What is EaaS?
Encryption as a Service, or EaaS, is a cloud-based solution that allows organizations to encrypt their data, whether it’s stored (at rest) or transmitted (in transit).
This service uses advanced encryption technologies, offering a secure and efficient way to protect sensitive information.
With EaaS, businesses can easily keep their data safe and secure while avoiding the hassle of managing complicated encryption infrastructure. This service is super scalable, making it an excellent fit for both small businesses and large corporations alike.
EaaS adjusts to the unique needs of different organizations, letting them implement strong, customized encryption strategies. This flexibility is especially advantageous in our current fast-paced, data-rich environment, where the amount and sensitivity of information keep increasing.
How Encryption as a Service Works?
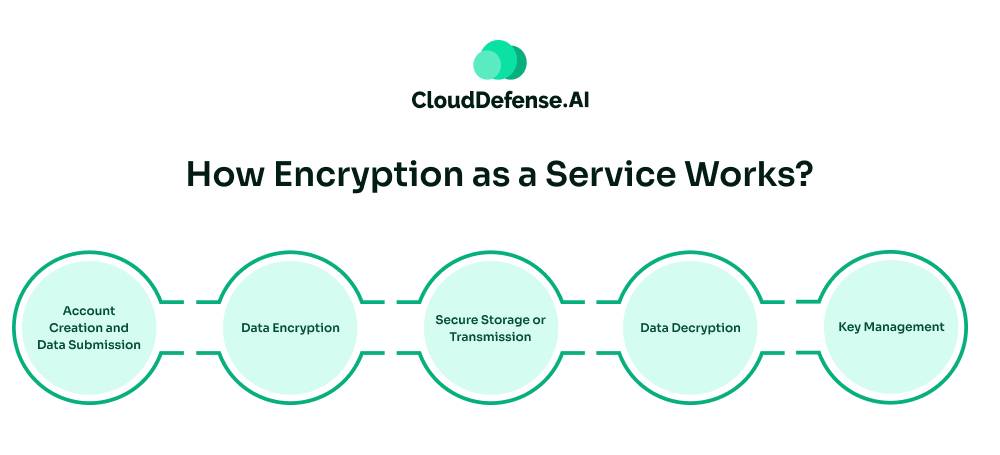
Encryption as a Service simplifies the process of securing data by offering a cloud-based platform that handles encryption and decryption operations. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how EaaS works:
Account Creation and Data Submission
Users start by creating an account with an EaaS provider. Once the account is set up, users can submit the data they need to encrypt through a user-friendly interface or an API provided by the service.
Data Encryption
The EaaS platform employs advanced encryption algorithms and techniques to secure the data. This process typically involves generating unique encryption keys for each data set. These keys ensure that the data is transformed into an unreadable format, protecting it from unauthorized access.
Secure Storage or Transmission
After the data is encrypted, the EaaS platform securely stores it in the cloud or transmits it to the intended recipient. The encrypted data can be safely stored without fear of unauthorized access, as only those with the correct decryption keys can revert it to its original form.
Data Decryption
When users need to access encrypted data, they request decryption through the EaaS platform. The service uses the appropriate decryption keys and algorithms to convert the data back to its original plaintext form, ensuring that only authorized users can decrypt and view the data.
Key Management
Effective key management is a critical component of EaaS. The service provider handles the generation, distribution, and storage of encryption keys, ensuring they are managed securely throughout their lifecycle. This reduces the risk of key compromise and simplifies the process for users.
Types of Encryption as a Service
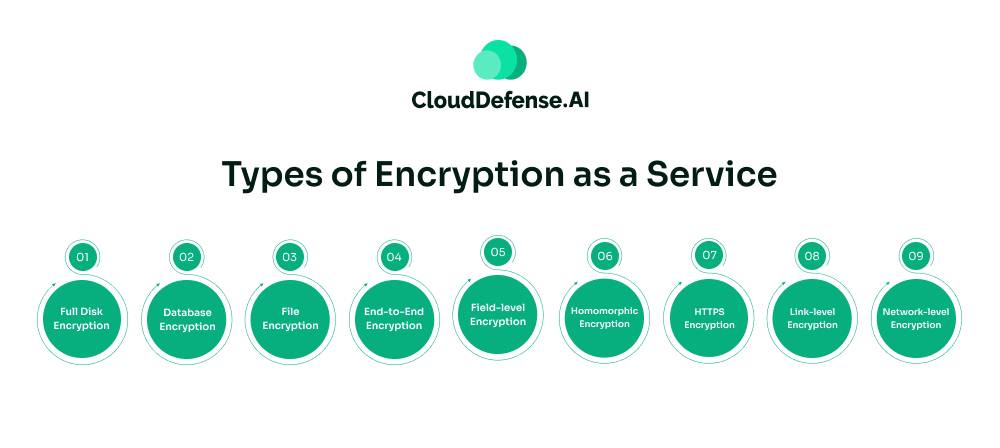
EaaS offers various encryption methods to protect sensitive information. This section explores different EaaS types, highlighting their unique benefits and applications in protecting data.
