
Benefits Of Zero Trust Architecture
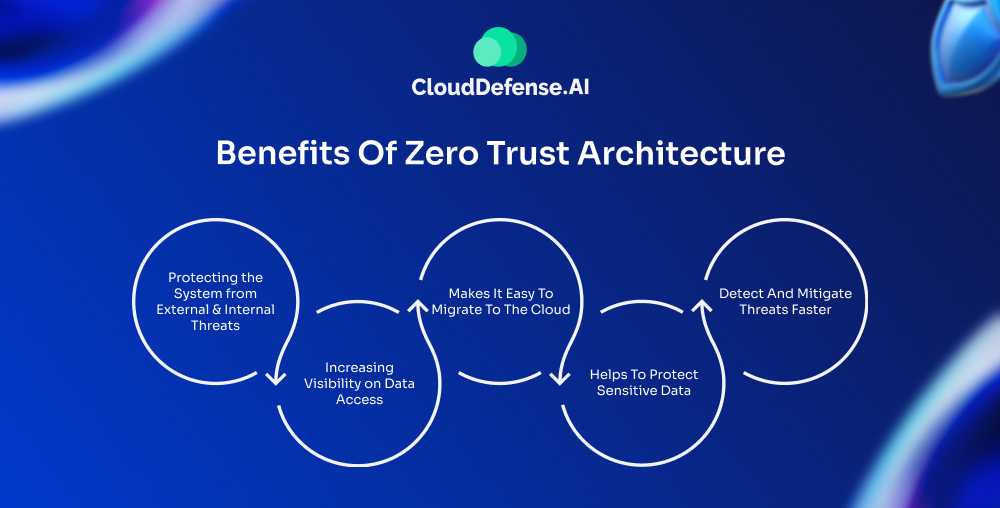
Organizations of all sorts love Zero Trust Architecture, as they witness fewer threats and data breaches from their system. We have outlined some of the zero trust benefits below.
Protecting the System from External and Internal Threats:
Intruding into a system from outside is relatively complex for hackers. As they need to use several methods to get in and exploit your data successfully. Some significant methods used by threat actors to attack a system externally include phishing attacks, malicious code, Trojans, DDoS attacks, etc.
External attackers primarily target an organization insider to gain access quickly. An unintended click on a phishing link opens the whole system to a hacker in seconds. Other than that, there are also employees in a company who intend to fiddle with the system, hoping to earn some money by selling company secrets.
With the Zero Trust Framework in action, Insiders and Outsiders are treated the same way when verifying their access to the network. Significantly reducing risks to your system.
Increasing Visibility on Data Access:
Access controls are a big plus in zero trust security, allowing users only to access the required data. The architecture is pre-loaded with data monitoring capabilities, which helps monitor how the user uses the data. This helps miraculously to identify any malicious activity and implement security measures.
Makes It Easy To Migrate To The Cloud:
Cloud migration has been rampant recently, with more companies opting for cloud-based environments. However, there are a lot of companies who are concerned about the amount of control they have over the cloud. Zero Trust strategy helps mitigate that by allowing the companies to place access control and data monitoring systems, making the cloud a more desirable place to be in.
Helps To Protect Sensitive Data:
Data breaches can be fatal for a company, and securing sensitive data should be its utmost priority. Zero Trust Architecture comes as a savior in this case. Besides its data monitoring and access control features, it also helps ensure that all the data is encrypted at rest and while being transferred, in turn, reducing data breaches.
Detect And Mitigate Threats Faster:
Zero Trust Architecture operates with a machine learning model that helps to automate threat detection and countermeasures. When a breach is detected, the framework mitigates the threat quickly before the impact materializes.
Adhering To Regulatory Compliance:
By uplifting the overall security measures in your organization, you are, in a sense, fulfilling all the regulatory requirements relative to your industry.
How Zero Trust Outshines Traditional Security Models?
Zero Trust beats traditional security models because it doesn’t make the mistake of trusting anything, ever. In older models, once you’re inside the network, you’re trusted—no questions asked. That’s a huge risk.
You could have a breach, and no one would know until it’s too late. Zero Trust changes that. It checks everything—every person, device, and request—before granting access. It doesn’t rely on “trusted” areas inside the network.
