What is Cloud Incident Response (Cloud IR)?
Cloud incident response is a structured approach to detecting, analyzing, and mitigating security incidents within cloud environments.
As organizations increasingly rely on cloud platforms, they face unique challenges, such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and misconfigurations.
Cloud incident response involves several key steps: identifying incidents through monitoring tools, assessing their impact, containing threats to prevent further damage, eradicating vulnerabilities, and restoring normal operations.
This process often uses automated detection mechanisms, AI-driven insights, and forensic tools to trace the root cause. Effective incident response requires collaboration between cloud service providers and the organization to ensure swift action.
Cloud Incident Response vs Traditional Incident Response
The differences between cloud incident response (IR) and traditional IR are rooted in the fundamental differences in infrastructure and complexity, reflecting the unique demands of cloud environments. Here’s how they diverge:
Data Storage
In traditional IR, data resides in on-premises data centers, providing physical control over storage. Conversely, cloud IR involves external servers managed by third-party providers. This externalization amplifies the risks, especially when misconfigurations arise, or security measures aren’t robust, making data more accessible to attackers.
Specialized Knowledge
While both traditional and cloud IR require expertise in identifying and mitigating incidents, cloud IR demands proficiency in cloud-specific methodologies. Professionals must understand cloud-native tools, shared responsibility models, and complex multi-cloud infrastructures.
Dynamic Environment
Traditional IR operates within relatively static environments, often relying on snapshots, endpoint logs, and pre-defined processes. In contrast, cloud IR deals with dynamic and distributed cloud ecosystems.
This complexity requires robust internal communication and meticulous log collection, including forensic data from multiple cloud services. Without these, investigating and remediating incidents becomes significantly harder.
Perimeter Redefinition
In traditional environments, firewalls establish the network perimeter. In the cloud, identity becomes the perimeter, with user accounts, API keys, and access credentials playing critical roles. Incident response must adapt accordingly.
For example, where traditional IR might block malicious IP addresses, cloud IR must focus on securing access points and mitigating risks across diverse user networks and endpoints.
The Cloud Incident Response Lifecycle
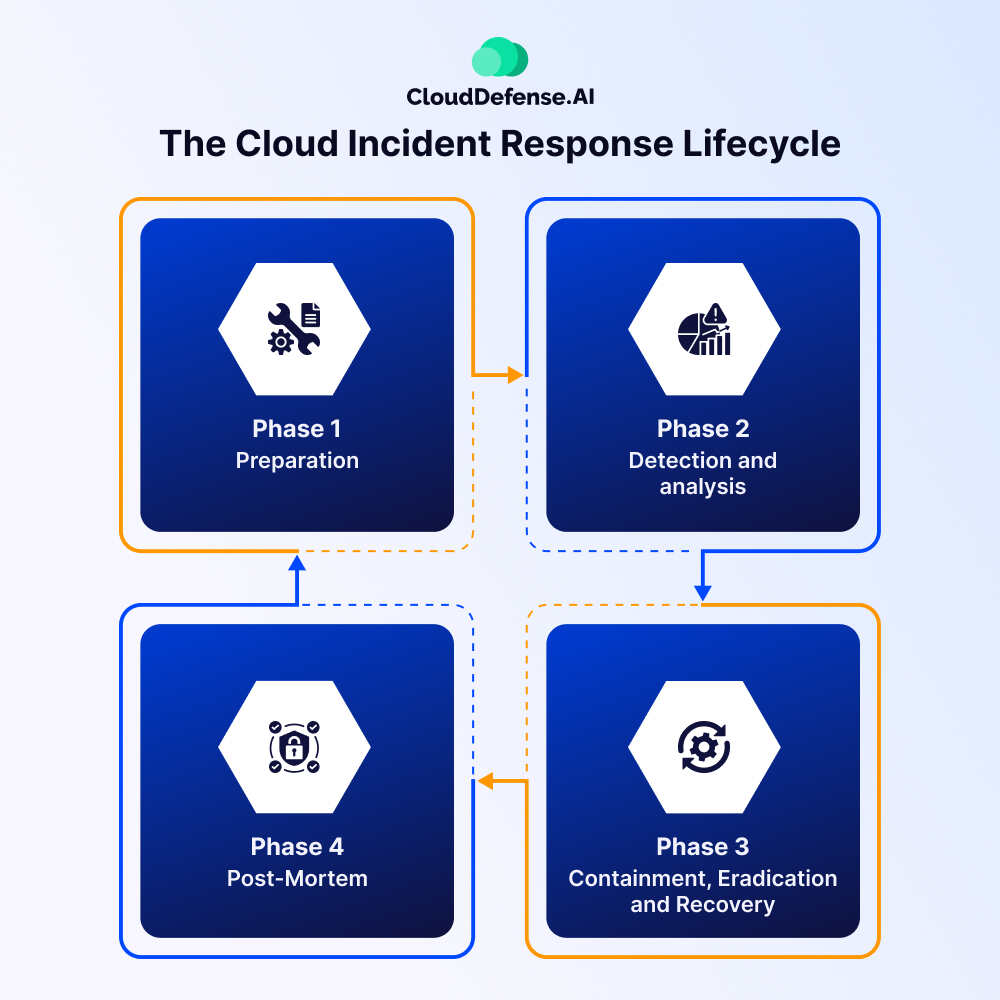
The cloud incident response lifecycle comprises four: preparation, detection and analysis, containment, eradication and recovery, and post-mortem.
