Cyber Attacks in 2025 have become more sophisticated, more targeted, and more devastating than ever before. From ransomware that halts entire operations to phishing emails that look eerily real, these threats are no longer “if” but “when.”
In this article, we’ll dissect the Top 10 Common Types of Cyberattacks in 2025 and elaborate on how you can prevent them.
What is a Cyberattack?
A cyber attack is a malicious action that is carried out by any individual or entity to access an information system and cause harm to it.
A person trying to carry out a cyber attack is often termed a ‘hacker’. While some attacks on a system are carried out for fun by rookie hackers, all of them have the potential to harm a company significantly.
Two major forms of cyber attacks are carried out:
- Financially Motivated Attacks: A majority of cyber attacks are financially motivated, with the hacker hoping to extract company secrets or data and sell them on the dark net.
- Cyber Warfare: Cyber attacks have also been used to derail rival companies or even nations by harming their IT infrastructure or stealing sensitive data. This type of cyber attack is often carried out by a team of hackers and is termed cyber warfare.
| Read More: Curious about cyber attacks? Check out our exclusive guide on “what is a cyberattack“ and the steps you can take to stay protected. |
The financial impact of cyber attacks
Cyber attacks are not just security risks—they’re expensive. Consider these alarming statistics:
- The global average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million (IBM).
- Cybercrime’s global annual cost is projected to hit $9.5 trillion in 2024 (eSentire).
These numbers highlight the severe financial repercussions of failing to address cybersecurity proactively. For businesses, every unpatched vulnerability or weak endpoint could mean millions in losses or, worse, irreparable reputational damage.
Top 10 Common Types of Cyber Attacks in 2025 & How to Prevent Them
Check out the top 10 common types of cyber attacks that are being used to harm companies around the world. We have also included information on how to prevent these cyber attacks as well.
1. DDoS Attacks
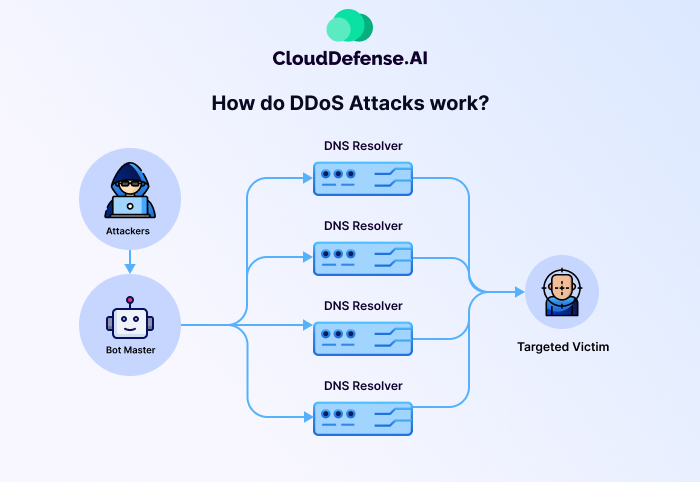
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack occurs when attackers flood a target’s server, network, or website with massive amounts of traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users. These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in network configurations, often leveraging botnets—networks of compromised devices—to execute the attack at scale.
Why Are They a Threat?
DDoS attacks are devastating because they:
- Disrupt business operations, causing downtime and lost revenue.
- Overload infrastructure, leading to service outages.
- Act as a diversion tactic, hiding more sophisticated attacks like data breaches.
Key Statistics:
- The average cost of a DDoS attack for businesses exceeds $218,000 per incident.
- Attacks are becoming more frequent, with one DDoS attack every 3 seconds globally.
How to Prevent DDoS Attacks
Preventing DDoS attacks requires a proactive and layered approach:
1. Invest in Scalable Infrastructure: Use cloud-based services that can handle large traffic spikes.
2. Implement DDoS Protection Services: Solutions like AWS Shield or Cloudflare DDoS Protection can detect and mitigate threats in real-time.
