What is Remote Access Trojan (RAT)?
A remote access trojan, or RAT, is a type of malware designed to enable an attacker to gain unauthorized control over a victim’s computer remotely.
Typically disguised as legitimate content, RATs are often distributed through seemingly harmless channels such as email attachments or bundled with unthreatening software.
Once installed on a target system, a RAT establishes a backdoor, granting the attacker full administrative privileges and the ability to issue commands and receive data from the compromised computer remotely.
RATs may also be used to multiply further infections, forming botnets under the attacker’s control. These malicious programs are experts at disguising themselves, posing significant threats to the security and privacy of affected systems.
How Does a Remote Access Trojan Work?
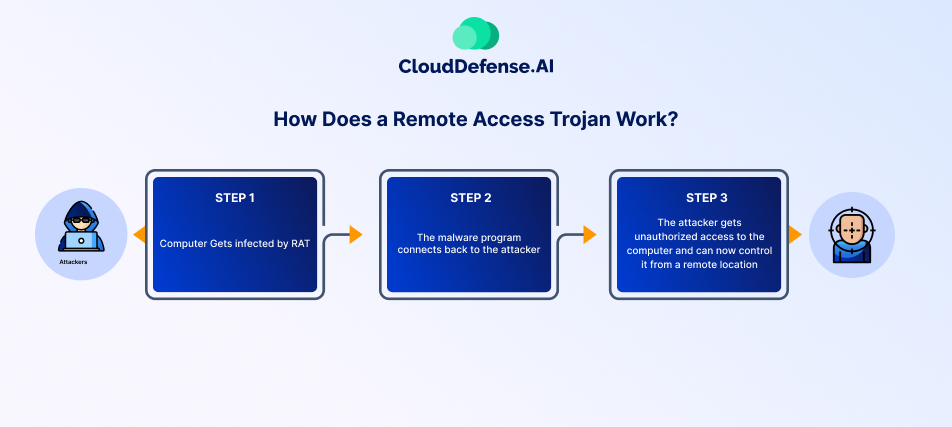
A Remote Access Trojan (RAT) operates stealthily, giving an attacker full control over an infected system while remaining undetected. It typically infiltrates a device through phishing emails, malicious downloads, or software vulnerabilities. Once executed, it establishes a covert connection with a remote server, allowing the attacker to manipulate the system at will.
Infiltration and Installation
RATs are often disguised as legitimate files or embedded in trusted applications. Common infection methods include:
- Phishing attacks with infected attachments or links.
- Compromised software downloads that appear authentic but contain hidden malware.
- Drive-by downloads from malicious websites that install the RAT without user knowledge.
- Exploitation of software vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access.
Once executed, the RAT embeds itself deep within the system, often disguising its processes to avoid detection by antivirus software.
Remote Control and Exploitation
After installation, the RAT establishes a backdoor connection to a command-and-control (C2) server. This allows attackers to:
- Monitor and log activity, including keystrokes, screenshots, and webcam/microphone access.
- Steal sensitive data, such as passwords, financial information, and business records.
- Modify or delete files and install additional malware.
- Disable security tools to avoid detection and maintain long-term access.
- Move laterally across a network, infecting other connected systems.
Advanced RATs allow cybercriminals to maintain persistence, meaning they can survive reboots and security scans, making them particularly dangerous.
Detection and Prevention
Since RATs are designed to be stealthy, detecting them can be difficult. However, implementing strong security measures can help prevent infections:
- Be cautious with email attachments and links, even from known contacts.
- Download software only from trusted sources and verify its authenticity.
- Keep operating systems and applications updated to patch vulnerabilities.
- Use endpoint security solutions that monitor for suspicious activity.
- Monitor network traffic for unusual remote connections that could indicate unauthorized access.
Why are Remote Access Trojans Dangerous?
By now, it’s clear that a RAT can infiltrate a system and grant attackers extensive control. However, what makes RATs particularly dangerous is their ability to operate stealthily, persist in systems long after infection, and execute a wide range of malicious activities. Here’s why they pose a significant threat:
Unrestricted Access and Control
When a RAT compromises a device, it grants attackers access similar to that of legitimate remote administration tools, but with harmful intentions. This unrestrained control enables cybercriminals to:
- Steal sensitive data, including personal and financial information.
- Monitor user activity in real time through keystroke logging and screen capturing.
- Modify or delete files, install additional malware, and even disable security software.
Unlike other types of malware that have specific functions, RATs offer hackers an open-ended ability to manipulate and exploit the compromised system in various ways.
