Cloud computing is changing the world as it has become a crucial part of each one of our lives. Everything we use today is connected to the cloud, with most of our data stored there. A critical stat from Cybercrime magazine points out that by 2025 the cloud will hold 200 Zettabytes of our data, which helps verify the claim of how popular cloud computing has become.
This comprehensive guide will break down everything you need to know about cloud computing, its benefits and disadvantages, and how you’re likely already using it in your day-to-day life. Let’s get started!
What Is Cloud Computing?
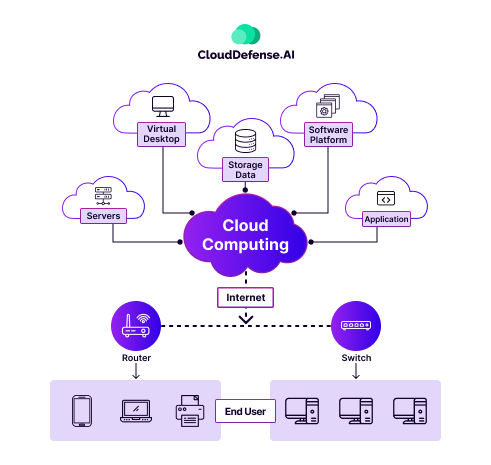
Cloud computing means delivering computing services—including storage, processing power, and applications—over the Internet. Instead of relying on local servers or physical hardware, users can access and utilize resources from remote data centers.
This model offers scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency, as users only pay for the services they employ. Cloud computing includes various services such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and serverless computing.
It enables businesses and individuals to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and deploy applications without the burden of managing complex infrastructures.
Example of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is ingrained in daily activities, often unnoticed. For instance, streaming services like Netflix rely on cloud infrastructure for seamless video delivery, sparing users the need for colossal server space. SaaS enables accessing applications via the cloud, eliminating the hassle of physical downloads and facilitating swift updates.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
Cloud computing functions by providing on-demand access to computing resources over the internet. It operates on a model that includes various service levels, such as:
- SaaS – Software as a Service;
- IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service;
- PaaS – Platform as a Service; and
- Serverless Computing.
Behind the scenes, cloud providers maintain data centers housing vast arrays of servers, storage, and networking equipment. Users access these resources remotely, typically through a web browser or an application interface.
The cloud provider maintains the infrastructure, ensuring scalability, reliability, and security. This shared and scalable nature of resources allows users to pay only for what they consume, offering flexibility and cost efficiency.
Overall, cloud computing has greatly helped to streamline IT operations, promote collaboration, and accelerate innovation.
Explaining the Different Cloud Computing Services
What Is SaaS?
SaaS or Software is a Service is a dominant form of cloud computing, valued for its profitability and convenience. It transforms software delivery into a subscription-based model, where users access centrally hosted applications without owning physical copies.
This model facilitates swift updates and additional services from developers. Widely adopted, SaaS is exemplified by Microsoft Office, epitomizing its prevalence.
Users and companies favor SaaS for its rapid software acquisition, consistent patches, and enhanced security measures that safeguard against alterations.
What Is IaaS?
IaaS or Infrastructure as a Service, similar to SaaS, delivers centralized server APIs to clients, offering instant and scalable computing infrastructure over the internet.
It enables companies to avoid the complexity and expense of managing physical servers and data centers, paying only for the resources they use.
IaaS becomes an extensive solution for outsourcing major computing tasks when combined with SaaS. Users can rent specific infrastructure components, optimizing resource utilization.
Notable IaaS examples, such as ICM Cloud and Microsoft Azure, are typical examples of its efficiency. They allow businesses to focus on core activities while leaving infrastructure management to capable service providers.
What Is PaaS?
PaaS, or Platform as a Service, mirrors other cloud computing models, providing a centralized server-based application platform. It furnishes a thorough cloud-based application development and deployment environment with the necessary resources for diverse business needs.
Clients pay for tailored resources accessible over the Internet without needing to download them individually.