3. Monitor Network Traffic: Use advanced threat detection tools to identify abnormal spikes or patterns early.
4. Rate Limiting: Restrict the number of requests a user or IP address can make within a specific timeframe.
5. Redundancy and Load Balancing: Distribute traffic across multiple servers to prevent overload on a single point.
2. Malware Attacks
Malware, or malicious software, is designed to infiltrate and damage systems, steal data, or gain unauthorized access. This includes viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, spyware, and adware. Malware is often delivered through phishing emails, infected websites, or compromised software downloads.
Why Are They a Threat?
Malware attacks remain one of the most common and dangerous cyber threats because they:
- Steal sensitive data, including financial and personal information.
- Disrupt operations by corrupting or encrypting files.
- Create backdoors for attackers to maintain persistent access to systems.
- Spread rapidly across networks, impacting multiple systems.
Key Statistics:
- Over 560,000 new pieces of malware are detected every day
- Ransomware alone caused $20 billion in damages globally in 2023
How to Prevent Malware Attacks?
To counter malware effectively, focus on robust defenses and user awareness:
- Install Reliable Anti-Malware Software: Use solutions with real-time scanning and automatic updates, like Bitdefender or Norton.
- Regularly Update Software and Systems: Patch vulnerabilities in operating systems, browsers, and applications.
- Restrict Administrative Privileges: Limit access rights for users and applications to reduce potential damage.
- Educate Employees: Train staff to recognize phishing emails and avoid suspicious downloads or links.
- Network Segmentation: Separate critical systems from less secure areas to contain malware spread.
- Use Application Whitelisting: Allow only pre-approved programs to run on your systems.
3. Phishing Attacks
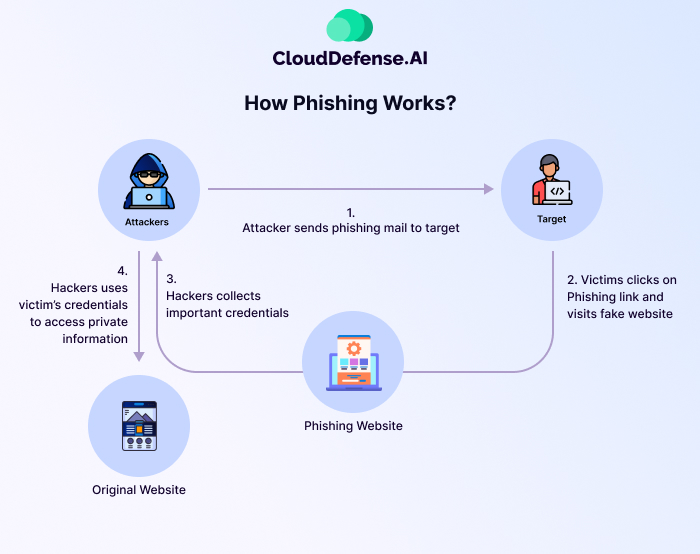
Phishing attacks manipulate human trust to steal sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial details, or personal data. Attackers pose as legitimate entities—like banks, colleagues, or trusted organizations—and send fraudulent emails, messages, or websites to deceive victims.
Why Are They a Threat?
Phishing attacks exploit the weakest link in cybersecurity: human error. They are highly effective because they:
- Bypass technical defenses, targeting users directly.
- Lead to credential theft, allowing attackers access to critical systems.
- Often act as a gateway to larger attacks, including ransomware or financial fraud.
Key Statistics:
- Over 3.4 billion phishing emails are sent daily.
- 82% of breaches in 2023 involved a human element, with phishing as a primary method.
How to Prevent Phishing Attacks
Phishing defense requires a combination of technology and user training:
- Deploy Email Security Solutions
- Use tools like Proofpoint or Mimecast to filter malicious emails.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Even if credentials are stolen, MFA prevents unauthorized access.
- Educate Employees on Phishing
- Regularly train staff to recognize red flags such as:
- Urgent requests for sensitive information.
