What is Healthcare Data Security?
Healthcare data security is the practice of protecting sensitive patient information, computers, and networks from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. This involves ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of healthcare data through the implementation of strong cybersecurity measures such as encryption, access controls, and network security protocols.
Why is Healthcare Data Security so Important?
The importance of healthcare data security cannot be overstated today. As healthcare organizations adopt more applications and store increasing amounts of patient information, the risk of unauthorized access grows.
Patient records, rich with personal data like medical history, diagnoses, and treatment plans, are prime targets for cybercriminals. If compromised, this data can lead to identity theft, insurance fraud, and jeopardized patient care.
The rise of electronic health records and interconnected systems has give rise to the threat of data breaches. Consequently, strong security measures are essential to protect patient privacy and maintain trust in the healthcare system. Ensuring healthcare data security not only secures sensitive information but also upholds the integrity and reliability of healthcare services.
Risks Factors Associated with Healthcare Data Security

Healthcare data security is has to come face to face with numerous risk factors that put sensitive patient information at risk. Below are some critical risk factors that healthcare organizations must address to protect their data effectively.
Outdated Systems with Security Vulnerabilities
Many healthcare organizations rely on outdated or legacy systems that are no longer supported by manufacturers. These systems often have unpatched security vulnerabilities, making them easy targets for cyberattacks. Without ongoing updates, these systems cannot defend against newer threats, leaving patient data exposed.
Email Scams and Malware Attacks
Healthcare organizations are prime targets for email scams that distribute malware. With a large number of employees, the likelihood of at least one person inadvertently installing malicious software is high. Once malware infiltrates one computer, it can quickly spread throughout the network, compromising sensitive information.
Insider Threats from Employees and Partners
The diverse workforce in healthcare, including employees, contractors, and vendors, often has varying levels of access to the network. If a hacker successfully installs malware on one of these individuals’ devices, every network access point becomes a potential entry for cybercriminals. This internal vulnerability poses a significant threat to data security.
Insecure Wireless Networks
Hospitals and clinics frequently offer wireless network access to patients and visitors, but these networks may lack adequate security measures. Hackers find these unsecured access points attractive, using them as gateways to infiltrate the main network and access confidential patient data.
Weak Password Practices
Weak passwords are a common issue in many healthcare organizations. Employees often use simple or repeated passwords across multiple accounts, making it easier for hackers to guess login credentials and gain unauthorized access to the network.
Insufficient Data Security Training
Ensuring that all employees understand and practice good data security measures is a considerable challenge, especially in organizations with high turnover rates. Without proper training, employees may unknowingly engage in behaviors that compromise data security, such as falling for phishing scams or mishandling sensitive information.
Insecure Data Transmission
Healthcare organizations frequently need to transmit data across different locations and to third parties like insurance companies. If these transmissions do not utilize secure technologies, such as encryption, the data can be intercepted and accessed by unauthorized individuals, leading to breaches of patient confidentiality.
Common Healthcare Data Security Challenges

Healthcare data security faces several unique challenges that must be addressed to protect sensitive patient information effectively. Here are some of the most pressing issues:
Complex Health Information Exchanges
Health information exchanges allow for the sharing of patient data among doctors, patients, and insurance companies. Ensuring these transmissions are secure and that proper digital channels are used can be a daunting task. Missteps in securing these exchanges can lead to significant data breaches.
User Error in Technology Utilization
Healthcare professionals are often under immense pressure, leaving little time to master new technologies. Whether due to lack of time or limited computer skills, users can make mistakes during technology adoption. These errors can lead to vulnerabilities in data security, emphasizing the need for comprehensive training and user-friendly systems.
Increased Threat from Hackers and Hacktivists
Hackers target healthcare organizations for monetary gain or access to sensitive data. Additionally, hacktivists may attack healthcare entities to protest specific actions or policies. The rise of such cyber threats requires strong security measures to protect against both financially and ideologically motivated attacks.
Risks of Cloud and Mobile Technology
While cloud and mobile technologies offer convenience and efficiency in managing healthcare IT systems, they also introduce security risks. For instance, a stolen password or mobile device can give hackers access to vast amounts of sensitive data. Securing these technologies requires strict access controls and encryption practices.