PaaS covers infrastructure, middleware, development tools, and database management systems, supporting complete web application development lifecycles.
This is particularly beneficial for developers seeking efficient, cost-effective solutions. Users manage their applications and services on the PaaS platform, while the cloud provider handles other aspects.
Examples like Heroku and Salesforce.com help illustrate the singular efficiency of PaaS in simplifying development processes.
What Is Serverless Computing?
Serverless computing is a cloud computing model where developers focus on writing code without managing the underlying server infrastructure. Functions automatically scale to handle individual tasks, eliminating the need for provisioning or maintaining servers. Users are charged based on actual function execution rather than pre-allocated resources, promoting efficiency and cost-effectiveness. AWS Lambda and Azure Functions are examples of serverless platforms.
Types of Cloud Computing
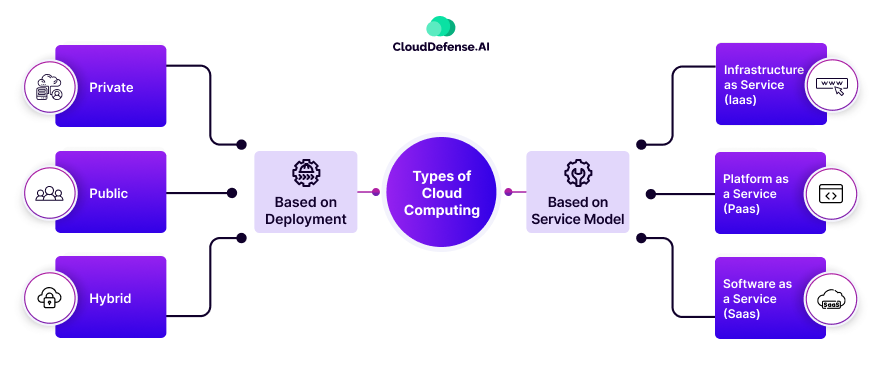
Cloud computing comes in a wide variety of types depending on users’ needs and the cloud providers’ goals. Let’s break down the different types of cloud computing you can encounter or request for your company.
Public Cloud
A public cloud refers to a cloud computing model where third-party service providers deliver computing resources, such as servers, storage, and applications, over the Internet.
These services are accessible to the general public, allowing organizations and individuals to use and pay for computing resources on a scalable and cost-effective basis.
Think of these as public digital spaces like parks or computer cafes where individuals can share computing resources with other tenants or renters. This is generally quite affordable and is a perfect choice for developing systems and Web servers or for those on tight budgets.
Popular public cloud providers include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is a dedicated cloud computing environment exclusively used by a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider.
In a private cloud, computing resources, such as servers and storage, are maintained for the exclusive use of the organization, offering enhanced control, security, and customization.
This deployment model is suitable for businesses with specific regulatory or data privacy requirements that require a higher level of control over their cloud infrastructure.
Most private cloud platforms are built in-house. This also means that most users physically own the cloud computing architecture, which can provide some legal or security benefits.
Security is often the number one reason big businesses will look to private cloud computing instead of public cloud computing.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is a cloud computing model that combines elements of both public and private clouds. It allows organizations to share data and applications between these environments.
Hybrid clouds offer flexibility, enabling workloads to move orderly between private and public clouds based on demand, cost, and performance considerations.
This model provides a strategic balance between the scalability of the public cloud and the control of a private cloud, providing you with the best of both worlds.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Although cloud computing is becoming more commonplace, many people still don’t understand how it operates. There are, in total, five primary cloud computing characteristics that are common in all cloud services:
Broad Network Access
This means that the user must be able to access the cloud computing servers from across the Internet using any device with Internet connectivity. This includes smartphones, tablets, and regular computers. The data or servers must be accessible through a standard web browser.
On-Demand Self-Service
This means that the user must be able to use the servers whenever necessary and can pay for that usage.
There should be no limits on accessibility at any time aside from payment, depending on the agreement made between the user and the cloud service provider.
