What is SaaS? Software as a Service Defined
SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a category of cloud computing services that delivers software applications over the internet. Instead of installing, maintaining, and running software on your local devices or servers, you can access and use the software through a web browser.
SaaS allows you to concentrate on development rather than the complex handling of hardware and software. SaaS providers host and maintain the infrastructure, handle software updates, and ensure the availability and security of the application.
How does SaaS Work?
SaaS operates through cloud-hosted infrastructure, enabling users to access applications via a web browser without local installation. Below is a structured breakdown of how SaaS works technically.
Cloud-Based Architecture
SaaS applications rely on cloud computing infrastructure, typically hosted on public cloud platforms (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP). This architecture consists of multiple layers:
- Presentation Layer: The front-end interface users interact with, usually accessed via a web browser or mobile app.
- Application Layer: The core logic that processes requests, executes business operations, and interacts with the database.
- Database Layer: Stores customer data, application states, configurations, and user settings in a secure, scalable environment.
This multi-tier architecture ensures high availability, performance, and security.
Multi-Tenancy Model
SaaS applications are designed to serve multiple customers (tenants) from a single instance while logically isolating their data. Multi-tenancy can be implemented in two ways:
- Scalability: Services scale independently based on demand.
- Fault Isolation: A failure in one service doesn’t impact the entire system.
- Faster Updates: Individual services can be updated without affecting the entire application.
APIs enable seamless integrations with third-party services, extending functionality (e.g., payment gateways, CRM tools, or security solutions).
Elastic Load Balancing & Auto-Scaling
SaaS providers use cloud-native services for automatic scaling and load distribution:
- Load Balancers: Distribute incoming traffic across multiple instances to prevent bottlenecks.
- Auto-Scaling Groups: Dynamically adjust resources based on real-time demand.
- Edge Computing & CDNs: Improve performance by caching static content closer to users.
This ensures high availability, even during peak traffic.
Security & Data Protection
Since SaaS applications operate in a shared environment, security is a top priority. Key measures include:
- End-to-End Encryption: TLS (for data in transit) and AES (for data at rest).
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Role-based access control (RBAC) and Single Sign-On (SSO).
- Threat Detection & Compliance: Advanced security tools like CloudDefense.AI help detect misconfigurations, enforce compliance, and monitor runtime threats.
SaaS providers must comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 to maintain trust.
Continuous Deployment & CI/CD Pipelines
Unlike traditional software, SaaS applications receive frequent updates without user intervention. This is made possible through:
- CI/CD Pipelines: Automate testing, deployment, and rollback mechanisms. Learn more about CI/CD here.
- Feature Flags: Gradually roll out new features without affecting all users at once.
- Blue-Green & Canary Deployments: Minimize downtime by deploying updates in controlled stages.
These strategies ensure reliability, quick bug fixes, and seamless feature enhancements.
Subscription & Billing Management
SaaS platforms typically operate on a subscription model with automated billing, including:
- Usage-Based Pricing: Charges based on API calls, storage, or active users.
- Tiered Plans: Different pricing levels with varying feature sets.
- Automated Invoicing: Integrated payment gateways handle recurring billing.
Advanced SaaS platforms use AI-driven analytics to optimize pricing and predict customer churn.
Software as a Service (SaaS) Characteristics and Features
SaaS has a tonne of unique features that help it to stand out. Here are some SaaS characteristics and features for you to check out.
Characteristics of SaaS:
- Multi-Tenancy: SaaS applications are multi-tenant, meaning a single software instance serves multiple customers. Each customer’s data is isolated and secure, and they can customize certain aspects of the application to suit their specific needs.
- Accessibility via the Internet: SaaS applications are hosted on a cloud infrastructure and can be accessed through a web browser. This eliminates the need for users to install, maintain, and update software locally.
- Subscription-Based Pricing: SaaS is typically offered on a subscription basis, where users pay a recurring fee to access the software. This pricing model often includes updates, support, and maintenance costs, making it a cost-effective solution for users.
