What is Spear Phishing?
Spear phishing is a highly targeted and deceptive cyberattack designed to trick specific individuals, groups, or organizations into revealing sensitive information, installing malware, or transferring funds to attackers. Unlike generic phishing scams, spear phishing leverages personalized details to create convincing messages that appear to come from trusted sources.
These attacks are often delivered via email, text messages, chat platforms, or even phone calls. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, phishing remains the leading cause of data breaches, with spear phishing being among the most effective methods. A report by Barracuda revealed that while spear phishing accounts for less than 0.1% of all emails, it contributes to a staggering 66% of successful breaches.
The average cost of a phishing-related breach is $4.76 million, but spear phishing attacks can escalate damages to as much as $100 million. Combating this threat requires combining employee training with sophisticated detection tools to mitigate risks.
How Does a Spear-Phishing Attack Work?
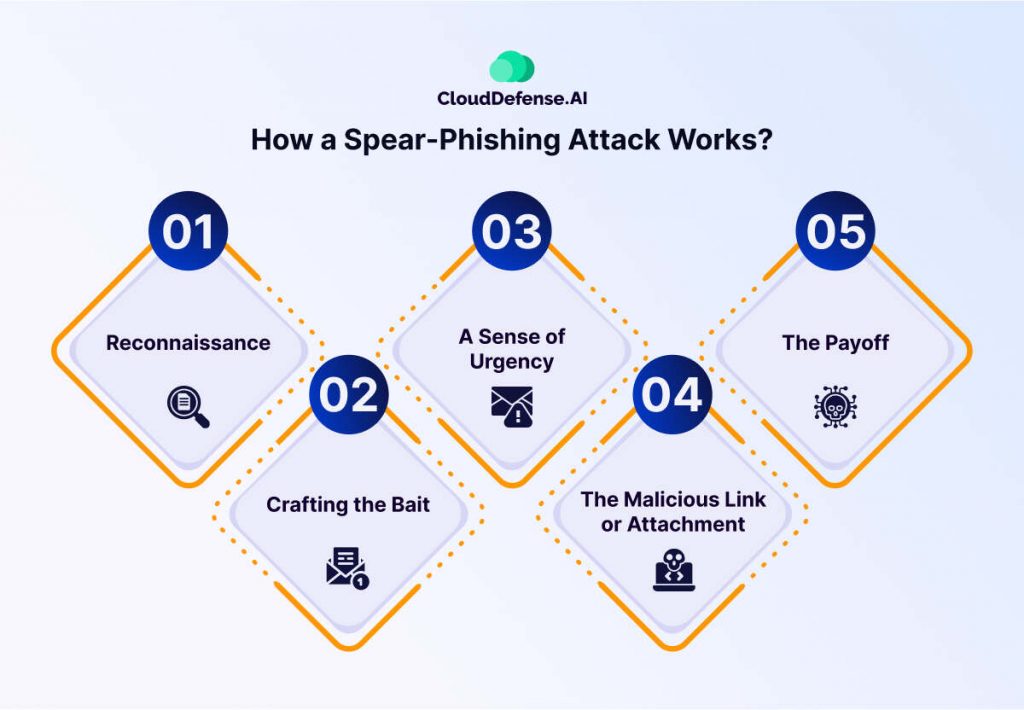
Spear phishing attacks are planned cyber scams designed to exploit trust and bypass defenses. These attacks unfold in distinct, calculated steps:
Reconnaissance
Attackers start by gathering detailed information about their target. They scour social media profiles, corporate websites, and even publicly available databases to piece together valuable details. This may include job titles, email addresses, ongoing projects, or personal interests, all of which help personalize their attack.
Crafting the Bait
Using the gathered intelligence, attackers create highly convincing messages. These emails often impersonate trusted figures, such as a company executive, a coworker, or a known vendor. They may reference specific projects, deadlines, or events to add authenticity. Personalized subject lines and content make the email appear legitimate.
Creating Urgency
To prompt quick, uncritical actions, attackers include urgent calls to action like “immediate response required,” “time-sensitive task,” or “critical update needed.” This urgency plays on the recipient’s instincts, clouding their judgment.
Delivering the Payload
The scam’s core lies in malicious links or attachments within the email:
- Links: Victims are directed to fake login pages designed to steal credentials.
- Attachments: Files containing malware infect devices upon download, granting attackers access to the system.
Exploitation
Once the target clicks the link or opens the attachment, attackers gain their desired access. This might involve:
- Stealing sensitive data or credentials.
- Installing malware to infiltrate the organization’s network.
- Manipulating the victim into making fraudulent financial transactions.
Spear phishing thrives on trust, urgency, and personalization. Combating it requires a mix of employee vigilance, robust email filtering, and advanced cybersecurity measures to detect and block these targeted attacks.