Elasticity
The nature of cloud computing means that the network and its processing or storage capabilities can grow or shrink rapidly and as much as possible.
This should not affect the traffic or speed of the users since the cloud can harness more servers and storage space whenever necessary.
Resource Pooling
Of course, cloud computing demands that resource pooling be available. If a network can’t access more resources and pull them together for high-traffic events or big jobs, it’s not cloud computing.
Measured Service
Lastly, cloud computing services usually measure how much their servers or resources are being used. In this way, cloud computing can be considered a kind of “utility” computing along the lines of electricity or heat.
Indeed, cloud computing is the closest that the Internet has come to a public utility since its original inception.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Ultimately, cloud computing wouldn’t be so popular if there weren’t significant advantages and benefits to using these types of services. This list covers most of the significant benefits of cloud computing.
Software Can Be Used on Any Device
One of the many advantages of cloud computing lies in universal software access across devices. It eliminates the need for device-specific installations, allowing seamless use on mobile devices, desktops, and laptops without individual downloads.
This is especially crucial for companies ensuring consistent program usage across all workplace devices, avoiding delays, and ensuring universal access to files and programs.
Easy File Retrieval
You can simplify global file access by maintaining a network over the internet using cloud computing. Individuals and companies leverage this to retrieve files without reliance on physical storage devices. Cloud storage prevents the loss of valuable photos or documents for personal use.
In a corporate context, it facilitates universal access to sensitive information, benefiting employees who frequently travel. As long as an internet connection is available, users worldwide can access necessary company data for business deals or other purposes.
Easy Backup for Files and Data
Cloud computing provides an effortless solution for file and data backup. Having both physical and digital backups stored in different geographical locations enhances security. This practice protects against physical theft, loss, or accidental erasure. In the event of an office blackout, data stored in the cloud can be easily retrieved once the power is restored.
Moreover, it helps individuals and companies save valuable storage space on local devices, especially when dealing with large data files like images or videos.
Big Savings for Companies
Before embracing modern IT services, companies faced substantial expenses in constructing and maintaining their infrastructure, including server farms and computing centers. This incurred ongoing costs for physical upkeep and employee salaries.
Modern services that offer flexible, location-independent access to information bring major cost savings for companies. This simplicity reduces expenses, making it more economical for businesses.
Faster Patching for Software
Cloud computing allows rapid and automated software updates, which is crucial for efficiently addressing security concerns. Unlike traditional models requiring manual downloads, centralized hosting allows automatic updates, ensuring that all users benefit from vital patches simultaneously. This saves costs and enhances company and developer reputations, contributing to strong cloud security practices.
Better Security in Some Ways
Hosting software on centralized servers enhances security for big companies. Dedicated IT security teams manage security effectively, and software patches are consistently deployed.
Unlike on-site storage, cloud computing reduces vulnerability to physical theft or manipulation, as no on-site servers exist. Although cloud servers can still face physical attacks, it’s less susceptible than storing company information within the same building.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Although cloud computing has a lot to offer, there are some disadvantages of which everyone should be aware.
Sometimes Security Is Still a Concern
While cloud computing enhances security, it introduces unique risks. Dependency on encryption creates vulnerability, as a lost key could lead to a breach. The effectiveness of cloud services relies on human factors.
Moreover, geographical risks emerge. For example, a California-based company using cloud servers in Texas could face instant access loss during a Texas power outage, contrasting with on-site storage.
Finally, even cybersecurity-focused states like California are prone to major ransomware attacks.
Mistakes Are Magnified
Sharing server resources in cloud computing is a double-edged sword. Mistakes from server management or individual users can quickly impact the entire network.
For example, a security breach affecting one company could expose the files and programs of others, turning a simple error into a severe issue due to the collaborative nature of cloud computing.