The complete life cycle refers to the response that security professionals need to make to address security incidents and safeguard sensitive information. Here are four phases in a cloud IR lifecycle:
Phase 1: Preparation
When it comes to cloud incident response, every organization requires preparation so that they can proficiently handle any security incidents. Every organization needs to create policies, methodologies, and agreements to prepare themselves for any incidents.
Security professionals must emphasize establishing a standard that will help them maintain business continuity after mitigating a security incident. It is also essential for organizations to assess the incident response strategies to make sure they will be effective for any security incidents in the cloud environment.
Phase 2: Detection and analysis
After preparing the cloud IR strategy, the security team has to constantly monitor for security events and identify and report all the threats.
Once any threat is detected, security teams must analyze it to identify what impact it can make and then make security updates accordingly.
Phase 3: Containment, Eradication and Recovery
When a security incident occurs, the cybersecurity team must take necessary steps to isolate the infected device, account, or system from others and then shut it down.
Once the system or device has been isolated, the team should change all the credentials and eradicate everything from the device or system. In the next step, the cybersecurity team must analyze the security event and find out the origin of the attack, which will help them establish security controls to mitigate any further impact.
When the security incident is addressed effectively, the security team will now have to conduct comprehensive checking of the system, perform all the recovery needed, and then, instead, the operation.
Phase 4: Post-Mortem
In the final phase, the organization needs to authorize a post-mortem where a team will analyze all the steps taken during cloud incident response.
After the analysis, the team will also highlight the areas in which the organization needs to improve its security measures. This analysis will be constructive for security teams because it will make them better equipped for future security incidents.
What are the Benefits of Cloud Incident Response (IR)?
There are many benefits associated with cloud incident response that greatly benefit the organization. These benefits are:
Scalability
Cloud IR adapts effortlessly to the needs of growing organizations. As your infrastructure expands, it scales to handle complex security incidents, ensuring robust protection across your cloud environment.
Centralized Monitoring
By consolidating data from multiple cloud services, Cloud IR enables centralized monitoring. This improves threat detection and ensures a faster response to incidents by reducing the chaos of managing data from different sources.
Global Reach
Cloud services operate beyond geographic boundaries. Cloud IR ensures seamless incident management across multiple locations, making it ideal for organizations with operations around the world.
Resource Efficiency
With automated tools and centralized processes, Cloud IR optimizes resource use. This minimizes manual tasks, reduces the risk of team fatigue, and enhances operational efficiency, enabling teams to focus on critical decision-making.
Main Challenges of Cloud Incident Response
Here are some primary cloud IR challenges that many organization faces on different occasions:
- Limited Visibility: Cloud environments are vast and ever-changing, making it difficult for security teams to maintain full visibility of activities, assets, and components. Using multiple cloud providers only adds to this complexity.
- Challenges in Evidence Collection: In multi-cloud setups, gathering incident logs from diverse sources is difficult. Automated processes, like VM deletions, often erase critical evidence, hindering post-incident analysis.
- Shortage of Expertise: There’s a lack of professionals skilled in modern cloud IR techniques. Traditional incident response methods haven’t evolved fast enough to address cloud-specific threats effectively.
- Restricted Control: Organizations often rely on external cloud providers, limiting their control over infrastructure. This hampers root-cause analysis and the ability to respond directly.
- No Physical Access: Cloud providers manage infrastructure, restricting incident responders from physically accessing systems for containment or forensic investigations.
- Outdated Methods: Legacy Digital Forensic and Incident Response (DFIR) techniques aren’t sufficient for today’s evolving threats. Teams must stay agile and adapt to emerging attack vectors.
Best Practices for Incident Response in the Cloud
Cloud incident response (IR) is crucial for maintaining a secure cloud environment. By following key best practices, organizations can better prepare for, detect, and respond to security incidents while minimizing risks. Here are some essential strategies to adopt:
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments and Security Audits: Frequent assessments help identify vulnerabilities and security gaps in the cloud infrastructure. By remediating these issues, organizations can proactively prevent incidents and reduce the potential impact of any exploitation.
- Address Default Configurations: Default configurations often limit the retention of security logs or fail to capture key events, making investigations difficult. Proper configuration management ensures logs are available and accessible for effective incident analysis.
- Train Employees and Develop Cloud IR Playbooks: Define team roles and response protocols through comprehensive playbooks. Include scenarios like VM compromises or storage breaches, and regularly test these plans using simulations. Ongoing training ensures employees are well-equipped to handle cloud-specific threats.
- Use a Cloud Sandbox Environment: A sandbox environment isolates suspected threats, enabling responders to investigate incidents without affecting live systems. This approach facilitates detailed analysis and containment of potential security breaches.
Conclusion
Cloud incident response serves as an essential aspect of modern cloud security strategy. Every organization should focus on cloud incident response plans as it will help them to address security incidents and minimize their impact. In this guide, we have provided all four components of Cloud IR and the best practices you should follow that will help you effectively address cloud security incidents.







