What is Two-Factor Authentication?
Two-factor authentication, also known as two-step verification, is a security process where users have to go through two separate authentication processes. It is a subset of a multi-factor authentication process where users are cross-verified in two different ways before they are given access to an application or network.
Usually, the first step involves entering user details and credentials. The second step involves verification through email, security token, biometric, or other authenticator tool. Two-Factor Authentication is implemented to bolster the protection of both the user’s credentials and organization’s resources.
It adds another strong layer of security to basic single-factor authentication. It makes it tougher for attackers to exploit lost or stolen credentials of users and gain access to the organization’s resources.
Nowadays, every cloud service provider is implementing 2FA to protect against phishing and social engineering attacks. So even if an attacker gets their hands on credentials, they won’t be able to access sensitive systems.
What are Authentication Factors?
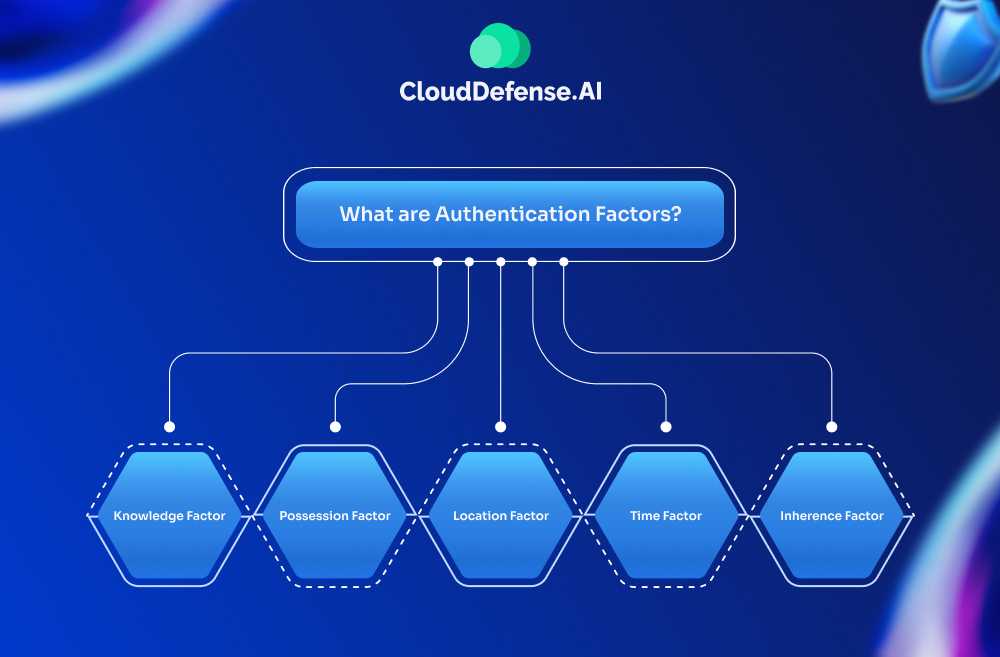
Authentication factors are those that help in confirming the identity of the actual users. It is a piece of information that users need to provide to a tool.
The authentication factors in 2FA mostly utilize possession and inherence factors for identification. Besides, there are many other authentication factors that are used for verification. Here are some common ones:
Knowledge Factor
It is the most authenticator factor used by security professionals. Knowledge factors verify the user’s identity by requesting the secret information that the user knows.
It usually indicates information like PIN, or any shared secret or password. This is private information and that is why it is used for identification.
Possession Factor
The possession factor is widely used because it is usually something that the user possesses or owns. The identity is verified by requesting the user to provide proof of information that the user can only possess.
It usually includes an ID card, driver’s license, mobile device, or a smartphone with an authenticator app. Tokens are the most common possession factors that are generated through authenticator apps. The app generates a passcode that keeps on changing so that attackers can’t guess the pattern and gain entry.
Location Factor
This usually involves identifying the location of the users from where the user is attempting to authenticate their identity. In this authentication factor, security professionals curb the authentication limit to specific devices in their usual location.
The limitation is often set by identifying the geographical location of the authentication source through IP address or GPS data. When an employee has registered from one specific geographical location. If all of a sudden they try to log in from different locations, it causes discrepancy.
Time Factor
It is a highly useful authentication factor type where authentication time is restricted to a specific time window. The user can log in to the organization’s service within a specific time.