- Suspicious links or attachments.
- Unfamiliar sender addresses.
- Regularly train staff to recognize red flags such as:
- Implement Browser Protections
- Use browser plugins to block access to known phishing sites.
- Simulated Phishing Campaigns
- Test employees with fake phishing emails to strengthen awareness.
4. Ransomware
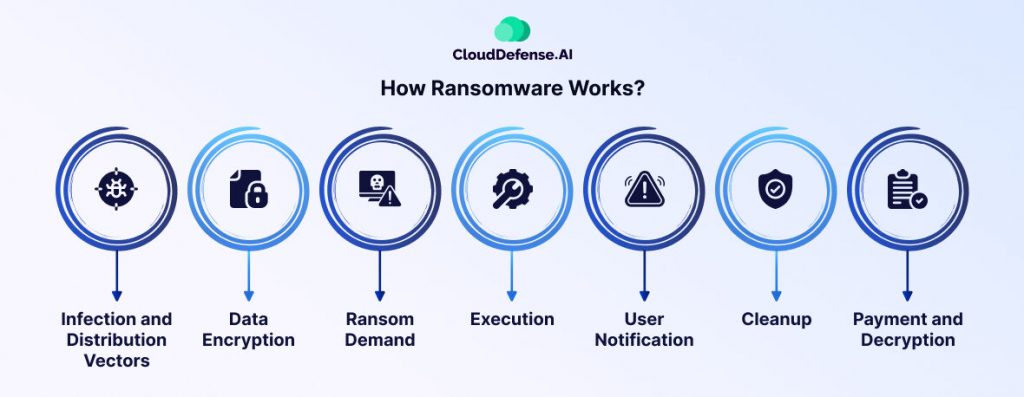
Ransomware is a form of malicious software that encrypts a victim’s data, locking them out of their own files and systems. The attacker then demands payment, typically in cryptocurrency, in exchange for the decryption key. Often, attackers threaten to leak sensitive data if the ransom isn’t paid.
Why Are They a Threat?
Ransomware is one of the most financially damaging cyber attacks because it targets critical systems and sensitive data. The risks include:
- Complete loss of access to files and systems, halting business operations.
- Reputation damage if data is leaked or operations are disrupted.
- Financial loss, both from the ransom itself and the recovery process.
Key Statistics:
- The global cost of ransomware attacks is projected to reach $20 billion by the end of 2024
- One in 5 organizations were hit with a ransomware attack in 2023.
How to Prevent Ransomware Attacks?
Effective prevention relies on strong cybersecurity practices and readiness:
- Back Up Data Regularly: Ensure backups are secure and stored offline or in isolated environments.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Isolate critical systems and data to prevent lateral movement by attackers.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for attackers to gain access.
- Update and Patch Systems: Apply security patches immediately to prevent known vulnerabilities from being exploited.
- Train Employees on Security Best Practices: Educate staff about recognizing phishing attempts, suspicious links, and unsafe attachments.
- Use Advanced Threat Detection Tools: Leverage endpoint protection and network monitoring to identify unusual activity.
5. SQL Injection Attacks
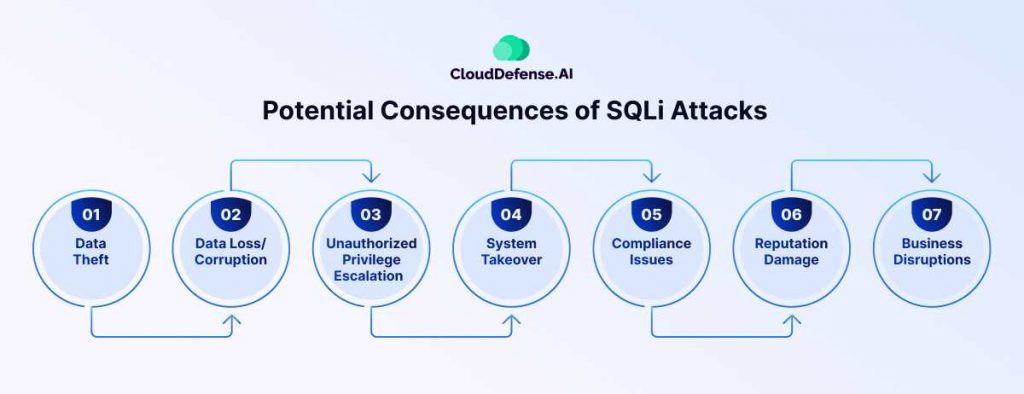
SQL injection (SQLi) is a type of attack where malicious SQL code is inserted into an input field (like a form or URL query) to exploit vulnerabilities in a website or application. This allows attackers to execute unauthorized SQL commands, which can compromise databases, steal data, or manipulate records.
