What is a Deepfake?
A deepfake is an advanced form of artificial intelligence technology that uses deep learning algorithms to generate highly realistic, yet entirely fabricated, images, sounds, or videos.
By manipulating or synthesizing media content, deepfakes can create convincing portrayals of people saying or doing things they never actually said or did.
This technology is often used to produce misleading or deceptive content, such as fake news or manipulated videos, that can influence public perception or spread false information.
The ability of deepfakes to blur the line between reality and fiction poses significant ethical and security challenges today.
How does Deepfakes Work?
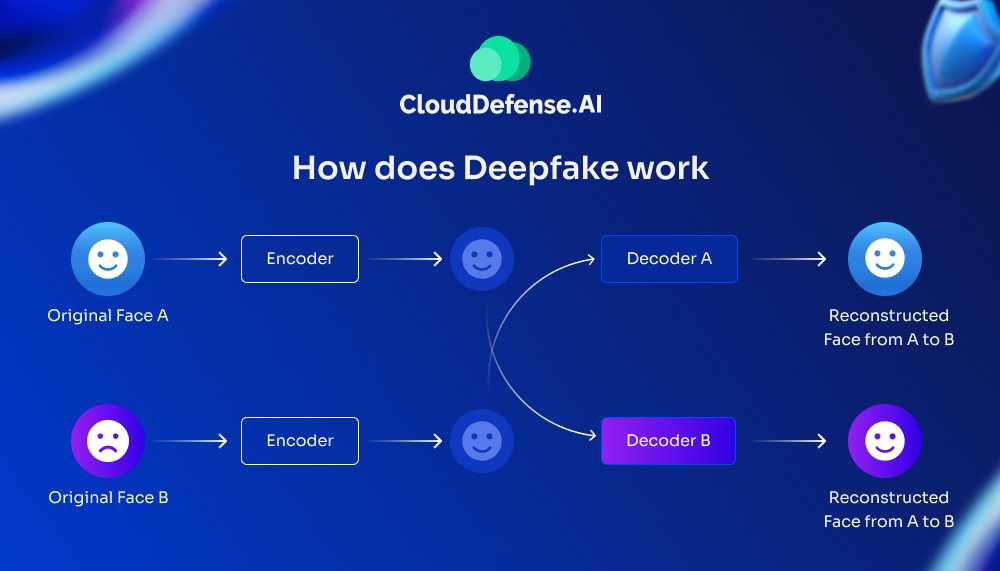
Deepfakes are not simple edits or photoshopped media; they are highly realistic, entirely synthetic content generated using advanced AI. At the core of deepfake creation lies a machine-learning model known as a Generative Adversarial Network.
This technology enables deepfakes to mimic facial features, voices, and even movements in a way that makes them nearly indistinguishable from authentic media. Here’s how the process works:
Understanding Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
A GAN is the backbone of deepfake technology and consists of two primary components working in tandem:
The Generator
- This is the creative engine that generates synthetic content, such as images, audio, or videos.
- It starts with a training dataset consisting of real-world media of the target, such as photographs, videos, or voice recordings.
- Using this data, the generator produces an initial version of the deepfake, which is often crude and unrealistic at the start.
The Discriminator
- The discriminator acts as the critic, analyzing the generated content to assess how closely it resembles real-world media.
- It compares the synthetic output with authentic examples from the dataset, identifying flaws or inconsistencies.
- Feedback is then sent to the generator, specifying areas that need improvement, such as refining facial features, movements, or synchronization.
This adversarial process repeats in a loop. Over time, the generator improves its output, and the discriminator sharpens its ability to identify imperfections, resulting in highly realistic deepfakes.
Creating Deepfake Images
To generate deepfake images:
- The GAN analyzes multiple photographs of the target individual taken from different angles and lighting conditions.
- The generator synthesizes new images by mimicking the subject’s facial features, expressions, and details like skin texture and hair.
- The discriminator evaluates these generated images for inconsistencies, such as unnatural angles or distorted features. The feedback loop refines the image until it appears seamless and authentic.
Creating Deepfake Videos
For videos, the process is more intricate and involves replicating motion, behavior, and speech:
- The GAN processes multiple frames from existing video footage of the target to learn their facial movements, gestures, and mannerisms.
- The generator uses this information to create synthetic video frames, ensuring that movements, expressions, and lip-syncing match the intended context.
- The discriminator evaluates every frame for flaws, such as jerky movements, mismatched lighting, or unnatural speech synchronization. The generator iteratively refines these details until the video looks convincingly real.
Voice Replication
In cases where audio is required, deepfake technology can synthesize a person’s voice by analyzing speech patterns, tone, and pitch:
- AI models process hours of voice recordings to capture the nuances of how the target speaks.
- Using this data, the generator produces synthetic audio that matches the rhythm, accent, and intonation of the person.
When combined with video, this ensures seamless integration of lip movements and speech.
