Definition — What Is Endpoint Security?
Endpoint protection is a cybersecurity measure meant to secure endpoints—such as laptops, smartphones, desktops, and tablets—by detecting and blocking potential threats. It ensures that devices connecting to the network remain safe from cyberattacks and malicious activity.
- Protects devices from malware, viruses, and ransomware.
- Detects and responds to abnormal behaviors on endpoints.
- Enforces security policies for device access and usage.
- Monitors device health and updates security software automatically.
- Provides real-time threat analysis and blocking.
With endpoint protection, you secure the first line of defense against cyberattacks, ensuring that your network remains intact and your sensitive data stays protected.
So, What’s considered an Endpoint?
An endpoint refers to any device that connects to a network, serving as a potential access point for cybercriminals. These devices interact with your network, making them vulnerable to security threats.
- Laptops and desktops used for work or personal tasks.
- Smartphones and tablets, including BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) devices.
- Servers that store and manage data.
- Printers and other connected peripherals.
- IoT (Internet of Things) devices like smart cameras or security systems.
Understanding what qualifies as an endpoint helps you secure every device that connects to your network, reducing the risk of an attack from any vulnerable point.
Why is Endpoint Security Important?
In the past few years, everything changed. People are working from home, from the office, and everywhere in between. About 12.2% of U.S. workers are remote, and 28.2% are on hybrid schedules. That’s a lot of devices connecting to networks.
But here’s the problem: each of those devices is a potential security risk. If a device is not protected properly, it’s an open door for hackers to get in. And they’re getting smarter.
So, why Endpoint Security Matters
- It’s the first line of defense. Devices like laptops, phones, and servers are the entry points for threats. Endpoint security blocks those threats before they can cause damage.
- Data protection is critical. Endpoint security helps you protect your most valuable assets—your data—keeping it safe from hackers.
- Breaches happen fast. Once a hacker gains access to an endpoint, they can quickly spread across the network. That’s why securing endpoints is essential.
In today’s world, where remote work is the norm, protecting all those devices that connect to your network is not just important—it’s a must. Without proper endpoint security, you’re leaving your entire network vulnerable to attack.
How Endpoint Security Works?
Endpoint protection is about securing every device that connects to your network. Here’s how it works, step by step:
Step I: Gather Information
The first thing you need to do is get all the facts. Know every device that connects to your network. These could be laptops, smartphones, servers, and any other device. You need to be clear about the sensitive data your network holds and understand who has access to it. This gives you a solid starting point to figure out what you need to protect.
Step II: Choose Security Solutions
Once you know what’s at risk, it’s time to pick the right security tools. Not all devices are the same, so you’ll need to choose solutions based on what works for each one. That could mean cloud protection, network protection, or securing hardware and software. Make sure you’re covering all bases.
Step III: Implement Security Solutions
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. Implement the security tools you’ve selected and start keeping a close eye on how well they perform. Check regularly for any gaps or vulnerabilities. If something’s not working, go back to the drawing board and make adjustments. It’s a constant process of fine-tuning.
Key Components of Endpoint Security
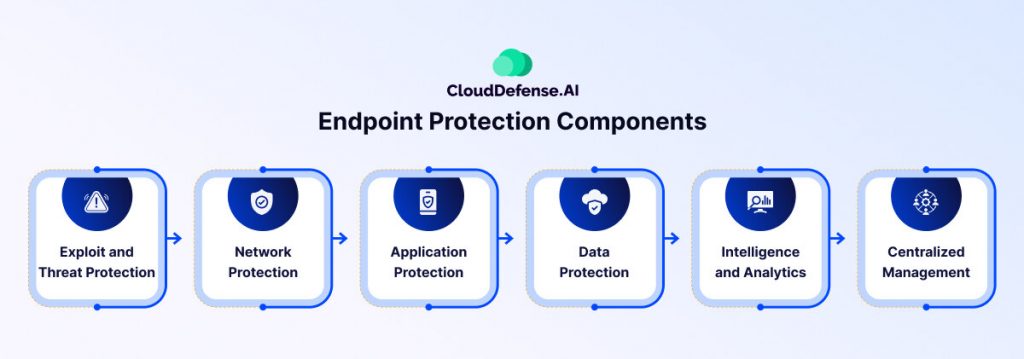
To keep your network secure, you need the right tools. Here’s what you need to know about the key components of endpoint security:
1. Device Protection
Device protection is crucial. You need tools that track every action happening on your devices. This is where Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) comes in. It monitors everything, identifies suspicious activity, and helps security teams respond before anything serious happens.
Along with EDR, you need antivirus and malware protection on every device. Today’s next-gen antivirus uses smart tech like machine learning to catch new threats, such as ransomware and advanced phishing attacks. You need this because traditional antivirus can’t keep up with these evolving attacks.