Internet Connection Required
Unlike traditional computing, cloud computing relies on an internet connection. Without it, access to data or programs is impossible. In areas with unreliable internet, cloud computing may be impractical. The risk of internet outages due to factors like natural disasters could temporarily halt cloud access even though the data remains stored on physical servers.
Cloud Security
One of the biggest issues by far for cloud computing and its future is server security. There’s a lot to digest about this particular topic. Cloud security is usually focused on a few key focuses or technologies. Many cloud computing services use firewalls as their primary security features.
These can protect the perimeter of network security and any users and protect traffic between apps that may be stored on the same cloud
The History of Cloud Computing
In the 1960s, companies rented server time instead of buying expensive computers. This cost-effective approach waned with the rise of personal computers. Now, cloud computing’s recent resurgence, driven by profitable services and providers, competes well with on-site hardware. Today’s stable and responsive network architecture makes cloud computing a practical choice, reviving the cost-saving vision from its earlier days.
The Importance of Cloud Security
Cloud computing offers companies elevated customer service, enhanced flexibility, and convenience. Yet, the risks of misconfiguration and cyber threats demand a secure cloud environment. This is where cloud security becomes essential for protecting digital assets, reducing the impact of human error, and minimizing the risk of avoidable breaches that could harm the organization.
The good news is that cloud computing security is evolving and rapidly. Since more and more companies are putting their eggs into the cloud computing basket, it’s of prime concern to find answers for many of the security questions that remain. While cloud computing offers unique data retrieval and backup solutions, these servers are still vulnerable to hacking and management mistakes.
As organizations shift towards modernizing operations, challenges arise in balancing productivity and security. The terms “digital transformation” and “cloud migration” signal a common need for change. Achieving the right balance requires understanding how interconnected cloud technologies can benefit enterprises while focusing on the importance of deploying strong cloud security practices.
Future of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is about to go through a big change, and between 2025 and 2030, a bunch of important things will happen that will shape how it works.
More and more, companies will use multiple cloud services, combining ones that everyone can use with ones that are just for them. This will make things more flexible and efficient.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will be a big part of this, making things run on their own and keeping the whole system in good shape. As people use cloud services more, they will also pay more attention to keeping everything safe.
Companies that provide cloud services are expected to use fancy technologies like AI and machine learning to make sure their security is really strong, protecting against online threats.
The mix of cloud computing and blockchain technology is going to change how we store and process data, making it more transparent and safe when it comes to public information.
On top of all that, more and more people will use edge computing, and there will be a focus on making things specifically for the cloud and making the cloud work faster.
FAQ
What are the five essential characteristics of cloud computing services?
The five essential characteristics of cloud computing services are on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service. These define the flexibility, scalability, and efficiency of cloud-based solutions.
What is an example of cloud computing?
An example of cloud computing is using services like Google Drive or Dropbox to store and access files online. These platforms leverage cloud technology, allowing users to store, share, and collaborate on documents from various devices through internet connectivity.
Is cloud computing safe?
Cloud computing can be safe, but it depends on various factors, including the security measures implemented by the cloud service provider and the practices followed by users. Properly configured and managed cloud environments with robust security measures can offer high safety, but users and providers must prioritize security best practices to mitigate risks.
What are the cloud computing trends for 2025?
Anticipated trends in cloud computing for 2025 include increased adoption of edge computing, enhanced security measures, continued growth in hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, and advancements in AI and machine learning integration.
What are the five applications of cloud computing?
Five cloud computing applications include data storage and backup, SaaS for applications, IaaS for scalable computing resources, PaaS for development, and cloud-based analytics for data insights.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has become an integral part of digital topography, shaping how we store, access, and utilize data. Understanding the vast cloud ecosystem becomes important as we utilize its various models and services. The cloud offers us unparalleled benefits and challenges through its range of services.
Amidst the advantages lie security considerations, potential risks, and the ongoing evolution of cloud technology. Embracing the cloud is not just a technological shift but a strategic move, magnifying the vital role of strong cloud security measures for companies extensively using cloud infrastructure.







