Definition – What is Endpoint encryption?
Endpoint encryption is a security method that encrypts data stored on devices like laptops, desktops, smartphones, and servers to prevent unauthorized access. Even if a device is lost or stolen, encryption ensures that sensitive data remains inaccessible without the correct decryption key.
Here’s why it matters:
- No encryption = instant data breach. If an unencrypted device falls into the wrong hands, your data is exposed.
- Encryption locks everything down. It secures files, applications, and even system data, making it unreadable to attackers.
- Physical theft isn’t your biggest threat. Cybercriminals use malware and remote attacks to steal unprotected data.
- Compliance requires it. Many regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS) demand endpoint encryption to protect sensitive information.
- It’s non-negotiable. If you’re serious about security, encrypting endpoints isn’t optional—it’s essential.
With endpoint encryption, everything on your device – files, apps, even system data gets locked down. Even if someone physically gets their hands on it, they can’t access a thing without the right encryption keys. No shortcuts. No backdoors. Just pure security.
If you’re not encrypting your endpoints, you’re taking unnecessary risks. The question isn’t if you should do it—it’s why haven’t you done it already?
What Endpoint Encryption Secures?
Cybercriminals, insiders, and even accidents can expose sensitive data if your endpoints aren’t locked down. Here’s what encryption helps you avoid:
1. Stolen or Lost Devices
Laptops, phones, and USB drives get lost or stolen every day. Without encryption, anyone who finds (or steals) your device can instantly access everything on it. Encryption ensures that even if they have the hardware, they can’t get the data.
2. Unauthorized Access
Just because someone has physical or remote access to a device doesn’t mean they should see everything. Encryption locks down data so that even if an insider, ex-employee, or hacker gets access, they still need the right decryption key.
3. Malware and Ransomware Attacks
Cybercriminals use malware to extract sensitive files or lock down systems for ransom. Encrypted data is useless to them because it can’t be read or exploited without proper decryption.
4. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
Attackers intercept data when it’s being transferred. Encryption ensures that even if someone captures your data in transit, it remains unreadable and worthless.
5. Regulatory Fines and Compliance Failures
If you store customer data, you’re legally required to protect it. Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS demand encryption to prevent breaches. If you fail to comply, expect hefty fines and legal trouble.
If your endpoints aren’t encrypted, your data is wide open for attackers. Hackers don’t always need to break into networks sometimes, they just find an unprotected device. Don’t make it easy for them.
Key Benefits of Endpoint Encryption
Without Endpoint Encryption, businesses risk financial loss, legal trouble, and reputational damage. Here’s why organizations must take endpoint encryption seriously.
Prevents Costly Data Breaches
Data breaches can cripple a business. The cost of a single breach, including legal fees, fines, and operational disruptions, can run into millions. But with endpoint encryption, even if an attacker gains access to a device, the data remains unreadable. This ensures that even in the worst-case scenario, stolen laptops, hacked systems, or insider threats critical business and customer data remains protected.
Ensures Compliance with Regulations
Regulatory bodies have made encryption a legal requirement for handling sensitive information. Laws like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and CCPA mandate data protection measures, and failing to comply can result in severe penalties. Enterprises that fail to encrypt their endpoints are not only exposing themselves to potential cyber threats but also opening the door to lawsuits and regulatory fines. Encryption is one of the most effective ways to ensure compliance and avoid legal headaches.
Protects Against Insider Threats
Security threats don’t always come from outside attackers. Employees, whether intentionally or accidentally, can expose critical data. A misplaced USB drive, a stolen laptop, or unauthorized access can all lead to severe breaches. Endpoint encryption ensures that even if someone inside the organization attempts to access sensitive files without authorization, they won’t be able to read or misuse the data.
Secures Remote and Hybrid Workforces
Modern businesses operate in a flexible environment where employees work remotely and use personal devices to access company data. This creates a massive security risk if endpoints are not encrypted. With endpoint encryption, organizations can enforce security policies that protect data across all locations, ensuring that remote work doesn’t become a weak link in their cybersecurity strategy.
Reduces the Impact of Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware is a growing threat that locks businesses out of their own data until they pay a ransom. However, when data is encrypted by the enterprise itself, attackers cannot access it, even if they manage to install malware on the system. This minimizes their leverage, making encryption one of the most effective ways to counter ransomware attacks.
Builds Customer and Partner Trust
In today’s digital world, customers and business partners expect their data to be handled with the highest security standards. A single data breach can destroy trust and lead to lost business opportunities. Organizations that implement strong encryption policies demonstrate their commitment to cybersecurity, making them more reliable partners in an increasingly security-conscious marketplace.