Full Disk Encryption (FDE)
Full Disk Encryption (FDE) secures data by converting all information on a hard drive into an unreadable format. This ensures that if the drive is moved to another machine, the data remains inaccessible without the decryption key. FDE can be pre-installed or added later, offering reliable security that protects data at the hardware level.
Database Encryption
Database encryption involves securing sensitive information within databases by transforming it into an unreadable format. Depending on the security needs, this can be applied at different levels, such as individual columns, rows, or the entire database.
By encrypting data within databases, organizations can protect against unauthorized access and ensure compliance with regulatory standards, safeguarding critical information like customer records and financial transactions.
File Encryption
File encryption focuses on protecting individual files by converting them into an unreadable format, accessible only with the appropriate decryption key. This method is essential for securing documents, spreadsheets, and other files containing sensitive information. File encryption can be used for both locally stored files and those shared over networks, providing comprehensive protection against unauthorized access and data breaches.
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE)
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) ensures that data transmitted between two parties remains secure and private, preventing any intermediaries from intercepting and accessing the information.
Unlike Transport Layer Security (TLS), which encrypts only the client-server communication, E2EE encrypts the entire data transmission process. Popular messaging apps like WhatsApp, Signal, and Facebook Messenger utilize E2EE to provide users with enhanced privacy and security.
Field-level Encryption
Field-level encryption targets specific types of sensitive data within a database or application, such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, bank account numbers, and health-related information.
Encrypting these specific fields enables organizations to protect their most sensitive information against unauthorized access. This approach is especially beneficial for websites and applications that manage personal and financial data, guaranteeing compliance with data protection regulations.
Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption allows encrypted data to be processed and analyzed as if it were still in its original form. This innovative approach enables complex mathematical operations to be performed on ciphertext without compromising its security. Homomorphic encryption is particularly valuable in scenarios where data needs to be analyzed or processed while remaining encrypted, maintaining privacy and usability simultaneously.
HTTPS Encryption
HTTPS encryption secures communications between a website and its users by running HTTP over the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. This requires the installation of a public key certificate on the web server, enabling it to encrypt all transmitted content. Using HTTPS ensures that data exchanged between the server and the user’s browser remains confidential and protected from interception, enhancing website security and user trust.
Link-level Encryption
Link-level encryption secures data at each point of transmission, encrypting it as it leaves one host and decrypting it at the following link before re-encrypting it for further transmission. This process continues until the data reaches its final destination, using different keys or algorithms at each stage. Link-level encryption is adequate for securing data as it moves through various nodes in a network, ensuring comprehensive protection throughout its journey.
Network-level Encryption
Network-level encryption applies cryptographic services at the network transfer layer, situated between the data link layer and the application layer. This type of encryption is commonly implemented through Internet Protocol Security (IPsec), a framework of open standards developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
IPsec provides secure communication over IP networks by offering data protection through authentication and encryption at the network level.
Benefits of Encryption as a Service
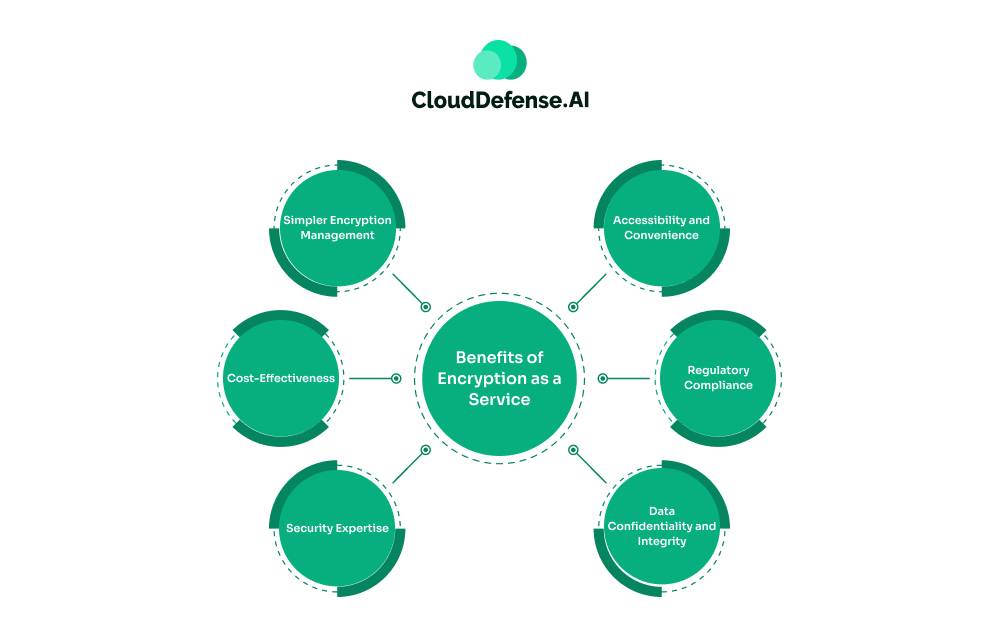
Encryption-as-a-Service offers a range of benefits that make it an attractive option for organizations looking to secure their data efficiently and effectively:
Simpler Encryption Management
With EaaS, organizations can outsource the management of the entire encryption process. This means businesses do not need to handle the complexities of encryption themselves, allowing them to focus on their core activities.
