What is AI?
Artificial intelligence, or AI, is a technology that enables machines to simulate human intelligence, including learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. It contains various subfields, such as machine learning and natural language processing, allowing computers to perform tasks such as speech recognition, decision-making, and data analysis.
AI applications range from digital assistants and autonomous vehicles to expert systems and intelligent data retrieval. While no single programming language is dominant, Python, R, Java, C++, and Julia are popular among AI developers. Artificial Intelligence is categorized into narrow AI, which focuses on specific tasks, and broader concepts like artificial general intelligence and artificial superintelligence, which aim to match or surpass human intelligence.
How does Artificial Intelligence work?
Artificial Intelligence combines vast amounts of data with sophisticated algorithms to identify patterns and make decisions or predictions. The process begins with data collection, gathering various input forms, like text, images, or sounds. In the processing stage, intelligent algorithms analyze this data, identifying correlations and patterns akin to neural networks in a brain.
The AI system learns behavior patterns through iterative analysis and refines its skills using machine learning techniques. Once trained, the AI utilizes its algorithms to make informed decisions or predictions based on new input, mimicking human judgment.
Finally, the output phase delivers decisions, recommendations, or actions derived from the learned data and decision-making process, aiming to provide human-like interactions and decision support for specific tasks.
Why is AI Important?
Artificial Intelligence has been revolutionizing how we live, work, and play by automating tasks traditionally performed by humans and enhancing efficiency and accuracy in numerous fields. In business, AI simplifies customer service, lead generation, fraud detection, and quality control, handling repetitive, detail-oriented tasks more effectively than humans. Its capacity to analyze vast data sets enables enterprises to gain insights into their operations, uncovering opportunities that might otherwise go unnoticed.
AI’s role in the success of companies like Alphabet, Apple, Microsoft, and Meta underscores its importance. For instance, AI powers Google’s search engine, drives advancements at the Google Brain research lab, and supports self-driving technology at Waymo. AI’s transformative potential is reshaping industries and creating unprecedented opportunities, exemplified by Uber’s success in revolutionizing ride-hailing services.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI, or generative artificial intelligence, is a technology capable of producing diverse content, such as text, images, audio, and synthetic data. It uses large datasets and generative models to create new and unique outputs.
GenAI systems utilize unsupervised or self-supervised machine learning, with their capabilities varying based on the data type they process. They can be unimodal, handling one input type, or multimodal, managing multiple input types.
Generative AI has broad applications across numerous industries, including art, writing, software development, healthcare, finance, gaming, marketing, and fashion. It powers tasks such as chatbot implementation, deepfake creation, music generation, and game development assistance, showcasing its versatility and transformative potential.
Types of Artificial Intelligence: Strong AI vs. Weak AI
AI can be broadly categorized into two types: weak AI and strong AI.
1. Weak AI
Weak AI, also known as narrow AI or artificial narrow intelligence, is designed to perform specific tasks and is prevalent in our daily lives. Despite its name, weak AI powers strong applications like Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri, and self-driving cars. It excels in its designated functions but lacks general intelligence.
2. Strong AI
Strong AI encompasses artificial general intelligence (AGI) and artificial superintelligence (ASI). AGI is a theoretical form of AI with human-like intelligence, self-awareness, and the ability to solve problems, learn, and plan. ASI would surpass human intelligence and capabilities.
Pros and Cons of AI
Artificial Intelligence has revolutionized various aspects of our lives, offering numerous benefits and presenting certain challenges. Understanding the pros and cons of artificial intelligence helps us navigate its impact on society and make informed decisions about its use.
Benefits of AI
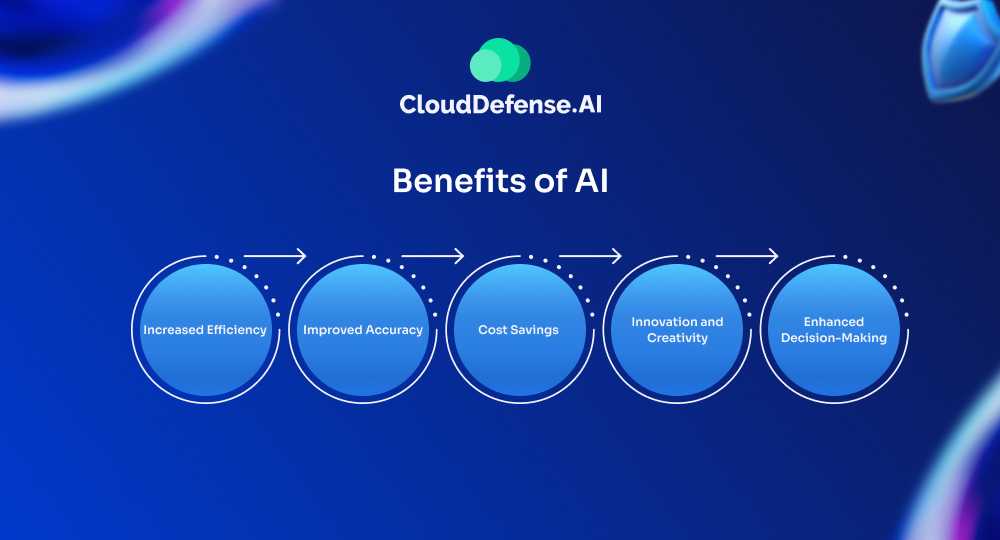
1. Increased Efficiency
Artificial Intelligence can handle repetitive and mundane tasks quickly and accurately, allowing humans to focus on more complex and creative work. For instance, artificial intelligence can process vast amounts of data in seconds, which would take humans much longer.