Endpoint Encryption Architecture Explained
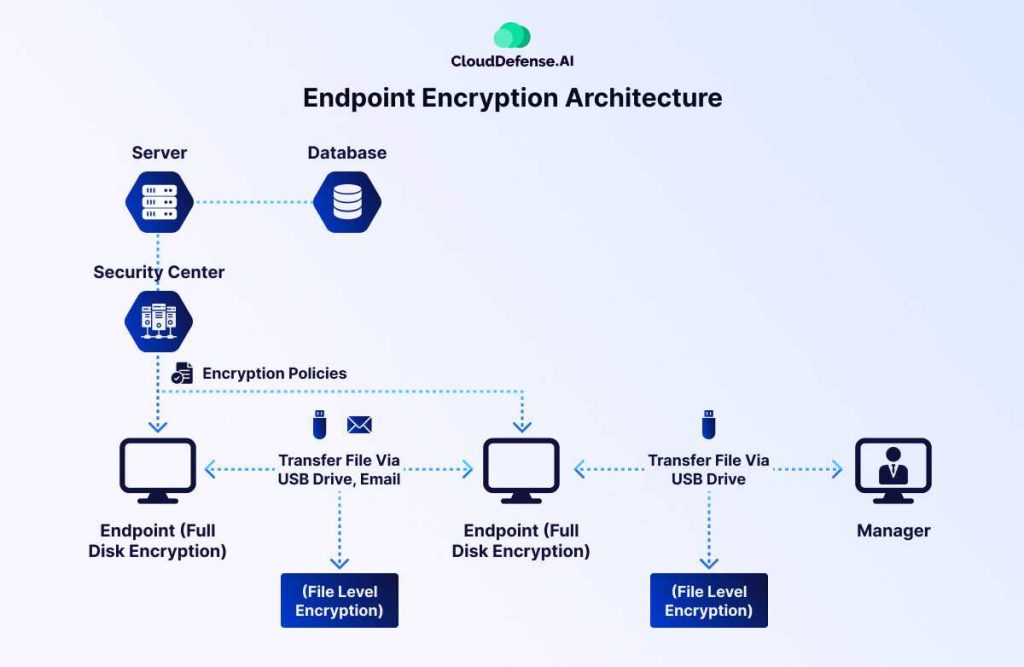
The image illustrates how endpoint encryption works within an enterprise security framework. Let’s break it down step by step.
Centralized Security Management
At the core of endpoint encryption is a security center that enforces encryption policies across all connected devices. This centralized management ensures that every endpoint, from employee workstations to executive devices, follows strict encryption protocols, minimizing security gaps.
Full Disk Encryption (FDE) for Endpoint Security
Each endpoint device is protected using full disk encryption (FDE), which encrypts the entire storage drive. This means that even if a device is lost or stolen, the data remains inaccessible without the proper credentials. FDE ensures that sensitive files, applications, and system data are always protected from unauthorized access.
File-Level Encryption for Data Transfers
Beyond device encryption, file-level encryption provides an additional layer of security for files transferred via USB drives, email, or external storage. This method ensures that even if an encrypted file is removed from the endpoint, it remains secure and unreadable to unauthorized users.
Secure File Access for Managers and Authorized Users
Managers and designated personnel can access encrypted files only if they have the correct decryption keys. This selective access control prevents unauthorized viewing, ensuring that sensitive information is only accessible to those who need it.
Stronger Compliance and Threat Protection
By integrating endpoint encryption with centralized security policies, organizations can ensure compliance with industry regulations, reduce the risk of cyberattacks, and maintain complete control over their sensitive data.
How Endpoint Encryption Works – Step by Step
Endpoint encryption secures devices and data by implementing encryption policies that protect information at rest and in transit. Here’s how it works step by step:
1. Setting the Rules
Everything starts at the security center, where IT teams define encryption policies. These rules dictate which devices need full disk encryption (FDE) and when file-level encryption should kick in. Once set, these policies are rolled out to all endpoints, ensuring that every device follows the same security standards.
2. Encrypting the Entire Device
Once a device receives the encryption policy, full disk encryption is applied. This means the entire hard drive is locked down, making the data unreadable without proper authentication. Even if a laptop gets stolen, the thief won’t be able to access anything without the decryption key.
3. Protecting Files Before Transfer
If files need to be sent via USB drive, email, or other methods, encryption policies ensure they’re locked with file-level encryption. This protects individual files, so even if someone manages to intercept them, they can’t read the contents without the right decryption key.
4. Controlling Who Can Access What
Encryption ensures that even when files are shared, only authorized users can decrypt them. If an employee sends an encrypted file to a colleague, that person must have the right permissions to open it. Unauthorized users? They’ll just see gibberish.
5. Managing Access for Teams
Managers and specific personnel get controlled access to encrypted data based on their roles. This limits the risk of internal leaks and ensures that sensitive information is only available to those who actually need it.
6. Monitoring and Keeping Everything Secure
The security team keeps a close eye on all encrypted devices and files, making sure no one is trying to break in. They track compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS, and if something suspicious happens like an unauthorized access attempt, immediate action is taken to lock things down.