Continuous Refinement
The generator-discriminator feedback loop is the key to achieving realism. As the generator produces increasingly convincing outputs, the discriminator sharpens its ability to identify subtle flaws. This iterative process continues until the generated content becomes nearly indistinguishable from real media
What Are Deepfakes Used For?
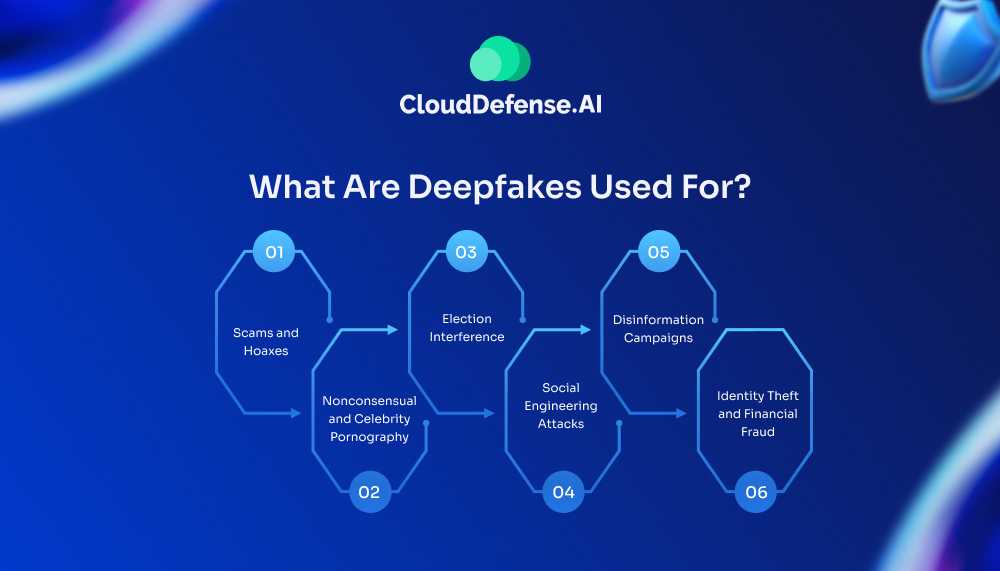
Deepfake technology, while a groundbreaking advancement in artificial intelligence, has unfortunately found a myriad of malicious applications alongside its potential for positive use. Its ability to create highly realistic but fabricated content has raised serious concerns across multiple sectors. Here’s a closer examination of the darker uses of deepfakes.
1. Scams and Hoaxes
Deepfake technology has become a tool for cybercriminals looking to craft convincing scams and hoaxes aimed at undermining organizations. For example, a deepfake video could falsely depict a high-ranking executive confessing to illegal activities or making damaging statements about their company. Such videos can result in significant financial losses, damage to corporate reputation, and even stock market fluctuations as companies scramble to debunk these false claims.
2. Nonconsensual and Celebrity Pornography
One of the most troubling applications of deepfake technology is in the creation of nonconsensual pornography. A staggering majority of deepfakes available online—up to 96%—involve this kind of content, primarily targeting celebrities. Beyond celebrities, deepfakes are also used to create revenge porn, leading to severe emotional and psychological distress for the victims.
3. Election Interference
Deepfakes pose a serious threat to the integrity of democratic processes by enabling election interference. Fabricated videos of political figures can be used to spread false information, manipulate public opinion, and potentially influence the outcome of elections. For instance, deepfake videos of prominent leaders like Donald Trump or Joe Biden could be designed to show them making statements or engaging in actions they never actually did, thereby misleading voters.
4. Social Engineering Attacks
Deepfake technology is increasingly used in social engineering attacks, where cybercriminals create fake audio or videos of trusted individuals to deceive victims into revealing sensitive information or transferring money. A notable case involved the CEO of a U.K. energy firm who was tricked into transferring €220,000 to a fraudulent account after being fooled by a deepfake voice that mimicked his parent company’s CEO.
5. Disinformation Campaigns
Deepfakes are a powerful tool in spreading disinformation. They can be used to create convincing fake news, conspiracy theories, or misleading information about political and social issues. For instance, a deepfake video could falsely portray a well-known figure making controversial statements, thus spreading misinformation that could rapidly go viral on social media platforms.
6. Identity Theft and Financial Fraud
Deepfake technology is also employed in identity theft and financial fraud. By creating realistic fake identities or mimicking a person’s voice, criminals can open bank accounts, authorize financial transactions, or commit other fraudulent activities under someone else’s identity. The convincing nature of deepfakes makes it difficult for both victims and security systems to detect these fraudulent activities before significant damage is done.
How to Spot a Deepfake?