Why Are They a Threat?
SQL injection attacks can have serious consequences for businesses:
- Unauthorized access to sensitive data, such as customer details, payment information, and internal files.
- Data corruption or loss, where attackers modify or delete crucial data.
- Complete control of the affected database, allowing further attacks like privilege escalation or data exfiltration.
Key Statistics:
- SQL injection remains one of the top 10 most common web application vulnerabilities (OWASP, 2023).
- 60% of database breaches are caused by SQL injection or other database vulnerabilities (Verizon DBIR 2023).
How to Prevent SQL Injection Attacks
Preventing SQL injection attacks requires a combination of secure coding practices and database configurations:
- Use Prepared Statements and Parameterized Queries: Ensure that all database queries are parameterized to prevent user input from being treated as executable code.
- Input Validation and Sanitization: Filter and validate all input fields, ensuring they accept only the expected data types (e.g., numbers, dates, text).
- Limit Database Permissions: Grant the minimum necessary permissions to the database user. Avoid using administrative privileges for normal operations.
- Use DevSecOps Solutions: Use an application security solutions like CloudDefense.AI to detect and block malicious SQL injections before they reach your application.
- Regular Security Audits and Code Reviews: Conduct regular reviews and penetration tests of your code and database to identify and fix vulnerabilities.
Why This Matters?
SQL injection is a simple yet powerful attack vector, and it doesn’t take much for attackers to exploit a poorly designed application. In 2024, it’s crucial to implement secure coding practices from the start.
The question is, are your web applications secure against SQL injections, or are you leaving the door open for attackers to walk right in?
6. Zero-Day Attacks

A zero-day attack occurs when hackers exploit a vulnerability in software or hardware that is unknown to the developer or vendor. Because there is no fix or patch at the time of the attack, these vulnerabilities are extremely dangerous. The term “zero-day” refers to the fact that the vulnerability has existed for “zero days” in the public domain without protection or mitigation.
Why Are They a Threat?
Zero-day attacks are particularly harmful because:
- There is no defense available when the attack occurs, making it difficult to detect and stop.
- The window for exploitation is wide open, with no prior knowledge or patching available to prevent attacks.
- They can remain undetected for long periods, giving attackers time to steal data, install malware, or take control of systems.
Key Statistics:
- In 2023, there were 1,100+ zero-day vulnerabilities reported, marking a 15% increase from the previous year (Google Project Zero).
- Zero-day attacks account for up to 50% of all targeted attacks against high-value targets (MITRE).
How to Prevent Zero-Day Attacks
Preventing zero-day attacks relies on proactive defense strategies and quick response capabilities:
- Maintain Up-to-Date Software: Regularly update all software and hardware, even if patches for known vulnerabilities are not available.
- Implement Behavior-Based Detection Systems: Use advanced threat detection tools that analyze system behavior for suspicious activity, rather than relying solely on signature-based detection.
- Adopt a ‘Zero Trust’ Security Model: Assume that no one, inside or outside the network, can be trusted by default. This reduces the impact of any breach by limiting access to critical systems.
- Monitor and Log All Activities: Continuous monitoring and logging of system activities help detect abnormal behavior that may indicate exploitation of a zero-day vulnerability.