By encrypting data at every level, businesses can protect their devices, secure file transfers, and ensure compliance without disrupting daily operations. It’s a smart, proactive way to keep sensitive information safe.
Best Practices for Implementing and Managing Endpoint Encryption
Implementing and managing endpoint encryption effectively requires a structured, well-thought-out approach. Here’s a refined breakdown of best practices, ensuring clarity, security, and compliance.
I. Foundational Planning and Policy
A. Identify and Classify Sensitive Data
- Conduct a comprehensive inventory of all endpoints, including laptops, desktops, mobile devices, and removable media.
- Categorize data based on sensitivity levels (e.g., public, internal, confidential, restricted).
- Determine which data must be encrypted based on regulatory and business requirements.
B. Develop a Robust Encryption Policy
- Establish clear encryption guidelines, covering:
- Which endpoints and data require encryption.
- Approved encryption algorithms (e.g., AES-256).
- Key management and recovery procedures.
- Incident response protocols.
- User roles and responsibilities.
- Ensure encryption policies align with industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and NIST standards.
C. Engage Key Stakeholders
- Involve IT, security, legal, compliance, and management teams in policy development.
- Clearly communicate policies and expectations to all users, ensuring organization-wide compliance.
II. Implementation and Deployment
A. Select the Right Encryption Solutions
- Choose encryption methods based on use case:
- Full-Disk Encryption (FDE): Encrypts entire drives, preventing unauthorized access to lost or stolen devices.
- File or Folder-Level Encryption (FLE): Secures specific files, useful for shared storage and cloud environments.
- Removable Media Encryption: Ensures external devices such as USB drives and external hard drives remain secure.
- Verify compatibility with operating systems, applications, and hardware.
B. Implement Secure Key Management
- Utilize a centralized key management system (KMS) for secure key storage and distribution.
- Enforce role-based access control (RBAC) to limit key access.
- Define key backup and recovery procedures to prevent data loss in case of key corruption.
C. Deploy in Phases and Conduct Thorough Testing
- Conduct pilot rollouts to identify and resolve compatibility issues before full deployment.
- Perform endpoint integrity checks to ensure encryption won’t disrupt system performance.
- Continuously monitor for unexpected system behavior or conflicts with business applications.
D. Enforce Encryption for Removable Media
- Require encryption for USB drives, external HDDs, SD cards, and other portable storage devices.
- Implement policies to restrict unencrypted external device access on corporate networks.
- Utilize device control solutions to monitor and enforce encryption compliance.
III. Ongoing Management and Monitoring
A. Continuous Monitoring and Compliance Enforcement
- Track endpoint encryption status using centralized security dashboards.
- Deploy Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools to detect unauthorized access attempts.
- Establish alerts for non-compliant devices or failed encryption processes.
B. Keep Encryption Software and Systems Updated
- Regularly patch encryption tools, operating systems, and firmware to address vulnerabilities.
- Automate software updates to reduce human error and maintain security hygiene.
C. User Training and Awareness
- Provide ongoing training on encryption best practices, data security, and compliance policies.
- Educate employees on secure password creation, phishing awareness, and handling encrypted devices.
- Reinforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) as an additional security layer.
D. Establish a Strong Incident Response Strategy
- Develop a clear plan for handling encryption-related security incidents such as lost or stolen devices and key compromise.
- Ensure security teams are trained in data recovery, forensic analysis, and regulatory reporting.
- Implement an emergency decryption process for critical business continuity scenarios.
E. Conduct Regular Audits and Compliance Reviews
- Perform periodic security audits to assess encryption effectiveness.
- Generate compliance reports to satisfy regulatory requirements and internal security governance.
- Utilize third-party penetration testing to identify weaknesses in encryption implementation.
IV. Key Considerations for Long-Term Success
A. Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)
- Restrict access to only necessary personnel to minimize insider threats.
B. Zero Trust Security Model
- Require continuous verification for all access requests, even from trusted users.
C. Automation and AI-Driven Security
- Leverage AI-driven tools to detect anomalies, automate key management, and enforce encryption policies.
D. Regular Data Backups with Encryption
- Ensure encrypted data is backed up in secure, geographically dispersed locations.
- Implement immutable backups to prevent ransomware from modifying stored data.
By following these structured best practices, organizations can ensure strong, scalable, and efficient endpoint encryption while minimizing security risks and compliance challenges.
Final Words
The tech space is constantly changing today. Protecting endpoints is no longer optional – it’s a must for organizations of all sizes. By strengthening the new perimeter with strong endpoint encryption solutions, businesses can protect their valuable data and mitigate the risk of costly breaches. With the assurance of a secure endpoint network, organizations can operate with confidence, knowing that they have taken proactive steps to defend against new cyber threats.







