What is Phishing?
Phishing is a social engineering attack aimed at stealing sensitive information like login credentials and financial details.
Attackers pose as trusted entities, such as banks, social media platforms, or government agencies, to deceive victims into clicking malicious links or downloading harmful attachments. These attacks often lead to identity theft, financial fraud, or system compromise.
In the third quarter of 2024, the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) recorded 932,923 phishing attacks, up from 877,536 in the previous quarter, marking a 6% increase. Furthermore, a 2024 report by Trend Micro revealed a 58% year-over-year rise in phishing attacks in 2023, underscoring the growing sophistication and frequency of these threats.
Phishing also serves as an entry point for larger cyberattacks, including ransomware and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). Businesses suffer severe financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties due to successful breaches.
How Phishing Works?
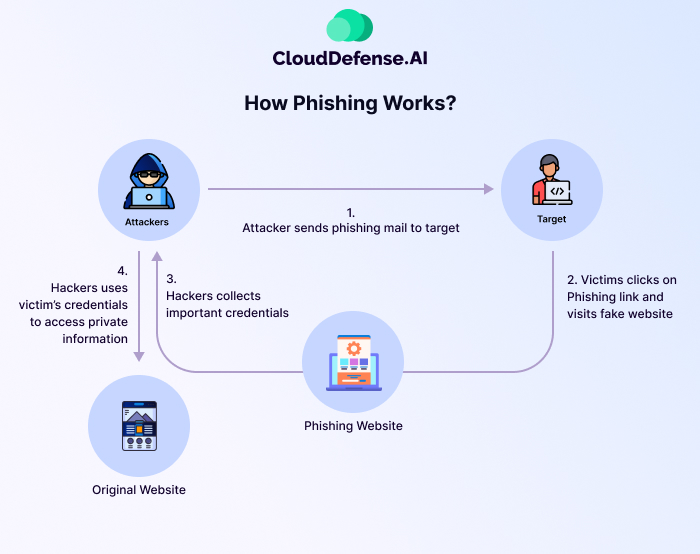
Phishing works in a simple manner, and whatever the malicious intent, the process starts with a message that is sent via email, text, or any other means. These attacks vary according to their intent, complexity, and scale, but they usually follow a similar type of pattern. Here are the five stages of a phishing attack:
Choosing a Target
The first task of the attack is to choose a target, which can be a large organization or a specific individual. The target is chosen based on the intent of the attack, and in general, attacks like to target large organizations to reap larger rewards.
Based on the target, the attacker gathers all the potential details, such as names, emails, official activities, and possible interests.
Registering a Domain
After analyzing the target’s activity and interests, the malicious actors create a domain that is similar to the victim’s bank, operation page, or workplace.
The attacker mostly registers domain names so that they can redirect the victims from the email or message to the targeted destination. To masquerade the true destination of the attached link in the phishing mail, the attackers often use URL shortening services like bit.ly, but this requires more technical support.
Crafting the Message
Now comes the main part, where the attacker crafts the message so that it appears to have come from a known contact or a trusted source. The messages are often kept simple, with a few lines of text along with the attached link or sometimes a well-decorated branded email from a well-known source like a partner organization or bank.
Weaponizing the Message
In this stage, the attacker has to weaponize its phishing email or message. If the main target is to infect the victim’s system or network, then the attacker adds malware to the attached file or link.
Sometimes malware is injected into the system through PDF and office documents. However, if the attacker wants to get the credential, then it might create a fake login page using a cloning website tool and make you believe that you are entering details at the right site.
With time attackers are getting sophisticated with their phishing attacks where they are creating almost similar authentic emails or messages and using modern marketing techniques.
How Dangerous Are Phishing Attacks for Your Business?
Phishing attacks can wreak havoc on your business, causing financial losses, reputational damage, and legal trouble. A successful attack can lead to ransomware infections, unauthorized system access, or stolen financial data, crippling operations.