- Engage in Active Threat Hunting: Proactively search for unknown vulnerabilities and anomalies within your network, rather than waiting for an attack to occur.
7. Supply Chain Attacks
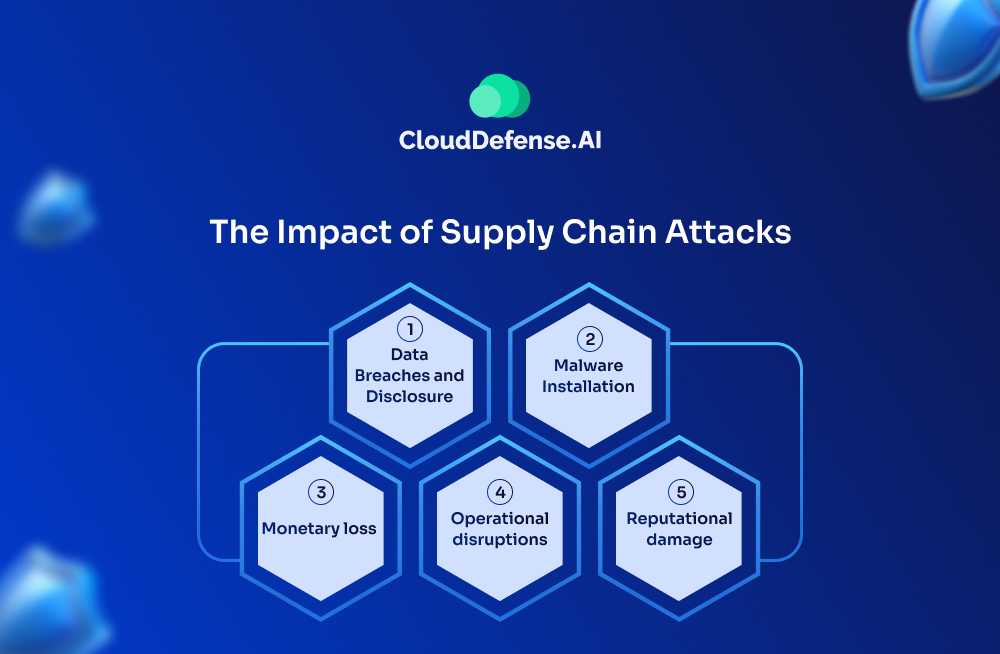
Supply chain attacks occur when cybercriminals target the less-secure elements within an organization’s supply chain to gain access to larger, more secure networks. Instead of directly attacking the primary target, they infiltrate vendors, contractors, or third-party services that have access to the target’s infrastructure, software, or data.
Why Are They a Threat?
Supply chain attacks can cause massive disruptions and data breaches. They are particularly dangerous because:
- They bypass direct defenses, leveraging trust in third-party vendors to gain access to target systems.
- The attack can spread quickly once it compromises a supplier, affecting many downstream systems and organizations.
- They target trusted relationships, making it harder for victims to recognize the threat until it’s too late.
Key Statistics:
- In 2023, 64% of organizations reported experiencing a supply chain attack.
- The SolarWinds attack in 2020 impacted thousands of organizations, including government agencies and private sector giants, due to a compromised software update.
How to Prevent Supply Chain Attacks
Mitigating supply chain risks requires careful vendor management and advanced security measures:
- Vet Third-Party Providers: Ensure your vendors have strong security protocols and compliance standards in place.
- Use Multi-Layered Security: Don’t rely solely on perimeter defense; use endpoint protection, network monitoring, and secure communication protocols to safeguard all levels of your network.
- Implement Zero Trust Security Models: Limit access to systems and data, even for trusted vendors, by enforcing strict access controls and continuous verification.
- Regularly Audit and Assess Vendor Security: Continuously assess your third-party vendors’ security practices and ensure they align with your organization’s security standards.
- Monitor for Anomalous Behavior: Implement continuous monitoring of systems to identify any unusual or unauthorized activities that could indicate a supply chain attack in progress.