Any other access attempt outside the specific time window will be restricted or sometimes blocked. This is usually suitable when the organization doesn’t want its employees to access certain resources or information beyond working hours.
Inherence Factor
Often known as a biometric factor, this factor indicates something that that user inherits in their physical self. It involves identifying any user using attributes that belong to the physical self of the user.
The attributes are mostly physical characteristics like fingerprints or faces that are mapped by the users. The fingerprint is the most common inherence factor because fingerprints, especially of the thumb, are unique for every individual in the world.
Voice recognition and behavioral biometrics are used as inherence factors. The users are identified based on their speech patterns, keystroke dynamics, and gait.
Despite the large number of authentication factors, most of the organization relies on the knowledge and possession factor. However, some high-end facilities involve an inherence factor.
How Does Two-Factor Authentication Work?
The working of two-factor authentication involves multiple steps. The process starts when a user attempts to access a service, network, or application. Here are detailed step-by-step guide of 2FA works:
Step-1: Providing Login Credentials
When an employee or user tries to log in or access an application, system, or network, they are tasked to provide the necessary credentials. The credentials are usually username and password. It serves as the first stage of the 2FA process.
Step 2: Initial Authentication
If the user credentials match the stored credentials in the website or application, then the system recognizes that the correct credentials have been given. The users recognize the employee or users trying to access the system.
Step 3: Alternate Initial Authentication
In some cases, the system or application might not require the user to enter login credentials. Instead, it generates a security key for the users based on specific factors.
When the user uses the security key, it is processed by the authentication. If there is a match, then the server moves to the second authentication process.
Step-4: Providing Second Authentication Factor
After initial authentication, the users are requested to put their second authentication factor. It is usually the possession, knowledge, or location factors that are preferred.
However, it entirely depends upon the authentication tool used by the organization. So if a service uses a possession factor for authentication, it will send a unique code to the mobile or email.
Sometimes it might generate a code through a specific authenticator tool like Google Authenticator. You will have to provide the second authenticator factor to the application.
Step-5: Final Authentication
Once the code is entered, the authenticator will verify it. If it is verified, the user will be authenticated and given access to the application or service.
However, if it fails, the user is prompted to repeat the process. In some cases, trying more than three times locks the account for the day.
How to Enable Two-Factor Authentication(2FA)
The process to enable two-factor authentication varies from website to website. Moreover, not all websites or applications come with two-factor authentication.
The process of enabling 2FA is pretty simple. Here we will provide two examples of activating two-factor authentication:
- Step-1: Open LinkedIn and head to the settings.
- Step 2: Open the Sign-in and Security option and look for two-step verification.
- Step 3: Enable the two-step verification.
- Step 1: Open your Google Account.
- Step 2: Head to the left navigation panel and open the Security tab.
- Step 3: Look for the Signing into Google option and select the two-factor verification option.
- Step 4: Follow the instruction for setting up 2FA using Google Authenticator through the smartphone.
Amazon
- Step-1: Open your Amazon account and click on the Login & Security option.
- Step 2: Click on the two-step verification Settings and enable it.
- Step 3: You will have to select the second authentication factor and follow the on-screen instructions.
Different Types of Two-Factor Authentication
When it comes to two-factor authentication, various types of 2FA help in the authentication process. Here are some common 2FA that are mostly utilized:
1. Hardware Token: Hardware tokens are the most common type used for authentication. It is a key-fob device that generates a random number after every 30 seconds.
During the 2FA authentication, users can open the key-fob device and put the number displayed on the device. Nowadays USB devices are also used for hardware tokens.
When a user tries to log into an account, they will have to enter the USB device and the system will automatically grab authentication from it.
2. Text Message: Text messages also serve as a popular 2FA factor that is used for authentication. When a user attempts to log in to their service or network, a message with a unique code is sent to the specific mobile device.
Many financial services, e-commerce sites, and banks still use this 2FA factor. However, organizations are shifting to other 2FA factors as there is a risk of intercepting messages by hackers.
3. Mobile Devices: Nowadays mobile devices, especially smartphones have become an effective choice for authentication. Fingerprint recognition, facial recognition through a camera, and voice recognition through a microphone have become a common 2FA factor.
Some organizations also leverage the GPS location to verify the location of the user as an additional 2FA factor.