Vulnerabilities in Outdated Technology
Many healthcare organizations rely on outdated technology that is costly to replace. These older systems often lack recent security updates, making them more susceptible to breaches. The persistence of outdated technology poses a significant challenge to maintaining data security.
HIPAA and HITRUST for Healthcare Data Security
Ensuring healthcare data security involves not only implementing strong cybersecurity measures but also adhering to regulatory standards like HIPAA and HITRUST. In the United States, healthcare organizations must comply with the HIPAA to protect patient information.
HIPAA establishes strict guidelines for data security and the protection of electronic health information, mandating organizations to implement measures that prevent unauthorized access. HIPAA compliance is crucial as it sets the foundation for how healthcare data should be protected.
Failure to adhere to HIPAA standards can result in severe penalties and significant reputational damage. Therefore, healthcare organizations must consistently review and update their security practices to align with HIPAA requirements.
The HITRUST offers an additional layer of security through its comprehensive framework for managing information security risks. HITRUST provides a standardized approach to assessing, managing, and communicating healthcare data security and privacy compliance.
Protecting Healthcare Data
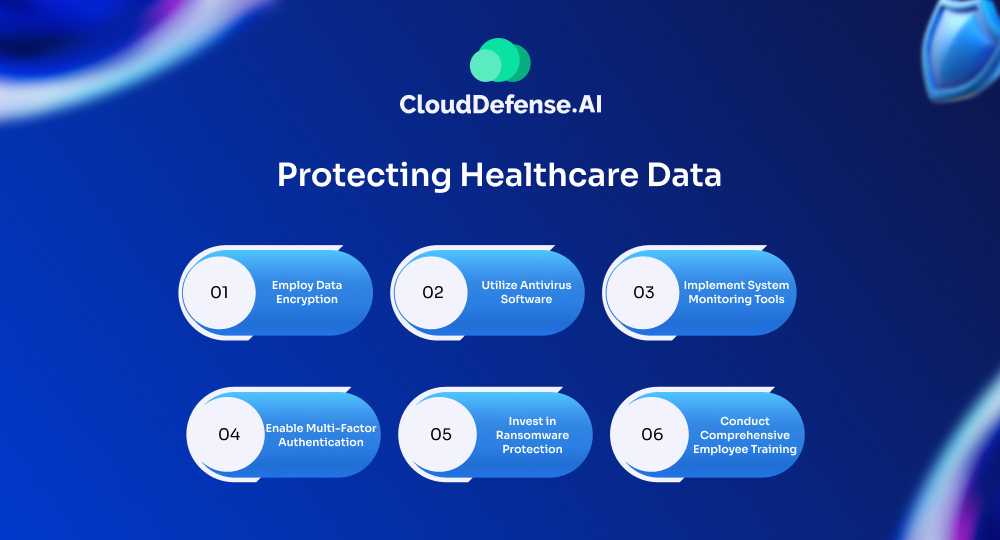
Healthcare data protection is crucial for maintaining patient privacy and ensuring the integrity of medical information. Here are several effective strategies to protect healthcare data:
Employ Data Encryption
Data encryption is essential for securely transmitting sensitive information within the healthcare sector. Encrypted data can only be deciphered by someone with the correct decryption key, ensuring that even if intercepted, the data remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Utilize Antivirus Software
Antivirus applications are critical in defending against a wide range of viruses that can infiltrate a healthcare organization’s network. These programs can detect and neutralize existing malware, providing a strong defense mechanism against potential threats.
Implement System Monitoring Tools
System monitoring applications enable IT teams to oversee all endpoints connected to the network. These tools help in detecting and investigating suspicious activities, ensuring that any anomalies are promptly addressed to prevent security breaches.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA enhances security by requiring additional verification steps beyond just a username and password. This might include answering security questions, using a physical device for authentication, or providing biometric data like fingerprints or facial recognition, thus adding an extra layer of protection.