Beyond financial loss, attackers often sell stolen customer or business data on the dark web or even to competitors, further escalating the damage. Worse, regulatory bodies may impose hefty fines and sanctions following a data breach, adding to the fallout.
Protecting your business requires vigilance. Educate employees, implement security measures, and remain alert to emerging threats to avoid becoming the next victim of cyber attacks, data breaches, or security vulnerabilities that could jeopardize your organization’s integrity.
Phishing Attacks: Statistics and Examples
Phishing is undoubtedly one of the most common types of cyberattack in the industry that has affected organizations for many years. Injecting malware through an attached file or malicious link serves as a popular choice for most attackers.
- 3.4 Billion Phishing Emails per Day: A report by ZDNet stated that around 3.4 billion phishing emails are sent every day, and this is increasing with time. It translates that one email in every 4200 emails is a phishing mail.
- Spear Phishing Attacks: As per a statistic by Norton, there are almost 88% of organizations have been affected by spear phishing attacks.
- Brand Name Deception: Recent data reveals that in March 2024, over 301 brand names were involved in phishing attacks worldwide. This highlights the widespread nature of these deceptive practices.
- Fast-growing cyberthreat: In 2024, phishing attacks surged by 58%, marking it as one of the fastest-growing cyber threats. Notably, 96% of these attacks exploited trusted domains, including platforms like SharePoint and Zoom, to deceive victims.
- AI in Phishing: The rise of artificial intelligence has further worsened the situation. Voice phishing attacks, or “vishing,” experienced a staggering 442% increase in 2024, with cybercriminals using AI to enhance their social engineering tactics.
- Mobile Phishing Attacks: Mobile devices are not exempt from these threats. There was a 26% global surge in mobile phishing attacks in 2024, with SMS and QR code scams leading the trend.
A notable example of Phishing is the recent Netflix email scam, where users received fraudulent messages prompting them to update their payment information, leading to potential account and financial theft.
Types of Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks have been present in the industry for a long time, and over the years, attackers have come up with a variety of phishing attacks. Here are some popular types of phishing attacks used by malicious actors:
| Phishing Type | Description |
| Email Phishing | Attackers create a fake domain and website of a real organization and send deceptive emails to lure victims into clicking malicious links or downloading infected files, leading to data theft or malware injection. |
| Spear Phishing | A targeted phishing attack where attackers focus on a specific individual using personal details like name, email, and job title to craft convincing fraudulent messages. |
| Smishing | Phishing attack via text messages where victims receive deceptive SMS with a malicious link or contact number, often tricking them into sharing credit card details or personal information. |
| Vishing | Phishing attack conducted over phone calls where attackers impersonate trusted individuals (e.g., bank employees) to extract sensitive information, sometimes using automated voice prompts. |
| Whaling | A high-profile phishing attack targeting senior executives (CEOs, CFOs) to gain privileged access to corporate systems or extract confidential company data. |
| Angler Phishing | Attackers use fake social media accounts of reputed organizations to solicit Personally Identifiable Information (PII) from victims by responding to their posts or messages with fraudulent offers or support links. |
| Pop-up Phishing | Attackers inject pop-up messages, often on smartphones, appearing as warnings or offers with malicious links designed to trick victims into entering personal information. |
What are the Signs of Phishing?
The wisest way to avoid getting impacted by a phishing attack is by knowing how to avoid them. When you are aware of the signs of phishing, it can save your organization in many ways. Here are some key signs you should be aware of:
Unfamiliar Request
When you receive an email with an unfamiliar request and ask you to perform a specific action without any explanation, then it might be a phishing attack. The attacker may pose an administrator team and ask you to furnish some credentials; then you can understand it is malicious mail.
Creating a Sense of Urgency
Attackers, through phishing messages or emails, always create a sense of urgency and compel users to perform specific functions. For example, a malicious actor might create a phishing mail mentioning that your corporate bank account has been compromised and you need to make changes through the attached link.
