Zero Day Malware Explained!
Zero-day malware refers to a type of malicious software that exploits vulnerabilities in software or systems that are unknown to the developer or vendor. These vulnerabilities, known as zero-day vulnerabilities, have not yet been patched or addressed by security updates. As a result, zero day malware can take advantage of these vulnerabilities to infiltrate systems and execute attacks before security measures can be put in place.
Unlike traditional malware, which may be detected by antivirus software using known signatures, zero-day malware operates undetected because its signature is unknown or unavailable to most antivirus solutions. This makes zero-day malware particularly dangerous as it can spread rapidly and cause significant damage before countermeasures can be developed and deployed.
What is a Zero Day Vulnerability?
A zero-day vulnerability refers to a software vulnerability or flaw that is unknown to the developer or vendor and has not yet been patched or addressed through security updates. This vulnerability creates an opportunity for malicious actors to exploit the software or system before a patch or fix is developed and deployed. When a malicious actor exploits such a vulnerability to launch an attack, it is known as a zero-day attack.
In the context of zero day malware, these vulnerabilities serve as entry points for malware to infiltrate systems, steal data, or cause other forms of damage. The term “zero day” signifies the lack of awareness or defense against the vulnerability at the time of the attack, highlighting the urgency for organizations to respond swiftly to mitigate the risk posed by zero-day threats.
Examples of Zero Day Malware
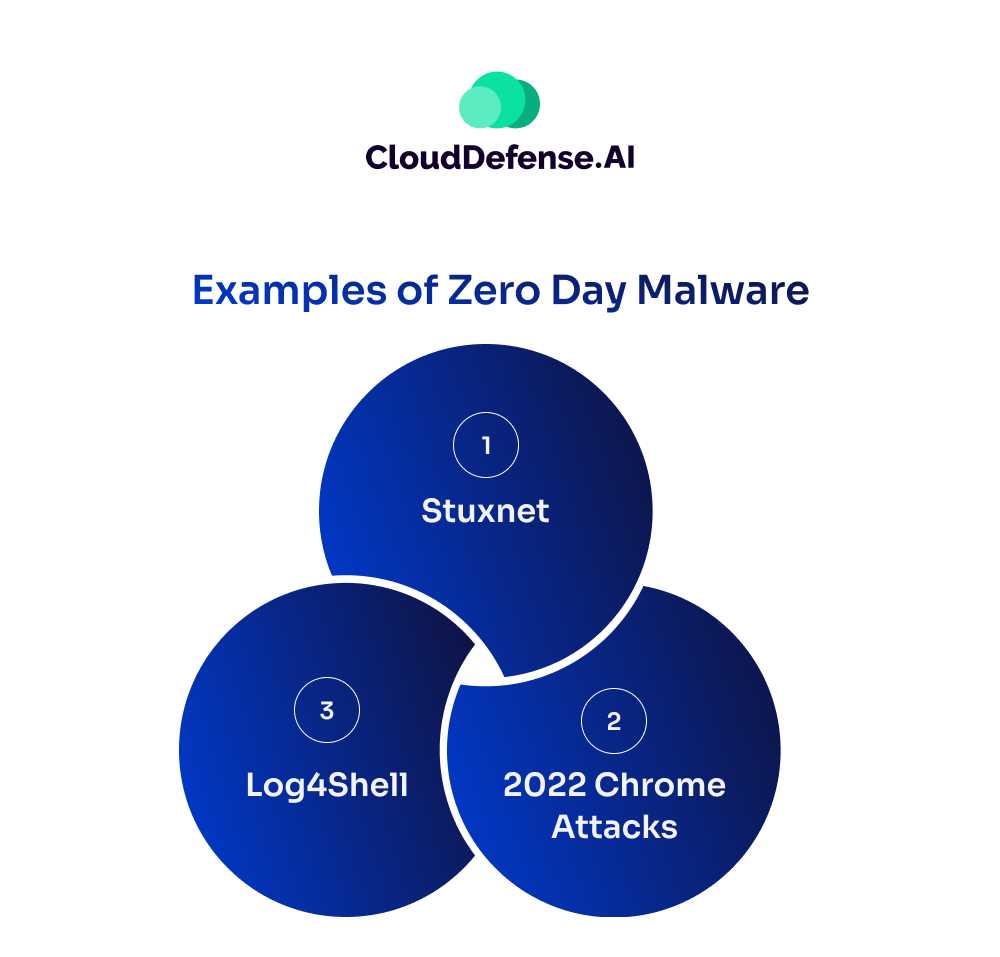
Zero day malware can affect a company any moment. Here are a few examples of widely known zero day malware.