8. Insider Threats
Insider threats are security risks that originate from within an organization. These threats can be malicious, where an employee, contractor, or business partner deliberately causes harm, or unintentional, where individuals inadvertently compromise security due to negligence or lack of awareness.
Why Are They a Threat?
Insider threats are often the hardest to detect because:
- Insiders have access to critical systems, data, and infrastructure, making it easier to bypass external security measures.
- The motives can vary: personal grievances, financial gain, or simply a lack of training.
- They can remain undetected for long periods, with malicious activities potentially continuing even after the individual has left the organization.
Key Statistics:
- Insider threats accounted for 30% of all data breaches in 2023.
- 80% of insider incidents are caused by employees, contractors, or third-party vendors.
How to Prevent Insider Threats
Mitigating insider threats requires a combination of security protocols and employee awareness:
- Implement Strict Access Controls: Implement CIEM solutions and follow the principle of least privilege: employees should only have access to the data and systems they need to perform their job.
- Monitor User Behavior: Use user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) tools to monitor unusual activity, such as large data transfers or access to sensitive information outside of normal working hours.
- Enforce Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policies: Deploy DLP systems that can detect and block attempts to exfiltrate sensitive data, whether through email, cloud storage, or USB devices.
- Conduct Regular Security Training: Regularly train employees on security best practices and raise awareness about the risks of insider threats, including how to identify suspicious behavior.
- Establish Clear Incident Response Plans: Have a clear plan in place to quickly identify, respond to, and mitigate any insider threats that occur, ensuring minimal disruption to operations.
9. Brute Force Attacks
Brute force attacks are like a battering ram for your passwords. Hackers systematically guess username and password combinations until they strike gold. These attacks are particularly effective against accounts with weak or commonly used passwords, giving attackers access to sensitive systems or data.
Why Are They a Big Deal?
Brute force attacks might sound old, but they’re still highly effective. Here’s why:
- Weak passwords make it easy for attackers to break in.
- Automated tools let hackers try thousands (or even millions) of combinations in a short time.
- Once they’re in, attackers can wreak havoc—stealing data, installing malware, or even locking you out of your own system.
Did You Know?
- In 2023, brute force attacks played a role in 80% of hacking-related breaches.
- A report shows that brute-force attacks, especially password spraying, have increased from 40 million in 2022 to nearly 200 million in early 2023.
How Do You Stay Safe?
Luckily, brute force attacks are preventable with a few smart moves:
- Use Strong Passwords: Skip the “123456” and aim for a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Limit Login Attempts: Set your systems to temporarily lock accounts after a few failed attempts.
- Turn on MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication): Even if a hacker guesses your password, MFA makes it much harder for them to get in.
- Add CAPTCHAs: Make CAPTCHAs tougher for bots to automate login attempts.
- Keep an Eye on Logins: Use tools to monitor for unusual patterns, like repeated failed attempts from one IP address.