2. Network Control
Network control is your first line of defense. It keeps track of all inbound traffic. It’s like a firewall that filters out any bad traffic before it enters your network. If you don’t have strong network control, you’re opening yourself up to a lot of risks.
3. Application Control
Application control is about knowing exactly what’s running on your devices. It limits access to only the applications that are authorized and necessary. This means controlling what endpoints can access on your network and what they can do.
Regular patching is part of this too. Patches fix security holes in software, so keeping your apps up to date is essential to avoid vulnerabilities.
4. Data Control
Data control is all about protecting your valuable data. It covers both data in transit and data that’s stored. It ensures no unauthorized users can get to it, and encrypts sensitive information so that even if it’s intercepted, it can’t be read by cybercriminals.
5. Browser Protection
Browser protection helps control what users can do online. With web filters in place, you can block dangerous websites and prevent employees from accessing risky sites. This stops cyber threats from entering through the browser.
Additionally, privilege management—also known as the principle of least privilege (POLP)—restricts user access to only what’s necessary for their job. It minimizes the chances of a breach by removing unnecessary admin rights. Less access means less risk.
Types of Endpoint Protection
Different types of endpoint security aim to protect devices and data from various threats.
Each type of security method serves a different purpose. Here are all the types of endpoint protection that you need to be aware of.
| Type of Security | Scope | Description |
| IoT Security | IoT Security | Protects IoT devices, important as they could be used as access points to digital assets |
| Network Access Control | Manages user and device access to the network | Uses firewalls to control interactions with sensitive segments |
| Data Loss Prevention | Data Security | Ensures secure data resources are protected against exfiltration through measures like phishing awareness and antimalware. |
| Insider Threat Protection | Access Control | Controls internal access and monitors activities to mitigate risks from within the organization, often utilizing zero-trust network access tools. |
| Data Classification | Data Protection | Identifies and isolates valuable and vulnerable data, pinpointing critical attack surfaces. |
| URL Filtering | Malware Protection | Blocks potentially malicious websites to prevent internal users from accessing them, typically using hardware or software firewalls. |
| Browser Isolation | Browser Protection | Executes browser sessions within isolated environments to prevent malicious code from affecting protected assets |
| Cloud Perimeter Security | Cloud Security | Protects cloud resources from unauthorized access by controlling user and device access using cloud firewalls and web filtering tools. |
| Endpoint Encryption | Data Encryption | Secures device data through encryption, ensuring only authorized users can access it. |
| Sandboxing | Testing and Security | Creates isolated environments to mimic user operating systems, protecting sensitive network areas |
| Secure Email Gateways | Email Protection | Inspects incoming and outgoing emails for threats, preventing access to suspicious links or files. |
Endpoint Protection Platforms vs. Traditional Antivirus
Endpoint protection platforms and traditional antivirus serve distinct but complementary roles in protecting devices and networks from cyber threats. Here’s a comparison between the two.
| Feature | Traditional Antivirus | Endpoint Protection Platforms |
| Device Coverage | Individual devices (laptops, PCs) | All connected devices across the entire enterprise network (endpoints, servers, virtual machines, etc.) |
| Protection from Threats | Focuses on known threats identified by signature-based detection | Offers a holistic approach to security, protecting against various threats such as data loss, fileless and signatureless malware, phishing attacks, and known risks. Utilizes advanced technologies like behavioral analysis for threat detection. |
| Continuous Protection | Relies on signature-based detection and manual updates | Connects to the cloud for automatic updates, ensuring users have the latest protection against threats. |
| Internal Protection | Can block malware but may not prevent data loss or leakage through unauthorized actions by employees | Offers advanced internal protection mechanisms such as data encryption and access controls to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. |
| Admin Control | Relies on manual updates by users, posing a risk of human error | Shift admin responsibility to IT or security teams, providing centralized control and management capabilities for monitoring, configuration, patching, and issue resolution across multiple endpoints. |
| Enterprise-wide Control | Provides limited visibility and requires manual investigation of threats | Offer a centralized portal for admins to monitor activity, investigate threats, and resolve issues remotely, enhancing efficiency and scalability for enterprise-wide security management. |
| Integration | Operates as a standalone program | Provide integration of various security solutions within a suite for comprehensive and seamless protection. |
Conclusion
Looking at how diverse the technological industry has become, companies must start adopting more advanced security measures. Modern security methods such as endpoint protection not only help to keep your endpoints secured but it is a proactive response to threat actors who are always on the lookout to harm your system.
We hope this article has helped you get a good understanding of endpoint security so that you can take that leap ahead and effectively protect your system from insider threats.