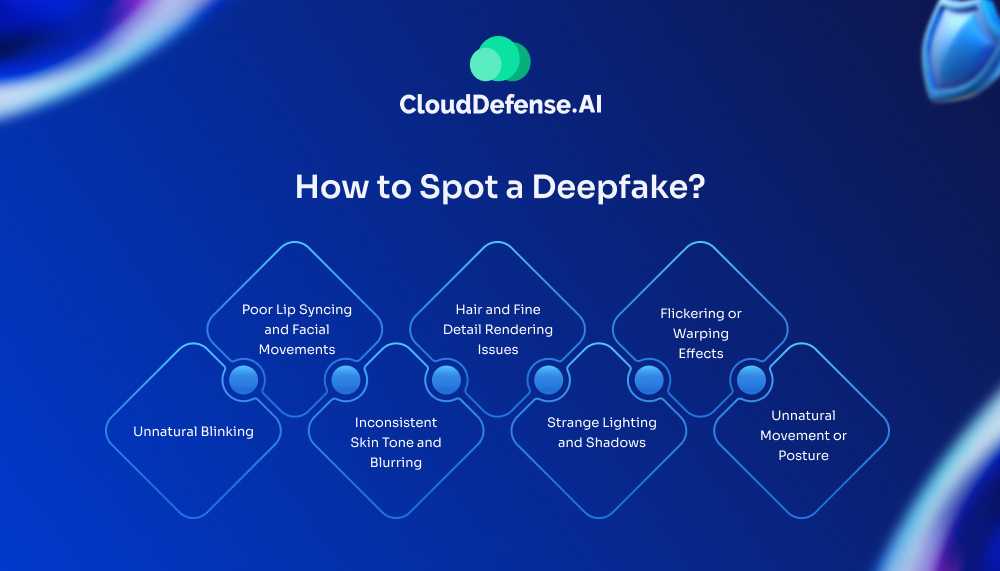
As deepfake technology evolves, spotting these artificial manipulations becomes increasingly challenging. However, certain techniques and signs can help you identify potential deepfakes.
1. Unnatural Blinking
Early versions of deepfakes often had a glaring flaw: the people in the videos didn’t blink normally, or at all. This was because the AI generating these videos was trained predominantly on images where subjects had their eyes open, leading to unnatural blinking patterns or the absence of blinking altogether. Although this issue has largely been corrected in more recent deepfakes, unnatural eye movement or blinking irregularities can still be a clue in detecting a fake.
2. Poor Lip Syncing and Facial Movements
One of the most telltale signs of a deepfake is poor lip-syncing. The synchronization between the audio and the movement of the lips might be slightly off, which can be noticeable to the trained eye. Additionally, facial expressions that don’t align with what is being said or that seem stiff and unnatural can also be a red flag.
3. Inconsistent Skin Tone and Blurring
Deepfakes often struggle with rendering realistic skin tones and textures. You might notice patchy or inconsistent skin colors across the face, especially where the face meets the hairline or neck. Blurring around the edges of the face or where it meets the background can also indicate that the video has been manipulated.
4. Hair and Fine Detail Rendering Issues
Creating realistic hair, especially individual strands, is particularly difficult for deepfake algorithms. Watch for hair that seems unnaturally smooth, blocky, or blurry. The fringe or flyaway strands might look odd, as the deepfake technology struggles to reproduce these fine details accurately.
5. Strange Lighting and Shadows
Lighting inconsistencies are a common issue in deepfakes. Look for unusual shadows or reflections that don’t align with the natural light source in the scene. For example, the illumination on the face might not match the rest of the body, or reflections in the eyes may not behave as they should, providing clues that the video has been tampered with.
6. Flickering or Warping Effects
Deepfakes can sometimes produce flickering or warping, especially around the edges of a transposed face. This can occur when the AI struggles to blend the fake elements seamlessly with the original footage, causing parts of the image to appear unstable or “glitchy.”
7. Unnatural Movement or Posture
Deepfake videos may display awkward or unnatural movements, particularly in the head, eyes, or limbs. This can be due to the AI’s difficulty in replicating the smooth and coordinated motions of a real person, leading to jerky or robotic-like actions.
Ongoing Research and Detection Efforts
To keep up with the advancements in deepfake technology, governments, universities, and tech companies are investing heavily in research to develop more sophisticated detection methods. For example, the Deepfake Detection Challenge, supported by major companies like Microsoft, Facebook, and Amazon, aims to accelerate the development of tools that can reliably identify deepfakes.
Social media platforms are also taking steps to mitigate the spread of deepfakes. For instance, Facebook has implemented policies to ban deepfake videos that are likely to mislead viewers, particularly in the context of political elections. However, the battle against deepfakes is ongoing, and as detection methods improve, so too do the techniques used to create more convincing deepfakes.
Final Words
Deepfakes pose a significant threat to our digital world, but with the right tools and knowledge, we can combat their deceptive power. By understanding the techniques used to create deepfakes and employing the latest detection methods, we can protect ourselves from falling victim to these digital illusions. As technology continues to advance, it’s necessary to stay informed and vigilant in the face of this challenge.