10. Spear-Phishing Attacks:
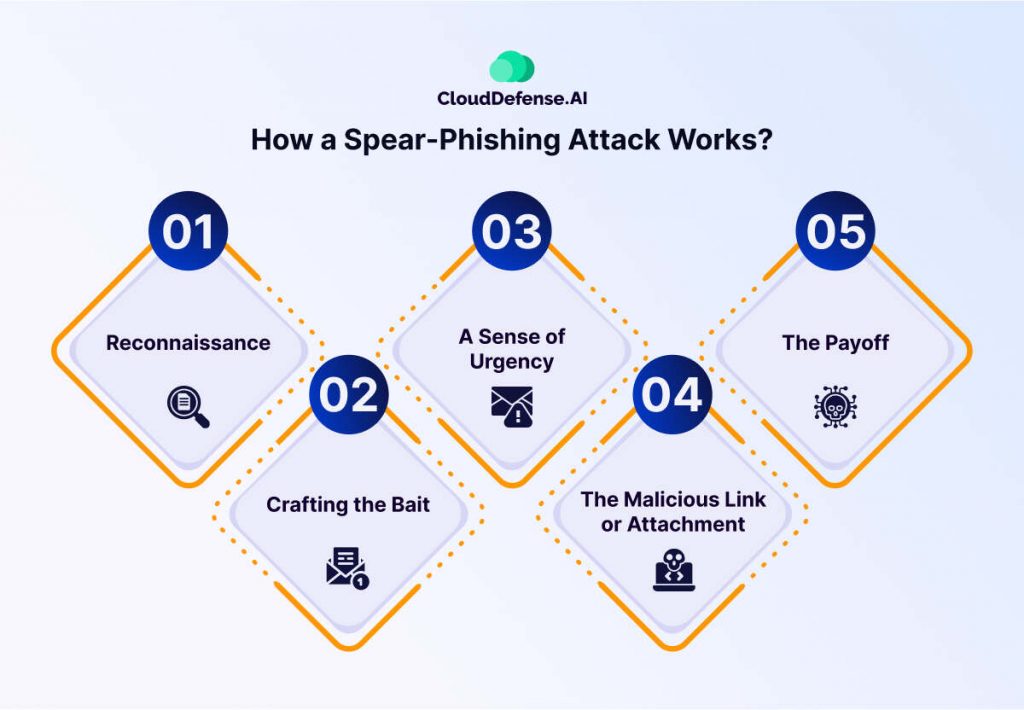
Spear-phishing attacks are a more targeted and sophisticated version of phishing. Attackers craft personalized messages aimed at specific individuals or organizations, using detailed information to make their attempts more convincing. The goal is often to steal sensitive information, deploy malware, or gain unauthorized access to systems.
Why Are They a Threat?
Spear-phishing attacks are highly effective because:
- They exploit trust and familiarity by referencing specific details, such as a person’s name, job role, or recent activities.
- They are difficult to identify, as they often appear to come from legitimate sources, such as colleagues or partners.
- They can act as an entry point for larger attacks, including ransomware, data breaches, and business email compromise (BEC).
Key Statistics:
- Studies reveal that 88% of organizations face spear-phishing attacks in a year, highlighting that businesses are targeted almost daily.
- The average cost of a successful spear-phishing attack can exceed $140,000, factoring in downtime, reputation damage, and recovery efforts.
How to Prevent Spear-Phishing Attacks
Effective prevention involves user awareness and technical safeguards:
- Educate Employees: Train staff to recognize spear-phishing attempts, including overly personalized emails, urgent requests, and slight misspellings in sender addresses.
- Use Email Authentication Protocols: Implement protocols like DMARC, DKIM, and SPF to verify the authenticity of incoming emails.
- Enable Advanced Email Security Tools: Use tools that detect and filter suspicious or fraudulent emails, such as Microsoft Defender for Office 365.
- Verify Suspicious Requests: Require employees to verify requests for sensitive information or fund transfers via a secondary communication channel.
- Regularly Update Contact Lists: Ensure that employee and vendor contact information is up to date to reduce the risk of impersonation.
Conclusion
As we’ve discussed, cyber attacks are a serious issue in 2025, and they’re only going to get worse. The Top 10 Common Types of Cyber Attacks in 2025 make it clear: businesses are being targeted more frequently, and the damage is real. From DDoS attacks to ransomware, these threats are too big to ignore. Every company, whether large or small, must be ready.
At CloudDefense.AI, we’re here to help you stay ahead of these threats. We offer top-tier security solutions that cover everything from code to the cloud. Our technology is built to handle the toughest threats and keep your systems secure. With CloudDefense.AI, you’re not just reacting to threats—you’re stopping them before they start.
You don’t want to wait until it’s too late. Now’s the time to get serious about security. With the right tools and a strong partner like CloudDefense.AI, you can protect your business from the top cyber attacks in 2024 and beyond. Book a free demo today and see how we can help protect your business.