Cost-Effectiveness
EaaS eliminates the need for upfront investments in encryption hardware, software, and infrastructure. Organizations can access these services on a pay-as-you-go basis, reducing costs and aligning expenses with actual usage.
Security Expertise
EaaS providers typically employ security experts who are well-versed in the latest encryption technologies, best practices, and compliance requirements. This expertise ensures that encryption solutions are in place and up to date.
Accessibility and Convenience
EaaS offers easy accessibility through cloud-based platforms. Users can encrypt and decrypt their data from anywhere using various devices, provided they have a secure connection to the service. This flexibility enhances productivity and convenience.
Regulatory Compliance
EaaS providers ensure their encryption services comply with relevant industry regulations and standards, helping organizations meet their legal and regulatory obligations without the need for extensive internal resources.
Data Confidentiality and Integrity
Encryption provided by EaaS helps protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or interception. This ensures that data remains confidential and maintains its integrity, safeguarding it against breaches and cyber threats.
Challenges and Limitations of Encryption as a Service
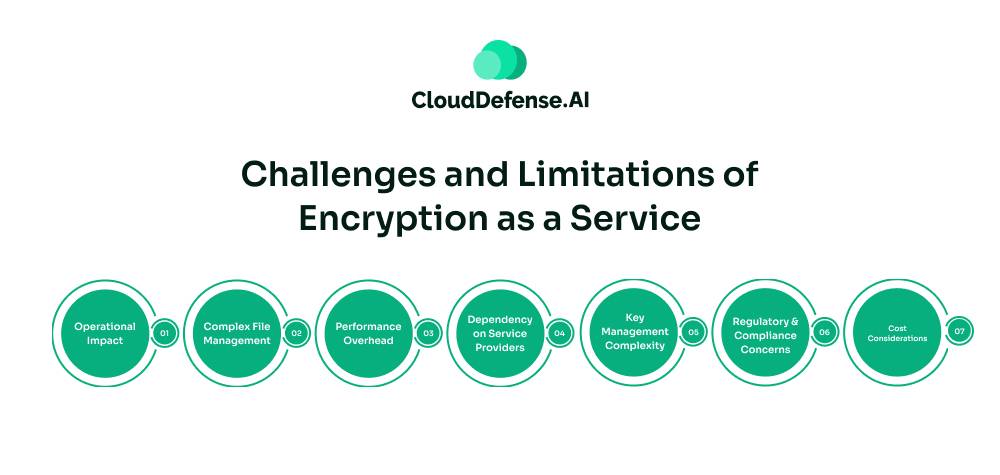
While Encryption-as-a-Service offers numerous advantages, it also presents specific challenges and limitations that organizations need to consider:
Operational Impact
Encrypting files, particularly those containing personally identifiable information (PII), can enhance security but may hinder employees’ ability to complete their work efficiently. Accessing, modifying, and sharing encrypted files can become cumbersome, leading to potential delays and productivity losses.
Complex File Management
In environments where employees frequently create, move, modify, copy, and share data, adding encryption can complicate file management. The additional steps required to encrypt and decrypt files can result in a disorganized and difficult-to-manage workspace, affecting overall workflow.
Performance Overhead
Encryption and decryption processes can introduce performance overhead, particularly for large volumes of data or real-time applications. This can slow down system performance and impact the user experience, especially if the encryption solution is not optimized for efficiency.
Dependency on Service Providers
Relying on an EaaS provider means entrusting them with the security of sensitive data. Any vulnerability or breach at the provider’s end can compromise the encrypted data. Additionally, organizations may face challenges if the provider’s services are disrupted or if there are issues with service availability.
Key Management Complexity
Effective encryption relies heavily on proper key management. If encryption keys are not managed securely, the overall security of the encrypted data can be compromised. Organizations must ensure that their EaaS provider has decent key management practices in place to prevent unauthorized access.
Regulatory and Compliance Concerns
While EaaS providers strive to comply with industry regulations, organizations still need to ensure that their specific regulatory requirements are met. This may involve additional audits, assessments, and ongoing monitoring to maintain compliance.
Cost Considerations
Although EaaS can be cost-effective by eliminating upfront investments in encryption infrastructure, the pay-as-you-go model can lead to unpredictable costs. Organizations need to carefully monitor usage and expenses to avoid unexpected charges that could impact their budget.
Final Words
Encryption-as-a-Service offers a practical and user-friendly method for safeguarding sensitive information, easing the burden of encryption management for organizations. Although there are challenges to consider, including possible workflow interruptions and the intricacies of key management, the advantages of robust data protection and compliance assistance render EaaS an essential resource. By skillfully addressing these challenges, companies can fully utilize EaaS, keeping their data secure while ensuring operational efficiency and tranquility.







