What is a software-defined perimeter?
Software-defined perimeter or SDP is a security approach that’s all about controlling who gets access to what in your network. Instead of relying on physical hardware to set up security boundaries, SDP uses software to create virtual barriers around your network resources.
The cool thing about SDP is that it doesn’t matter where your stuff is located – whether it’s in a data center, the cloud, or spread across different places. SDP can protect it all by essentially making it invisible to anyone who shouldn’t be poking around.
What makes SDP special is how it handles access. Instead of just letting anyone on your network see everything, it checks who each user is and what they’re allowed to do. Only then does it let them see and use specific resources. This way, even if someone unauthorized gets on your network somehow, they can’t see or do much.
Another cool thing about SDP is that it can actually hide your infrastructure from outsiders. This makes it much harder for potential attackers to even know what to target. It’s a big step up in security, especially for organizations dealing with lots of remote work or cloud services.
Key Components of SDP
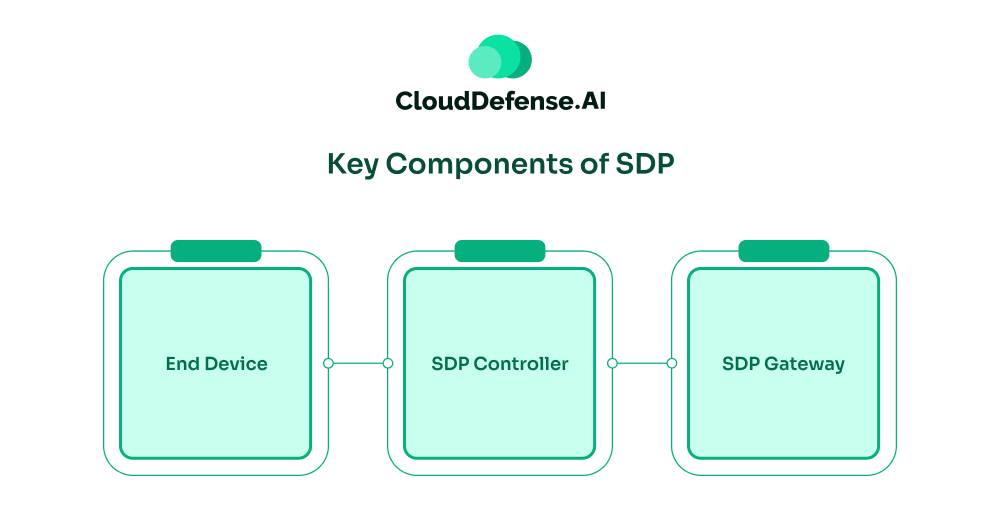
Let’s break down the main parts that make up an SDP system. There are three big players here:
End Device
First up, we’ve got the device you’re using – could be your laptop, phone, or tablet. This is where it all starts. To use an SDP system, you need to install some special software on your device. This software helps prove that you are who you say you are and that your device is legit. It’s like your digital ID card.
SDP Controller
Next, we have what’s called the SDP controller. This is the brains of the operation. It’s job is to check if you and your device are allowed in. It looks at who you are, what device you’re using, and decides if you should get access. If you pass the test, it tells the next component that you’re good to go. It also gives your device a special, temporary pass to use.
SDP Gateway
Finally, there’s the SDP gateway. It stands guard over all the important stuff you’re trying to access. When you try to connect, it checks the special pass that the controller gave you. If everything checks out, it sets up a secure connection between you and whatever you’re trying to access.
Together, these three parts work to make sure that only the right people on the right devices can get to the right information. It’s a team effort that keeps your company’s data locked down tight, no matter where people are working from.
How Did the SDP Come About?
Back in 2007, the Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) came up with this idea. They were looking for a better way to handle security, something that would only give access to people who really needed it. They wanted a system that could keep an eye on things and adjust trust levels based on what was going on.
The main goal? Make it so that all those applications and infrastructure stuff weren’t just sitting out there on the internet for anyone to see. This way, it’d be a lot harder for the bad guys to launch attacks like DDoS, ransomware, or just snooping around your servers.
A few years later, around 2011, the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) got interested. They saw potential in this concept and started working on fleshing out the SDP framework.
Now, here’s where it gets cool—Google was one of the first big companies to jump on this bandwagon. They developed their own version called Google BeyondCorp, which was pretty cutting-edge stuff at the time.
Fast-forward to today, and SDP is becoming a big deal. More and more companies are using it to upgrade their security across the board—for devices, cloud systems, and apps. It’s especially useful now that so many people are working from home or basically anywhere.