- Centralized Updates and Maintenance: SaaS providers centrally handle software updates, patches, and maintenance. Users do not need to worry about installing updates or managing the underlying infrastructure, as the service provider performs these tasks.
- Scalability: SaaS applications are designed to scale easily, allowing users to adjust their subscription levels based on their needs. This scalability makes it convenient for businesses to adapt to changing requirements, whether scaling up or down.
SaaS Features:
- User Authentication and Authorization: SaaS applications typically include robust user authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized individuals can access the system. Role-based access controls (RBAC) are often employed to manage permissions based on user roles.
- Data Storage and Management: SaaS applications provide a centralized and secure storage system for user data. This includes features for creating, updating, deleting, retrieving data and organizing and structuring information effectively.
- Collaboration Tools: Many SaaS applications are designed to facilitate collaboration among users. This may include features such as real-time document editing, commenting, file sharing, and communication tools like chat and messaging.
- Integration Capabilities: SaaS applications often offer integration with other third-party services and applications. This allows users to connect their SaaS tools with existing software and services to streamline workflows and enhance functionality.
- Customization and Configuration: Users often have the ability to customize and configure certain aspects of the SaaS application to meet their specific needs. This may include settings, preferences, and branding options.
- Scalability: SaaS applications are designed to scale easily to accommodate changes in user load and data volume. This scalability ensures that the software can grow or shrink based on user needs.
- Reporting and Analytics: SaaS applications often include built-in reporting and analytics tools. Users can generate various reports and analyze data to gain insights into their activities, performance, and trends.
Different types of SaaS (Software as a Service)
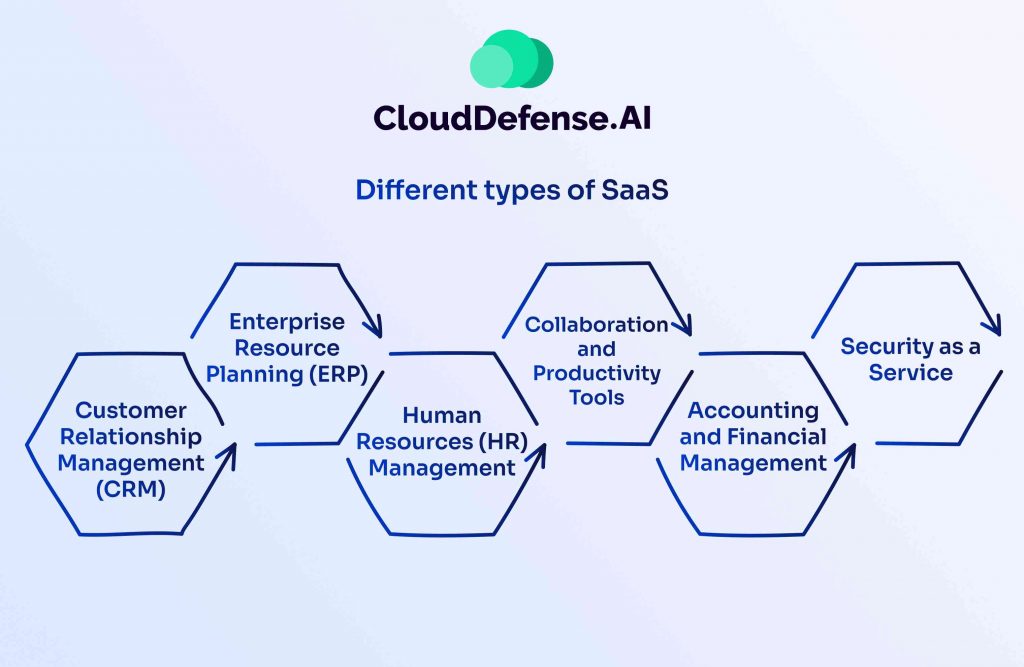
SaaS solutions span a wide range of industries, providing businesses with cloud-based tools to enhance efficiency, collaboration, and security. Here are some of the most common SaaS categories:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM solutions help businesses manage customer interactions, track sales leads, automate marketing campaigns, and improve customer service. Popular CRM platforms centralize customer data, providing actionable insights to boost sales and retention.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP SaaS solutions integrate business operations such as finance, supply chain management, HR, and inventory control. They streamline workflows, enhance decision-making, and ensure smooth business operations across departments.