Spear Phishing vs Phishing vs Whaling:
Understanding the distinctions between phishing, spear phishing, and whaling is crucial in defending against these cyber threats. While they share similarities, their scope, tactics, and targets vary significantly.
Phishing: The Broad Attack
Phishing is the most common type of email attack, often executed at scale. These emails:
- Tactics: Use generic scare tactics like “Your account has been suspended!” or enticing offers such as “Claim your free prize now!”
- Characteristics: Contain generic greetings (“Dear Customer”) and are riddled with grammatical errors, making them easier to spot.
- Goal: Operates as a numbers game, relying on casting a wide net to lure unsuspecting victims into clicking malicious links or downloading malware.
Spear Phishing: The Targeted Strike
Spear phishing is a more calculated and focused form of phishing, where attackers:
- Tactics: Conduct detailed reconnaissance to craft highly personalized messages. These emails often appear to be from trusted sources, referencing specific details like job roles, projects, or colleagues.
- Characteristics: Precision-crafted to exploit human trust, making them more convincing and harder to detect than generic phishing emails.
- Goal: Gain access to sensitive data, install malware, or trick the recipient into financial fraud.
Whaling: The High-Stakes Scam
Whaling takes spear phishing to the next level by targeting high-profile individuals, such as C-suite executives or prominent public figures.
- Tactics: Exploits insider knowledge about deals, board meetings, or major transactions to craft compelling and highly believable emails.
- Characteristics: Professional, free of errors, and often disguised as critical business communications or urgent financial requests.
- Goal: Steal confidential data, initiate massive financial transfers, or tarnish the victim’s reputation.
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | Phishing | Spear Phishing | Whaling |
| Target Audience | Broad | Specific individuals/organizations | High-profile individuals |
| Research Effort | Low | Medium | High |
| Email Personalization | Generic | Targeted | Highly personalized |
| Attack Goal | Steal data, login credentials | Same as Spear Phishing + financial gain, compromise systems | Same as Whaling + damage reputation |
While phishing casts a wide net, spear phishing and whaling zero in on specific individuals, with whaling targeting the most influential figures. Defending against these attacks requires vigilance, cybersecurity training, and robust security measures tailored to each type of threat.
How to Prevent Spear Phishing Attacks
Spear phishing attacks can be cunning, but there are steps you can take to protect yourself and minimize the risk of falling victim. Here are some key strategies to fortify your defenses:
1. Scrutinize Sender Information: Don’t be fooled by a familiar name in the sender’s field. Double-check the email address itself. Spear phishers often use addresses that closely resemble legitimate ones, with slight variations in spelling or extra characters.
2. Beware of Urgency Tactics: Be wary of emails that create a sense of urgency or panic. Phrases like “urgent,” “important,” or “time-sensitive” are often red flags. Legitimate senders are unlikely to pressure you into immediate action.
3. Verify Requests Directly: If you receive an email requesting sensitive information or urging you to click on a link, don’t respond directly. Instead, contact the sender through a trusted channel, like a phone call or a verified email address, to confirm the legitimacy of the request.
4. Hover Over Links (Before Clicking): Most email platforms allow you to hover your cursor over a link to see the actual URL it directs to. Be suspicious of links with nonsensical lettering or those that don’t match the text displayed in the email.
5. Beware of Attachments: Unless you’re expecting an attachment from a specific sender, avoid opening them altogether. Spear phishers often use malicious attachments disguised as documents or invoices.
6. Educate Yourself (and Others): Staying informed about the latest spear phishing tactics is crucial. Familiarize yourself with common red flags and share this knowledge with colleagues, friends, and family.
7. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification step beyond your password when logging into accounts. This makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain access even if they steal your login credentials.
8. Keep Software Updated: Outdated software often contains vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Regularly update your operating system, web browser, and other applications to patch these vulnerabilities and minimize the risk of malware infection.
9. Report Suspicious Emails: If you receive a suspicious email, report it to your IT department or email provider. This helps them track phishing campaigns and develop better filtering mechanisms.
Conclusion
So, there you have it! Spear phishing is a complex threat, but with the right strategies, you can protect yourself and your organization from falling victim. By staying vigilant, questioning unexpected requests, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, you can turn skepticism into your strongest defense in the digital age.
For businesses, protecting sensitive data and applications requires more than just awareness—it demands a proactive, comprehensive security strategy. Solutions like CloudDefense.AI provide cutting-edge tools to secure cloud environments and applications against even the most advanced threats. With features like real-time threat detection, vulnerability management, and robust phishing defense, it ensures your infrastructure stays resilient against cyberattacks.
Curious about what true protection looks like? Schedule a free demo with CloudDefense.AI and discover how it can fortify your organization’s defenses. Stay ahead of the curve and protect what matters most—your data, your applications, and your peace of mind.