So yeah, SDP has come a long way from its military roots to become a key player in modern cybersecurity. It’s all about adapting to how we work now and keeping things locked down no matter where people are logging in from.
How Does SDP Work?
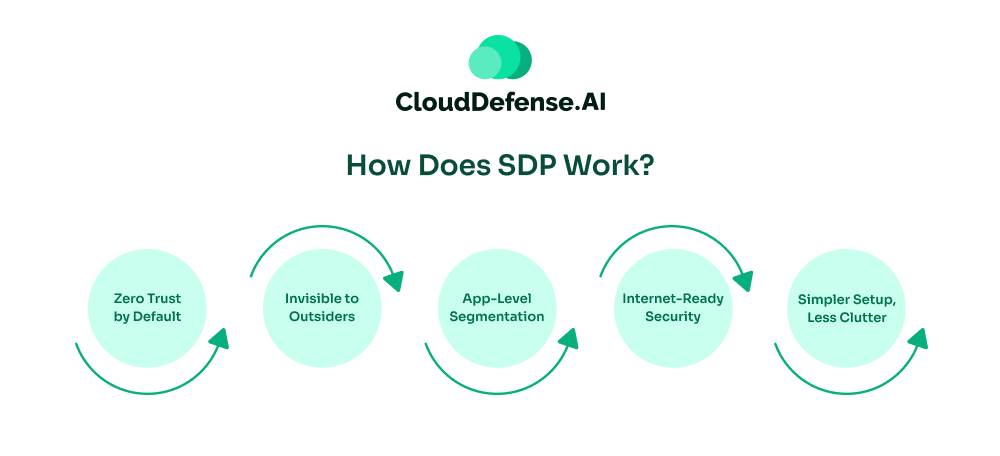
SDP operates on a set of principles that set it apart from traditional security methods. Let’s explore these key aspects:
Zero Trust by Default
In the SDP world, nobody gets a free pass. Users have to prove they’re legit before they can access anything. Once they’re verified, they only get to use specific apps they’re allowed to use – not the entire network. It’s like having a bouncer who checks your ID and only lets you into certain rooms of a club.
Invisible to Outsiders
One of SDP’s clever tricks is that it doesn’t accept incoming connections. Instead, it only sends outbound connections when needed. This approach makes your network and apps practically invisible to the internet. If potential attackers can’t see your setup, they can’t target it.
App-Level Segmentation
Instead of trying to wall off different parts of your network (which is a huge headache), SDP puts each app in its own protective bubble. This makes it way easier to control who gets in where, and it’s much simpler for your IT folks to manage.
Internet-Ready Security
With everyone working from everywhere these days, SDP shifts focus from protecting your office network to securing connections between users and apps, wherever they might be. It’s like having a secure tunnel from you to your work stuff, no matter where you’re sitting.
Simpler Setup, Less Clutter
One big advantage of SDP is that it cuts down on the need for lots of security appliances. You can say goodbye to managing a bunch of VPNs, DDoS protection systems, and firewall boxes. This streamlined approach makes life easier for IT teams and can save organizations a lot of headaches.
SDP Use Cases
Let’s explore some real-world scenarios where Software-Defined Perimeters really shine. Organizations often start using SDP in one of these four areas:
Replacing Outdated VPNs
Many companies are fed up with traditional VPNs. They’re clunky, can be a security risk, and are a pain to manage. SDP steps in as a modern alternative, offering smoother remote access without the headaches. It’s no wonder that a good chunk of organizations are looking to switch things up, especially those juggling both on-site and cloud setups.
Securing Multi-Cloud Environments
These days, it’s common for businesses to use a mix of cloud services. You might have Workday for HR, Microsoft 365 for productivity, and then use AWS and Azure for different parts of your infrastructure. SDP is great for this because it can secure connections to all these services based on your company’s policies, no matter where your users are logging in from.
Tightening Up Third-Party Access
Giving outside contractors or partners access to your systems can be risky. Often, they end up with more access than they really need, which is a security nightmare. SDP tackles this by making sure these external users can only access the specific applications they need, without ever getting into your main network.
Speeding Up Mergers and Acquisitions
When companies merge, integrating their IT systems can be a massive headache that drags on for years. You’ve got to deal with merging networks, sorting out overlapping IP addresses – it’s a mess. SDP makes this whole process much simpler and faster. It lets you quickly set up secure access between the merging companies without having to completely redesign your network infrastructure.
These are just a few examples, but they show how SDP can solve some pretty common and frustrating problems that many businesses face. It’s all about making security simpler, more flexible, and better suited to how companies actually work today.