Human Resources (HR) Management
SaaS HR platforms offer employee onboarding, payroll processing, benefits administration, and performance tracking. They help organizations automate HR tasks, ensuring compliance and improving workforce management.
Collaboration and Productivity Tools
Remote and hybrid work environments rely on SaaS collaboration tools, including project management software, document sharing platforms, and video conferencing apps. These solutions enhance communication, task management, and real-time collaboration.
Accounting and Financial Management
SaaS accounting tools simplify bookkeeping, invoicing, expense tracking, and financial reporting. They provide businesses with real-time financial insights, ensuring compliance with tax regulations and industry standards.
Security as a Service (SECaaS)
With the rise of cyber threats, businesses turn to Security as a Service (SECaaS) for cloud-based protection. This category includes SaaS solutions for identity and access management (IAM), antivirus, threat intelligence, and compliance monitoring.
CloudDefense.AI: A Next-Gen Security SaaS
Among leading SECaaS providers, CloudDefense.AI stands out with its AI-powered CNAPP. Offering CSPM, CIEM, and other cloud security solutions, CloudDefense.AI helps businesses secure their cloud environments with real-time risk mitigation and policy enforcement.
SaaS has revolutionized industries by offering scalable, cloud-based solutions for various business needs. From CRM to security, these tools enhance efficiency, drive innovation, and ensure better operational control in an increasingly digital world.
SaaS vs. On-Premise Software
Before SaaS’s inception, companies heavily relied on on-premise software. The word “On-premise” is used to refer to infrastructure that is hosted locally in a company. Check below for a detailed comparison of SaaS benefits over on-premise software.
| On-premise Software | Software as a Service | |
Deployment |
Software is installed and runs on local servers and infrastructure. | It is hosted in the cloud and does not require local installations or on-site servers. |
Accessibility |
Access is limited to the physical location where the software is installed and cannot be accessed from off-premise. | Accessible from any location with an internet connection. Often supports various devices (laptops, tablets, smartphones), allowing easy access. |
Maintenance |
The in-house IT team is responsible for updates, patches, and maintenance. Updates may cause downtime and require manual intervention. | The SaaS provider manages and applies updates centrally. Users typically receive the latest features automatically without worrying about tedious maintenance. |
Scalability |
Scalability may require additional hardware and resources. IT team is responsible for scaling infrastructure. | Easily scalable to accommodate changes in user load. Providers handle infrastructure scaling. |
Cost |
Upfront capital is required for software licenses and hardware. Additional costs for maintenance, updates, and support. | Subscription-based pricing with recurring fees. Costs often include updates, maintenance, and support. |
The Benefits of Using SaaS (Software as a Service)
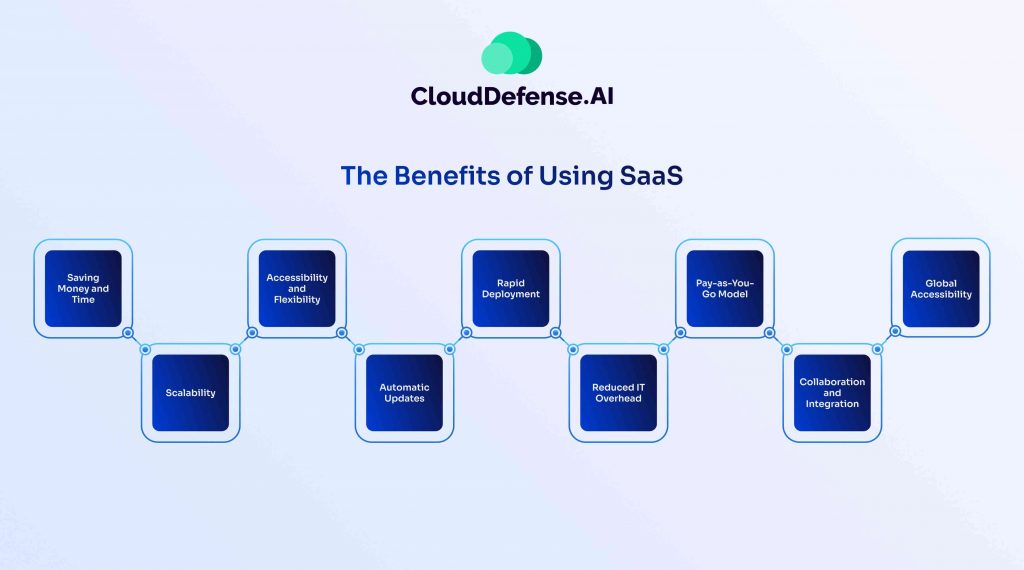
SaaS has many benefits that companies scramble to move from on-premise options. We’ve discussed some of these throughout the article, but here is a summary of all the benefits.