Inconsistency in Domain Name
An easy way to identify phishing is by going through the inconsistency in the domain name, email address, and link. The attacker may pose as a reputed brand, but it will be different from the original. Hovering the mouse over the link is always a smart move to check the actual link destination.
Grammatical and Spelling Errors
Grammatical and spelling errors are one of the easiest ways to identify a particular mail as a phishing email. Many automated spell checkers will highlight the spelling mistakes and it will help you identify the phishing sign.
Writing Style
The written style of the message or email can help you determine whether it is a phishing message or not. A message with a poor tone or informal greeting should give you the clue that the message hasn’t originated from the actual source.
Even though modern phishing attacks have become sophisticated, signoff and greeting styles can help you identify phishing.
Short Message
Phishing emails are often kept short without much information. If you find any email that lacks all the essential details, then it can be a phishing attempt.
Requesting Payment Information or Credentials
Usually, attackers, through phishing emails, ask to enter payment information or credentials through a fake login page. However, banks or institutions don’t ask for payment information or credentials all of a sudden, so you can understand it is a phishing attack. Even if you have to make changes, it is best to visit the login page directly.
How to Protect Your Organization from Phishing?
Phishing attacks are dangerous, but with the right approach, you can prevent most of the phishing types. Here are a few ways that can help you protect your organization:
Implementing Appropriate Anti-Phishing Measures
To protect your system from phishing, you should focus on implementing appropriate anti-phishing solutions along with spam filters and anti-virus. When you have the right solutions in place, it will filter out phishing attempts and help you maintain optimum security posture.
Employee Awareness
Along with implementing an anti-phishing solution, you also need to conduct awareness programs for your employees regarding phishing attacks and how they can identify phishing attempts. The awareness program should cover how employees should identify a trusted website and be assured it is not a fake site.
Email Security
It would be a smart move to implement a highly effective email security solution because it can help in filtering out suspicious mail that might lead to phishing attacks.
The email security solution can not only identify malicious links and spam content but also attachments that might contain malware. Some solutions even utilize sandboxing technology to check whether mail contains malware or not.
Using Multi-Factor Authentication
Implementing multi-factor authentication will create an additional layer of defense between the system and the attacker. The attacker has to go through additional verification to get their hands on sensitive data. Even if the attacker gets hold of the username and password, they will require additional verification to get entry.
Utilizing Phishing Attack Test
Another effective measure you can utilize is conducting simulated phishing attacks. This test will not only evaluate your employee’s awareness of phishing attacks but also the effectiveness of the awareness program and how they perceive the attack.
Since phishing attacks are evolving with time, the phishing attack test should also evolve and it should be conducted at regular intervals.
Limiting User Access to Sensitive Data
Privileged accounts are the primary target of cyber attackers during phishing attacks. However, the impact of phishing can be limited by restricting user access to the system that will protect the sensitive. Enforcing the least privilege will restrict user access and only provide access to specific databases that they need for operation.
Automated Data Backup
Your organization should conduct regular backups of all the sensitive data to a remote server that is completely off the grid. This sensitive data would be helpful if there is an unfortunate data breach due to phishing. The backup data can be used for recovery and you can use it to maintain business workflow.
Phishing Protection and Prevention with CloudDefense.AI
When you have CloudDefense.AI by your side, phishing protection and prevention won’t be a concern for you. CloudDefense.AI offers you a combination of web app security, data protection, and ransomware to help you prevent your organization from phishing attacks.
This platform makes use of Zero Trust protection, real-time monitoring, and rapid incident response to protect your system from any kind of phishing attack. The use of advanced threat protection ensures that if there is any attack, all the data is protected before being extracted.
The chance of data loss is minimal with CloudDefense.AI because it takes an effective remediation process and recovers lost data with a simple command. To learn more about how CloudDefense.AI helps you with phishing protection and prevention, you should request a live demo.







