Let’s consider a scenario where you’re logging into your bank account, typing away numbers and letters, confident that your information is secure.
But what if, unbeknownst to you, a hidden program was recording every keystroke? This is the unsettling reality of keyloggers, a malicious piece of software that hides in the shadows, stealing your sensitive data.
Every password, message, and bank account number you type is meticulously logged, potentially exposing your sensitive information to cybercriminals.
Keep reading as we explore what keyloggers are, how they work, and the different forms they can take. We’ll also equip you with the knowledge to identify and defend yourself against these digital spies, ensuring your online activity remains private and secure.
Let’s dive right in!
What is a Keylogger?
The term itself is quite descriptive: a keylogger, or keystroke logger, is a type of spying software designed to secretly record the keys pressed on a keyboard. It acts like a silent observer, capturing every keystroke you make, including:
- Letters and numbers you type
- Symbols and special characters
- Login credentials (usernames and passwords)
- Personal information like credit card details
- Messages and emails you compose
This information is then stored or transmitted by the keylogger, potentially exposing it to criminals who can misuse it for various malicious purposes. Since you’re typically unaware of a keylogger’s presence, it becomes a dangerous tool in the hands of cybercriminals who can exploit your stolen data for nefarious purposes.
The Threats of Keyloggers
Keyloggers pose a significant threat because they steal your sensitive data directly at the source – your fingertips. Once captured, this information can be used for a variety of criminal purposes, putting your financial security, online identity, and even your privacy at risk.
They Aren’t Always Illegal
While the malicious use of keyloggers is certainly illegal, it’s important to understand that they do have some legitimate applications. For instance, IT departments might use keyloggers to diagnose technical issues or monitor employee activity on company computers.
On a personal level, some parents might use keyloggers to keep an eye on their children’s online activities. The key distinction lies in intent – keylogging becomes a threat when used with malicious intent to steal data from unsuspecting victims.
Simply put, installing a keylogger on a device you own is legal, but secretly installing one on someone else’s device to steal information is a crime.
How Keyloggers Work
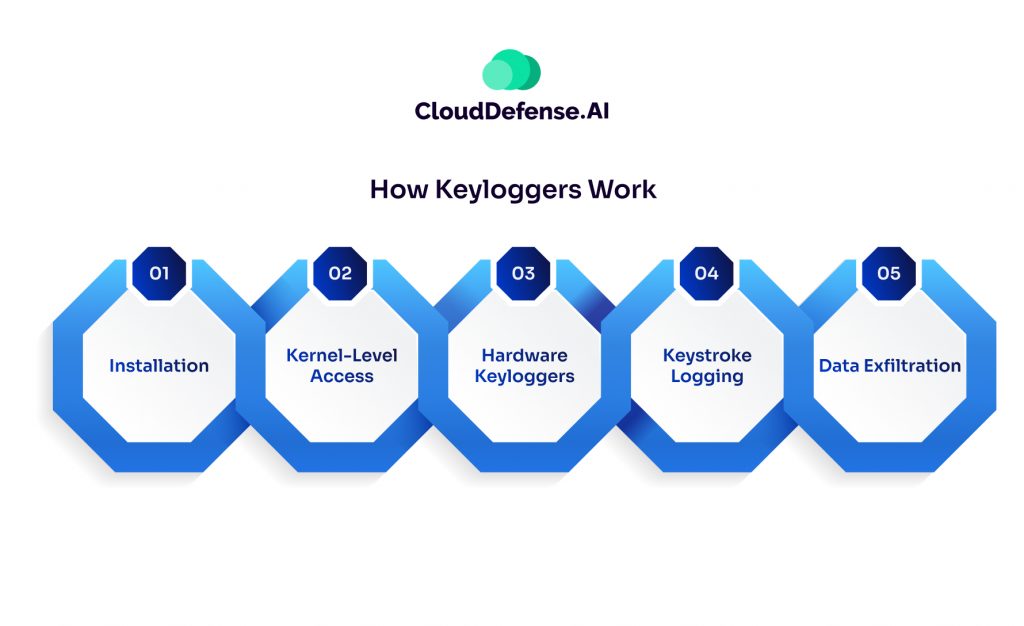
While seemingly simple in concept, keyloggers can employ various techniques to infiltrate your device and steal your keystrokes. Here’s a breakdown of their modus operandi:
1. Installation: Just like any other software, malicious keyloggers can trick you into installing them. This can happen through phishing emails with infected attachments, clicking on suspicious website links, or downloading untrusted programs.
2. Kernel-Level Access: Some sophisticated keyloggers target the core of your operating system, the kernel, to gain deeper access and remain hidden. This grants them the ability to intercept keystrokes before they reach the intended application.
3. Hardware Keyloggers: While less common, hardware keyloggers are physical devices attached to your keyboard cable or USB port. These external devices silently record your keystrokes and store them on internal memory or transmit them wirelessly to attackers.
4. Keystroke Logging: Once installed, the keylogger operates in the background, silently recording every key you press. This data is often stored locally on your device in a hidden file.
5. Data Exfiltration: Depending on the keylogger’s design, the stolen information might be periodically uploaded to a remote server controlled by the attacker, emailed directly to them, or simply stored on your device for later retrieval.
Types of Keyloggers
Keyloggers come in two main flavors: hardware and software. Let’s explore each type in more detail:
1. Hardware Keyloggers:
These are physical devices that act like middlemen between your keyboard and computer. They typically connect between the keyboard cable and the USB port, resembling a regular connector or adapter. Their small size makes them easy to hide, making them a sneaky tool for someone wanting to monitor your activity.