Importantly, authenticator applications like Google Authenticator have become a popular choice. It changes the one-time code every 30 seconds, making it difficult for an attacker to get unauthorized entry.
4. Push Notification: Another well-known 2FA factor is push notification. To authenticate a user, the authentication system sends push notifications through specified applications.
The notification shows that a user is trying to access the application or service. If you have made the access request, you can tap on the approval button. However, if someone else is trying to get an unauthorized entry, you need to tap on the Decline button.
Benefits of Two-Factor Authentication

The key benefits of two-factor authentication are immense and help organizations in many ways. These benefits are:
Reduces Attack Surface
Two-factor authentication serves as a crucial solution that helps reduce the attack surface in an organization. Maintaining a large number of passwords with appropriate hygiene is a daunting task.
Attackers often exploit such vulnerabilities and perform identity theft. However, introducing 2FA makes it almost impossible for the attacker to bypass the second authentication step.
Reassures Consumer Identity
Identity theft is a common issue that affects organizations across industries. Attackers due to human error can steal login credentials and steal sensitive data.
When two-factor authentication is implemented, it creates an additional protection layer for the user account. So even if an attacker steals login credentials, they won’t be able to retrieve the second piece of information.
Simple to Implement
Two-factor authentication is quite simple to implement and they are non-invasive. Neither does it introduce complexity in the workflow or system of the organization nor consume a lot of resources.
It comes with a user-friendly authentication process that helps users to pick them up with zero effort.
Helps in Building Zero-Trust Security Model
Two-factor authentication plays a vital role in helping organizations to build a zero-trust security model. What this model does is that it assumes all the users, devices, or applications connected to the system are not trustworthy.
It ensures all the internal and external users and networks require additional authentication to pass through. It helps in bolstering the access points with an additional security layer.
Promotes BYOD Policies
In the massive surge of the work-from-home model, organizations are moving towards BYOD policies. It is causing them to allow devices and external networks to access their system having sensitive data.
Cyberattackers often exploit this opportunity to attack the system. However two-factor authentication requires the employees to go through an additional authentication process and when authenticated they get the entry.
Leveraging Hardware Advancements
The advancement of hardware and computing capabilities has been eminent in recent times. Nowadays traditional users are gradually shifting to powerful hardware and making use of modern equipment.
Thus, using two-factor authentication for securing data does make sense for every organization as both the parties are properly equipped. If one of the entities doesn’t leverage the capabilities of 2FA, then the whole implementation becomes completely useless.
Helps in Complying With Industry Standards
Two-factor authentication has been highly useful in helping organization comply with industry standards.
By introducing an additional layer, it protects the system from unauthorized access to sensitive data. It ensures only the designated employee or user can access the data that the account possesses.
Quick Comparison of 2FA vs MFA
2FA and MFA are two popular authentication processes that are widely used by organizations across the industry.
The two-factor authentication may be a subset of multi-factor authentication but they are different from each other in some aspects. The major difference between the two is that 2FA needs only an additional authentication process to verify a user.
2FA offers a convenient and useful authentication process where the user needs to input only one authentication factor. Even if an attacker steals an employee’s credentials, it won’t be able to steal the additional authenticator factor lying with the employee.
2FA might use only one additional authentication factor. But it usually involves strict authentication factors like location behavior, biometrics, Mobile Push, and many other stringent factors. This makes it extremely difficult for attackers to get access.
MFA on the other requires the user to go through multiple authentication processes before they are granted access to the account. Since attackers have to go through multiple authentication factors, it becomes difficult for them to get unauthorized entry.
Importantly, MFA forms an important component of the IAM solution as it perfectly ensures that the user trying to access the account is who they claim to be. However, the security offered by MFA entirely relies on authentication methods utilized in the process.
MFA mostly relies on OTP, FaceID, password, and secret questions for authentication. So MFA might involve a lot of authentication methods but the 2FA authentication process is much more secure.
Conclusion
Two-factor authentication has become a common choice before any user is given access to any service or application. Since it uses more than login credentials, it has become effective in minimizing unauthorized entry to networks or applications carrying sensitive data.
Even though 2FA has been used by many, still there are some security flaws that researchers are trying to overcome. As time goes on, researchers are coming up with better authentication factors that are hard to capture.