Stuxnet
Launched in 2010, Stuxnet was a sophisticated computer worm designed to target nuclear facilities in Iran. It exploited multiple zero-day vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows operating systems, causing significant damage to centrifuges used for uranium enrichment.
2022 Chrome Attacks
In early 2022, North Korean hackers exploited a zero-day remote code execution vulnerability in Google Chrome browsers. They used phishing emails to lure victims to malicious sites, installing spyware and remote access malware on their machines.
Log4Shell
Discovered in 2021, Log4Shell exploited a zero-day vulnerability in Log4J, a widely used Java logging library. This flaw allowed hackers to remotely control devices running Java apps, posing a severe risk to millions of devices.
Why Traditional Cybersecurity Strategies Are Ineffective Against Zero Day Malware?
Traditional cybersecurity strategies often fall short in combating zero-day malware due to their reliance on known vulnerabilities and established patterns. Zero-day malware exploits vulnerabilities that are newly discovered and often lack patches or signatures, rendering traditional defenses ineffective.
Strategies such as patch management, which rely on applying updates to address known vulnerabilities, are futile against zero-day threats since patches are not yet available. Similarly, signature-based detection systems, which identify malware based on known patterns, cannot detect zero-day malware due to the absence of established signatures.
Additionally, exploit detection methods, which detect exploitation of vulnerabilities, are ineffective without the presence of signatures for zero-day vulnerabilities. In the ongoing race between cyber defenders and exploit developers, the advantage often lies with the latter when organizations rely solely on traditional cybersecurity approaches.
How to Prevent Zero Day Malware?
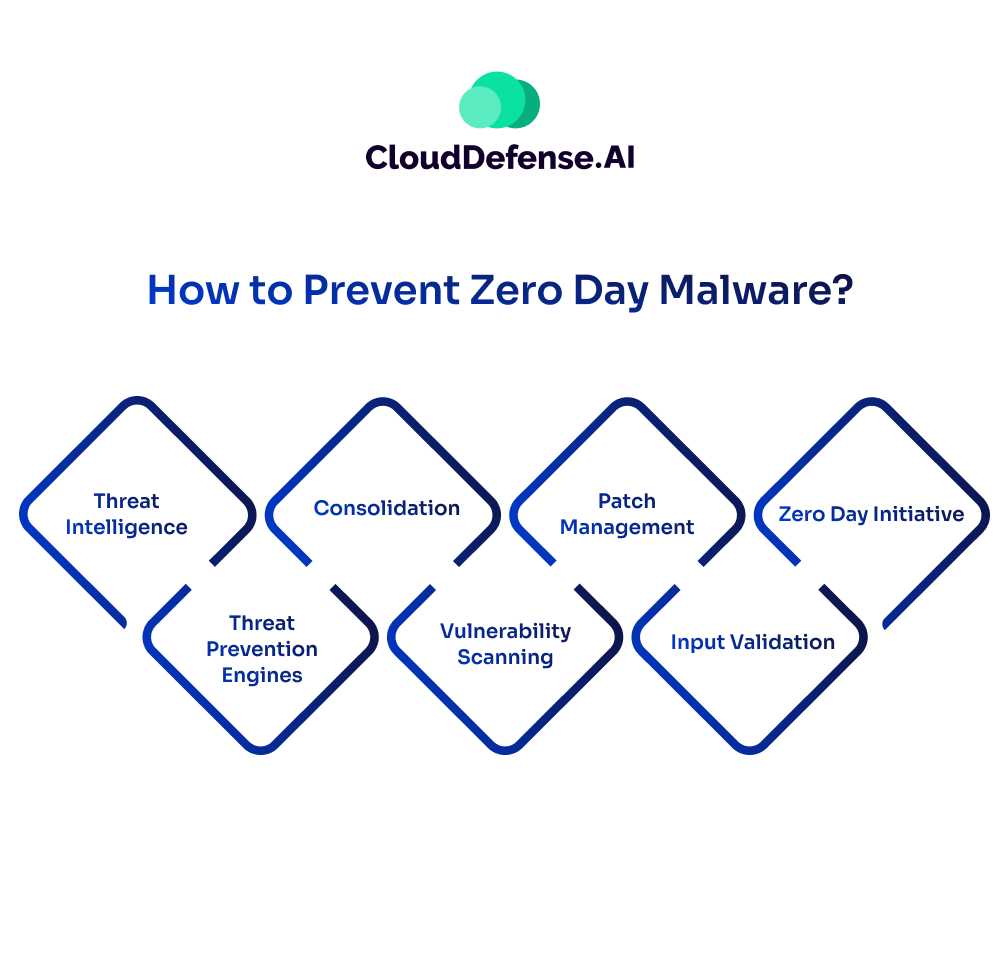
Even though most security measures fall flat when it comes to provide protection against zero day malware attacks, these are a few ways you can prevent this harmful malware.
1. Threat Intelligence
Utilize comprehensive threat intelligence databases, such as Threatcloud, which leverage AI to analyze vast amounts of data and detect zero-day malware campaigns early.
2. Threat Prevention Engines
Deploy threat prevention engines that monitor for suspicious activities and techniques commonly used by malware, such as return-oriented programming or known malicious code, to detect and block zero-day malware.
3. Consolidation
Implement consolidated security solutions that streamline an organization’s security architecture, enabling coordinated and automated responses against threats, including zero-day malware attacks.