Stealth and Persistence
One of the most dangerous aspects of a RAT is its ability to remain undetected. Attackers use various evasion techniques to conceal their presence, such as:
- Hiding processes so they don’t appear in task managers or system monitors.
- Using minimal system resources to avoid noticeable performance drops.
- Embedding themselves deeply within system files to survive reboots and security scans.
This persistence allows attackers to maintain long-term access, sometimes for months or even years, without the victim realizing their system has been compromised.
Lasting Damage Even After Removal
Even if a RAT is identified and removed, the damage doesn’t necessarily end there. Many RATs modify system settings, leave backdoors open, and record sensitive information, such as passwords and credentials. This means attackers can:
- Reinfect the system through hidden backdoors.
- Use stolen credentials to gain access to other accounts and systems.
- Corrupt or delete important data, leaving lasting consequences for individuals and businesses.
Versatile and Widespread Attack Vectors
RATs can be deployed through various attack methods, making them a widespread threat. Common delivery tactics include:
- Phishing emails with malicious attachments or links.
- Compromised software that appears legitimate but contains hidden malware.
- Exploit kits that take advantage of software vulnerabilities.
Once inside a system, RATs don’t just target individuals. They can infiltrate businesses, government agencies, and even critical infrastructure, leading to espionage, financial theft, and operational disruptions.
Common Remote Access Trojans
Common RATs include a variety of malicious tools utilized by cyber attackers to gain unauthorized access and control over targeted systems. These RATs are often deployed through various means such as phishing emails, malicious downloads, or exploit kits. Here are some of the most notorious RATs frequently encountered in cyber threats:
| Types of RATs | Description |
| DarkComet | Widely recognized for its extensive capabilities, DarkComet allows keylogging, screenshot capturing, and password theft, granting attackers full control over compromised systems. |
| NjRat | Infamous for its usage in the Middle East, NjRat enables attackers to spy, steal data, tamper with information, and execute arbitrary commands. Notably, it was implicated in the 2014 breach of the Sands Casino Las Vegas, allegedly perpetrated by Iran. |
| PoisonIvy | A longstanding RAT used in numerous high-profile attacks, PoisonIvy targets victim files and executes malicious activities once the PIVY server is installed on the compromised computer. |
| Gh0st | Providing real-time control over victim machines, Gh0st RAT possesses features such as audio recording and camera utilization, enabling attackers to eavesdrop on conversations and capture images. |
| Adwind | A versatile RAT capable of wreaking havoc across multiple platforms, including Linux, Windows, and Mac. It has been responsible for a substantial number of attacks, including data theft, keystroke logging, and malware distribution. |
| Sakula | Also known as Viper, Sakula facilitates interactive commands on host devices, allowing attackers to remotely control and execute commands as desired. |
| Blackshades | Spread through social media links, Blackshades transforms infected machines into botnets, launching DDoS attacks. |
| CrossRAT | Notoriously difficult to detect, CrossRAT infects various operating systems, including Windows, Linux, Solaris, and macOS, granting attackers broad infiltration capabilities. |
How to Protect Against a Remote Access Trojan
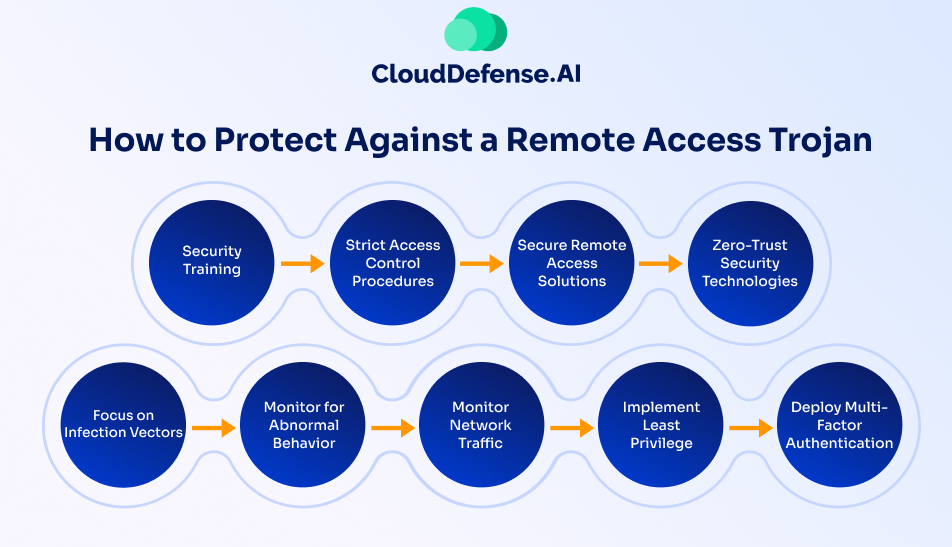
Defending against Remote Access Trojans (RATs) requires a proactive, multi-layered security strategy. These stealthy threats bypass traditional defenses, making it essential to combine awareness, strict access controls, and advanced detection techniques to prevent infections and mitigate risks.