Every request gets verified, no exceptions. This constant, active verification makes Zero Trust tougher on attackers. Traditional systems don’t do that. They leave gaps. With Zero Trust, you get a stronger, more reliable system that always stays ahead of threats. It’s smarter, safer, and more effective.
Steps of Implementing Zero Trust
Developing a Zero Trust Architecture is essential to any company serious about protecting sensitive data. You can follow these zero trust principles to develop an effective Zero Trust Architecture Framework.
- Defining An Attack Surface: Identifying the probable surface attack is essential for Zero Trust cyber security. This includes all your devices, databases, applications, clients, and networks.
- Controlling Network Traffic: Implementing network controls to your network helps you monitor its traffic and identify anything malicious.
- Implementing Zero Trust: Now comes the part where you implement the core principle of Zero Trust, “Trusting no one on the network.”. Applying Multi-Factor Authentication for vetting users before granting access and setting up a next-gen firewall for segmenting the network can help to achieve this.
- Real-time Network Monitoring: Constantly monitoring your network can ensure real-time protection for your system. This also helps to identify threats and mitigate them rapidly.
Zero Trust Use Cases
Companies hire remote workers more these days as it is considered more productive. These remote workers often need to access IT assets from a different location, which can pose risks to the network. Other than remote workers, Multinational companies have branches worldwide connected to the HQ. ZTA ensures security in these connected locations.
Third-party vendors and other contractors often need to connect to a company’s digital assets to provide their services, and it is also essential to secure these connections.
A report by Cisco predicted there will be approximately 14.7 billion IoT devices by 2023. IoT devices are the most vulnerable devices that cyber attackers can easily hack. Therefore, IoT devices connected to a network need to be secured by a framework such as Zero Trust Policy.
What Are The Main Zero Trust Best Practices?

These are some of the best practices you can implement for zero trust architecture.
Verifying User With MFA:
Multi-factor authentication can help reduce hacks by phishing and malware attacks by replacing user IDs and passwords. MFA is used to authenticate a user’s identity before they are granted access to the server. Multi-layered security should be applied at every stage or process in your company, even if it is very minor.
Validating The Devices:
Verifying a device connected to the network is just as important as verifying the users. A compromised account can be used from any device, and your system needs to detect that. Allowing only trusted devices to access your system can be a great way to reduce threats.
Keep Your Security Measures Updated:
An effective security system needs to be constantly updated to keep it at par with new threats emerging in the market. Always ensure you have resources ready to update your system or change the required components.
Implementing Access Limit:
Employees often have too much access to company resources and data. This puts your company at risk just in case one of your employees has compromised accounts or devices. Access limit provides the least possible access to your staff, allowing them to view and use the required data to complete their tasks.
FAQ
Check out some of people’s queries regarding Zero Trust Architecture.
What are the 7 pillars of Zero Trust Architecture?
These are the 7 Zero Trust Pillars:
- Making sure devices are secured.
- Make sure the network is secured.
- Implementing a Zero-trust principle to protect data.
- Implementing automation for zero trust architecture.
- Increasing visibility on all activities.
- Making sure the employees are kept secure.
- Protecting all IT assets involved in the country.
What is the main goal of Zero Trust?
Zero trust mainly wants to protect your system by regulating the access your users are given and constantly verifying their identity.
Why Zero Trust is the future?
Zero trust is a robust security system that people love. In an age where it is tough to trust any new connection to the system, the zero trust approach can be considered a future security feature. Plus, the rise of cloud computing asks for a security feature that can adapt to its scalability.
What are the three main concepts of Zero Trust?
The three main concepts of a zero trust model are awareness of all the risks involved, implementing privilege controls, and constantly verifying all users and devices trying to connect to the system.
Conclusion
A shift to cloud computing meant that companies could run more efficiently, but also introduced more security challenges when it came to protecting sensitive data. According to IBM’s 2023 Data Breach report, the average cost of a data breach is $4.45 Million this year. This is highly alarming and also tells us how expensive data breaches can be for a company.
The inception of Zero Trust Architecture has greatly helped in solving this one big problem that cloud computing had, making it more effective. A robust security feature that is as strict as it should be to protect your expensive data and other company resources.