2. Improved Accuracy
When properly trained, AI systems can perform tasks with a high level of precision. This is particularly valuable in fields like healthcare, where artificial intelligence can assist in diagnosing diseases by analyzing medical images more accurately than human doctors.
3. Cost Savings
By automating routine tasks, AI can reduce operational costs for businesses. This is evident in customer service, where AI-powered chatbots handle inquiries without the need for human intervention, saving companies money on staffing.
4. Innovation and Creativity
AI tools enable new forms of creativity and innovation. In the arts, for example, AI can generate music, write stories, and even create visual art, opening up new possibilities for artists and creators.
5. Enhanced Decision-Making
AI can analyze complex data sets and provide insights that help in decision-making. Businesses use AI to predict market trends, optimize supply chains, and personalize customer experiences, leading to better outcomes and strategies.
Challenges of AI
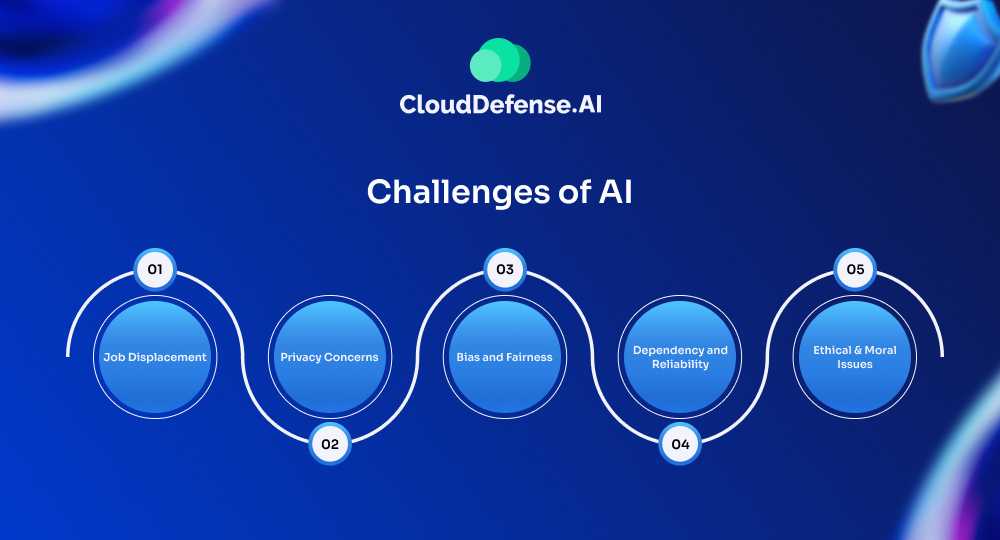
1. Job Displacement
AI’s efficiency in automating tasks can lead to job losses, particularly in sectors like manufacturing and customer service. While AI creates new job opportunities, the transition can be challenging for displaced workers.
2. Privacy Concerns
AI systems often require access to large amounts of personal data. This raises concerns about data privacy and security, as sensitive information could be misused or hacked.
3. Bias and Fairness
AI systems can inherit biases from their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Ensuring fairness and transparency in AI decision-making is a significant challenge.
4. Dependency and Reliability
Over-reliance on AI systems can be risky. If these systems fail or malfunction, it can disrupt operations and cause significant problems, especially in critical sectors like healthcare and finance.
5. Ethical and Moral Issues
The use of AI in areas like surveillance, military applications, and deepfake technology raises ethical questions. Balancing the benefits of AI with potential moral implications is crucial.
Deep Learning vs. Machine Learning
Machine learning and deep learning are key subfields of AI, with deep learning being a subset of machine learning. Both utilize neural networks to learn from vast datasets, mimicking the brain’s decision-making processes through interconnected nodes.
Machine learning algorithms typically employ neural networks with an input layer, one or two hidden layers, and an output layer. They rely on supervised learning, where humans must structure or label data. In contrast, deep learning uses deep neural networks featuring an input layer, multiple hidden layers, and an output layer.
This structure allows deep learning to perform unsupervised learning, automatically extracting features from large, unlabeled datasets. This capability enables deep learning to scale effectively, surpassing traditional machine learning in handling complex and unstructured data without requiring extensive human intervention.
AI in Cybersecurity
AI-powered cybersecurity monitors, analyzes, detects, and responds to cyber threats in real-time. By analyzing vast amounts of data to identify threat patterns, AI can scan networks for vulnerabilities and prevent common cyber attacks. It establishes behavioral baselines to detect anomalies and restrict unauthorized access.
AI also prioritizes risks and instantly identifies malware and intrusions. When implemented correctly, AI automates repetitive security tasks, freeing up employee time and reducing human error.
CloudDefense.AI uses advanced AI and ML models to deliver exceptional cloud security solutions. Experience the future of cybersecurity—book a free demo today.