4. Vulnerability Scanning
Regularly scan for vulnerabilities in software code, simulate attacks, and review code for errors to detect and address potential zero-day exploits. Act promptly on the results of vulnerability scans to prevent exploitation.
5. Patch Management
Ensure prompt deployment of software patches upon discovering vulnerabilities to reduce the risk of zero-day attacks. However, recognize that patch management alone may not prevent attacks if exploits are developed before patches can be deployed.
6. Input Validation
Implement input validation measures to thoroughly test and validate input supplied by applications or users, preventing improperly formed data from entering the system and mitigating the risk of zero-day attacks.
7. Zero Day Initiative
Participate in programs like the Zero Day Initiative, which incentivizes security researchers to disclose vulnerabilities rather than sell them on the black market. Encourage bug bounty programs to compensate individuals for reporting vulnerabilities, building a community of researchers dedicated to identifying and addressing software vulnerabilities before they are exploited by hackers.
How Can CloudDefense.AI Help Protect from Zero Day Malware?
CloudDefense.AI is at the forefront of preventing zero-day malware attacks, offering a comprehensive suite of solutions customized to protect cloud-native applications. Their exclusive Hacker’s View™ solution provides valuable insights by continuously monitoring for vulnerabilities and potential pathways of intrusion, empowering organizations to anticipate and mitigate attacks proactively.
CloudDefense.AI’s Noise Reduction technology prioritizes critical risks, allowing users to focus on actionable insights and effectively reduce actual threats. Through simplified integration with development processes, their “Code to Cloud” approach ensures that security best practices are embedded from the earliest stages, preventing vulnerabilities from propagating into production environments.
With an all-inclusive security suite covering infrastructure scanning, real-time threat detection, and automatic remediation, CloudDefense.AI delivers comprehensive protection for cloud environments. Moreover, their user-friendly dashboard makes threat management accessible to both technical and non-technical users, enabling informed decision-making and swift response to security incidents.
By using CloudDefense.AI’s expertise and proactive prevention measures, organizations can effectively defend against zero-day malware. Book a free demo now to learn more about this next-gen cloud-based security solution.