Strengthen Employee Awareness with Security Training
Human error is one of the leading causes of RAT infections. Conduct organization-wide security awareness training to educate employees on:
- Recognizing phishing emails, suspicious links, and malicious attachments.
- Understanding social engineering tactics used to deploy RATs.
- Practicing safe browsing and email hygiene to avoid exposure to malware.
A well-trained workforce is the first line of defense against cyber threats.
Enforce Strict Access Controls
RATs exploit stolen credentials and weak access policies. Prevent unauthorized access by:
- Implementing two-factor or multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all critical accounts.
- Using strong, unique passwords and enforcing regular password changes.
- Setting up IP whitelisting and firewalls to restrict remote access to trusted sources.
These measures limit an attacker’s ability to move laterally within the network.
Secure Remote Access Points
Unprotected remote access solutions create entry points for RATs. Reduce the attack surface by:
- Using secure VPNs or hardened remote access gateways for encrypted connections.
- Deploying clientless remote access solutions to minimize reliance on third-party plugins.
- Blocking unnecessary remote access tools to prevent unauthorized use.
Only authorized, encrypted connections should be allowed.
Adopt a Zero-Trust Security Model
A Zero-Trust approach operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” This includes:
- Restricting access based on strict authentication and authorization policies.
- Enforcing granular access controls to limit lateral movement across systems.
- Verifying both device and user identity before granting access to sensitive resources.
Zero-Trust prevents attackers from freely navigating a compromised network.
Address Infection Vectors at the Source
Attackers deploy RATs through phishing emails, malicious downloads, and software vulnerabilities. Reduce exposure by:
- Using advanced anti-phishing solutions to detect and block malicious emails.
- Regularly updating and patching operating systems, applications, and security software.
- Enforcing secure browsing policies to block access to known malicious websites.
Eliminating these entry points significantly reduces the risk of RAT infections.
Monitor for Abnormal System and Network Behavior
RATs operate covertly, but they leave traces. Detect them by:
- Tracking unauthorized remote connections or unusual outbound traffic.
- Identifying sudden changes in system performance that may indicate RAT activity.
- Using endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to analyze suspicious behaviors in real time.
Early detection is critical to preventing widespread damage.
Implement Least Privilege Access
RATs exploit excessive user permissions to escalate control. Limit their impact by:
- Granting users and applications only the permissions they need.
- Restricting admin privileges to essential personnel.
- Segmenting networks to contain potential breaches.
The fewer permissions an attacker can exploit, the harder it becomes for them to operate.
Deploy Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Everywhere
Even if credentials are compromised, MFA adds an extra security layer. Strengthen authentication security by:
- Requiring MFA for all sensitive systems and accounts.
- Using adaptive authentication to trigger additional security checks for unusual login attempts.
- Implementing biometric authentication or hardware security keys where possible.
With MFA in place, stolen credentials alone will not grant attackers access.
Remote Access Trojans are among the most dangerous cyber threats, granting attackers full control over infected devices. However, a structured security approach – combining training, access controls, Zero-Trust policies, and continuous monitoring – can significantly reduce the risk.
Prevent RAT Infections with CloudDefense.AI
Keeping your organization safe from RAT infections has never been simpler! With CloudDefense.AI, you have access to a state-of-the-art cybersecurity solution that uses advanced threat detection and response. Our AI/ML technology quickly spots and tackles RATs along with other cyber threats with ease.
Thanks to our unified threat visibility and quick investigation features, organizations can easily understand potential RAT infections, allowing them to take proactive steps for mitigation. CloudDefense.AI’s risk-based prioritization helps ensure a smooth incident response, focusing on the most critical threats, while our advanced attack simulations work to bolster defenses against RAT attacks.
CloudDefense.AI offers a comprehensive suite of cybersecurity solutions designed to protect your digital assets, from code to cloud. With an intuitive interface and expert support at your fingertips, organizations can confidently face security challenges and combat cyber threats effectively. Stay one step ahead of attackers and safeguard your organization’s data effortlessly with CloudDefense.AI!