Invest in Ransomware Protection
Ransomware protection focuses on identifying and stopping malware designed to lock down systems and demand ransom payments. Specialized antimalware tools and decryption keys provided by cybersecurity companies can help regain control of affected systems without capitulating to attackers.
Conduct Comprehensive Employee Training
Employee training is vital in fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness. Training programs should educate staff on best practices for protecting their credentials, securing devices, and recognizing cyber threats. Empowered employees can act as a frontline defense against data breaches.
How to manage a Healthcare Data Breach?
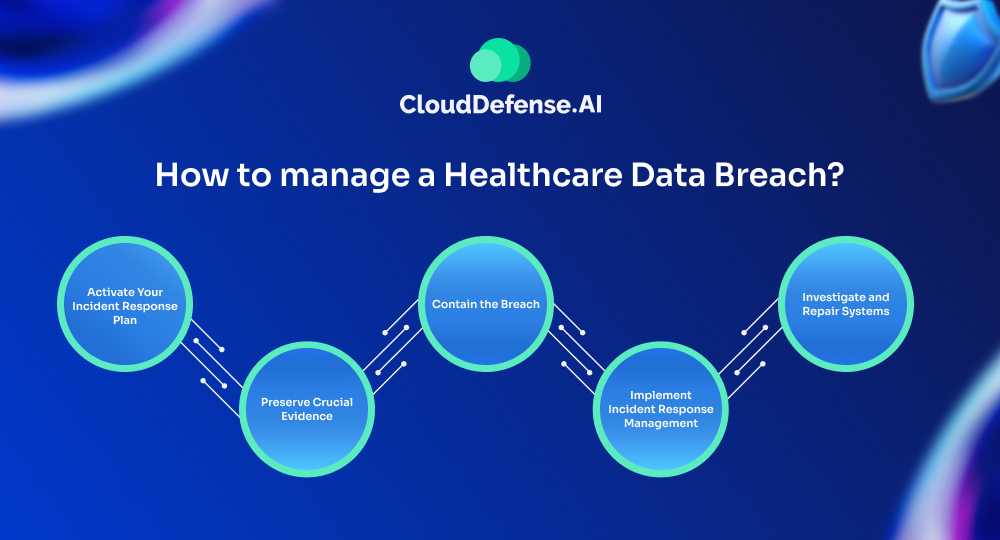
Managing a healthcare data breach requires a calm, systematic approach to minimize damage and restore security. Here are five crucial steps to handle a breach effectively:
Activate Your Incident Response Plan
The first step is to initiate your incident response plan, which provides clear, step-by-step instructions for handling a breach. This plan ensures a coordinated and calm response, helping everyone involved to follow a structured procedure during the crisis.
Preserve Crucial Evidence
Preserving evidence is vital for multiple reasons: it aids in identifying and apprehending the cybercriminals responsible, provides insights to prevent future breaches, and supports efforts by collecting and securing all logs, affected systems, and other relevant data.
Contain the Breach
Containing the breach involves isolating affected systems to prevent further damage. This may include shutting down computers, disconnecting networks, and notifying external partners to avoid remote logins until the threat is neutralized. Quick containment helps stop the spread of the breach and limits its impact.
Implement Incident Response Management
Following containment, start your incident response management plan to resume operations safely. This plan should outline steps for mitigating the attack, such as scanning devices for malware. Employees may need to surrender their devices for inspection, ensuring they are free from malicious software before reconnecting to the network.
Investigate and Repair Systems
Conduct a thorough investigation to understand the breach’s extent and fix affected systems by performing detailed malware scans on all compromised devices, removing malware, or in severe cases, wiping and restoring systems from backups. The goal is to eliminate any remnants of the attack and reinforce security to prevent recurrence.
Final Words
Healthcare data security gives high hopes to patient when it comes to trusting healthcare providers with their data, helping to maintain trust in the healthcare system. As regulatory changes loom, more specific guidelines are expected to emerge, providing clearer directions on using technology to protect healthcare data. Organizations must stay vigilant and proactive in adopting security measures to keep up with evolving standards and threats. By doing so, they can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical healthcare information.