2. Software Keyloggers:
Software keyloggers are malicious programs that infiltrate your device, often disguised as legitimate software or snuck in through phishing emails or downloads. Once installed, they operate silently in the background, capturing your keystrokes in a few different ways:
- User-mode keyloggers: These utilize the operating system’s built-in functions (like GetAsyncKeyState or GetKeyState) to monitor your keystrokes. They require the attacker to actively monitor each key press.
- Kernel-mode keyloggers: These are more sophisticated and operate with higher system privileges. They can be harder to detect and even modify the internal workings of your computer.
- Form grabbers: These software keyloggers specifically target web forms and applications, capturing only the information you enter within those programs. They’re particularly dangerous for login credentials and financial data entered on websites.
Remember, both hardware and software keyloggers can steal your sensitive information. Software keyloggers might be easier to install remotely, while hardware keyloggers require physical access but leave less of a digital footprint.
What are Keyloggers Used For?
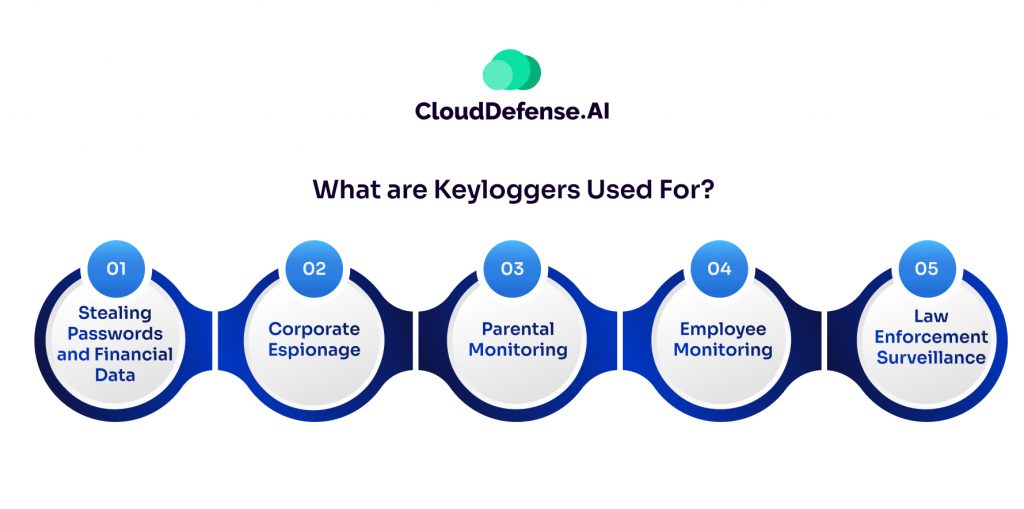
While keyloggers themselves aren’t inherently malicious, their ability to capture sensitive data makes them a favorite tool for cybercriminals. Here’s a glimpse into the dark side of keyloggers:
Stealing Passwords and Financial Data: This is the biggest and most nefarious use of keyloggers. Hackers and cybercriminals plant them to secretly record passwords, credit card numbers, bank account logins and other sensitive info as you type it. With that data, they can drain accounts, commit identity theft and fraud, or sell the info on shady markets.
Corporate Espionage: Some companies may use keyloggers to steal trade secrets, intellectual property and other confidential data from competitors, partners or their own employees. It allows them to digitally eavesdrop on proprietary info being typed.
Parental Monitoring: On a (somewhat) less shady note, some parents use keylogging software to keep tabs on what their kids are typing and the websites they visit online. The idea is to monitor for inappropriate content or communication with strangers.
Employee Monitoring: Similar to the parental controls, keyloggers allow employers and IT admins to monitor staff activity and internet usage on company computers and networks. Whether this is an ethical practice is up for debate.
Law Enforcement Surveillance: The authorities can potentially use keyloggers during criminal investigations to remotely capture suspects’ communications and digital activities as legal evidence.
So in summary, while keyloggers have some legitimate uses for monitoring, their biggest purpose is the unethical and illegal theft of sensitive data and logins. That’s why it’s so crucial to secure systems against these sneaky programs.
How to Detect and Remove Keyloggers
As far as we discussed, needless to say, having a keylogger on your system is bad news. So how do you know if you have one of these digital snoops installed? There are a few telltale signs:
- Your computer is acting sluggish or programs are crashing frequently. Keyloggers running in the background can really hog system resources.
- You get bizarre error messages or your desktop wallpaper has been changed without your doing. Signs that something is amiss.
- Your internet searches aren’t private – you keep getting pop-ups related to what you’ve recently typed.
If you suspect a keylogger, here’s what you can do:
First, get updated anti-malware tools and run a deep scan on your whole system. The good ones like Malwarebytes can usually sniff out and remove most common keyloggers.
If that doesn’t work, you may need to take more drastic action like booting your computer in “Safe Mode” to prevent keyloggers from loading. From there, you can try manually deleting any shady looking programs and files.
As a last resort, you may just want to back up your personal data and do a complete reformat and reinstall of your operating system to really clean house.
And going forward, stay protected with good anti-virus/anti-malware defense, firewall enabled, and think twice before opening any sketchy emails or downloading unfamiliar programs. Better to play it safe than have your passwords and private info fall into the wrong.
Final Thoughts
At the end of the day, staying ahead of keyloggers is an endless cat-and-mouse game. As soon as you think you’ve outsmarted one type, another pops up to cause headaches. That’s why having robust security solutions in your corner is so important.
Companies like CloudDefense.AI specialize in keeping applications and cloud systems secure from all the latest threats, keyloggers included. Our comprehensive security platform detects vulnerabilities, monitors for breaches, and automatically deploys protection across your cloud and apps.
If you’re serious about shoring up your defenses against various cyber risks, it’s time to explore CloudDefense.AI’s industry-leading app and cloud security solutions. Book a free demo today and get a firsthand look at how our AI-driven tech can safeguard your digital assets.