Benefits of implementing SDP
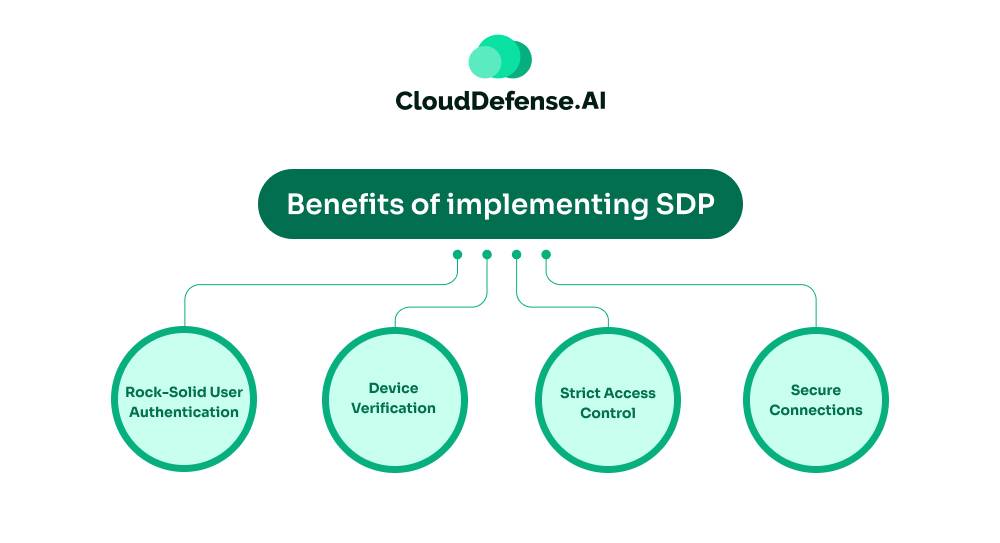
Let’s talk about why businesses are getting excited about Software-Defined Perimeters. There are some real advantages to using this approach:
Rock-Solid User Authentication
SDP is all about making sure you are who you say you are. Before you can access anything, it puts you through a thorough authentication process. This isn’t just a simple password check. SDP can use things like multi-factor authentication to really verify your identity. This helps protect against issues like weak passwords or those sneaky phishing attacks that try to steal your login info.
Device Verification
It’s not just about checking who you are, but also what you’re using to connect. SDP can enforce rules about which devices are allowed to access certain information. This might mean only letting company-issued laptops connect to sensitive data, or making sure your device is up-to-date with all the latest security patches before letting you in.
Strict Access Control
SDP follows a “zero trust” approach. This means no one gets a free pass to roam around the network. Instead, you only get access to the specific things you need for your job. Your access is based on your role in the company, and it’s carefully controlled to make sure you’re not seeing stuff you shouldn’t.
Secure Connections
When you connect to a resource using SDP, it sets up a direct, one-to-one connection. This connection is encrypted, which means others can’t eavesdrop on what you’re doing. Plus, SDP can scan the content of these connections to block any potential threats. This helps keep your work safe from prying eyes or malicious attacks.
SDP vs. VPN: Key Differences
| Feature | SDP | VPN |
| Security Model | Zero Trust | Perimeter-based |
| Access Control | Granular, application-level | Broad, network-level |
| Visibility | Applications are invisible on the network | Entire network is visible |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for cloud and mobile environments | Can be complex to manage for large or dynamic networks |
| Performance | Lower latency due to direct application access | May experience latency due to tunneling the entire network connection |
How to Choose:
- SDP is ideal for: Cloud-based deployments, mobile workforces, organizations with a “zero trust” security model, and those requiring granular access control.
- VPN is a good fit for: Traditional on-premise networks, occasional remote access needs, and situations where full network visibility is necessary.
The Takeaway:
While both VPNs and SDPs have their place, SDP offers a more modern and secure approach for today’s dynamic work environments. Its focus on zero-trust principles, granular access control, and cloud-based architecture make it a compelling option for organizations seeking robust application security.
Final Words
The business world is no longer confined by physical walls. The rise of cloud computing, mobile workforces, and the ever-present threat of cyberattacks demand a new security paradigm. SDP’s laser focus on user identity, device health, and context-aware access paints a future where only authorized users get to the applications they need, while threats lurk in the shadows, oblivious to the digital fortress protecting your data.
So, ditch the outdated VPN mentality and embrace the future of application security. With SDP, you can empower your workforce and safeguard your critical resources, all while maintaining complete control. The choice is clear: it’s time to build a security posture that’s as dynamic and adaptable as your business itself.