Access to Sophisticated Applications
SaaS provides access to advanced enterprise applications, such as ERP and CRM, without requiring significant upfront investment in hardware, middleware, or software. This makes sophisticated tools affordable and accessible for organizations with limited resources, allowing them to benefit from capabilities they might not otherwise afford.
Cost-Efficiency with Pay-as-You-Go
SaaS operates on a subscription-based model, where businesses pay only for what they use. This scalability ensures cost savings, as the service can adjust dynamically based on usage levels, reducing the need for overprovisioning or underutilization.
Elimination of Special Client Software
Most SaaS applications can be run directly from a web browser, eliminating the need for downloading, installing, or purchasing additional software. This simplifies onboarding and reduces compatibility concerns, though some apps may require minimal plugins.
Workforce Mobility
SaaS supports easy mobilization of teams by enabling access to applications and data from any internet-connected device. Since service providers handle cross-platform compatibility and device security, businesses save time and resources on developing platform-specific apps or addressing mobile security issues.
Anytime, Anywhere Data Access
With SaaS, data is stored securely in the cloud, enabling users to access their information from any location or device with an internet connection. This also safeguards against data loss in cases where user devices are damaged or fail.
Automatic Maintenance and Upgrades
SaaS providers handle all updates, security patches, and maintenance tasks, ensuring users always have access to the latest software version without the need for manual interventions or costly upgrades.
Simplified Collaboration
By centralizing data and applications in the cloud, SaaS facilitates seamless collaboration among team members. Real-time updates and shared access ensure smooth workflows and improved productivity.
Enhanced Security
Reputable SaaS providers prioritize data security, implementing robust measures such as encryption, regular audits, and compliance with industry standards. This ensures the protection of sensitive data without requiring in-house expertise.
Challenges of SaaS (Software as a Service)
While SaaS provides numerous benefits, organizations must also address certain challenges associated with its adoption and implementation.
Data Integration Across Applications
One of the most significant challenges with SaaS is integrating data across multiple cloud applications, especially when working with solutions from different providers. Seamless data sharing often requires custom workflows built using APIs (application programming interfaces). For organizations without in-house developers skilled in API integration, achieving smooth interoperability can become a time-consuming and resource-intensive task.
Managing Hybrid Environments
The transition to a fully SaaS-based IT ecosystem is rarely immediate. Many organizations operate in a hybrid environment, blending cloud-based and on-premise applications. Managing this dual-state infrastructure can lead to higher maintenance costs and increased complexity, as IT teams must ensure compatibility, performance, and security across diverse systems.
Dependency on Service Providers
SaaS solutions place a significant portion of infrastructure, data, and updates under the control of the service provider. Any downtime, outages, or disruptions on the provider’s end can directly impact business operations. Additionally, organizations may face challenges when switching providers due to data migration complexities and potential vendor lock-in.
Security and Data Privacy Concerns
While SaaS providers implement robust security measures, organizations must trust third parties with their sensitive data. Compliance with regional regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) and concerns over data breaches or unauthorized access require careful evaluation of the provider’s security standards and data handling practices.
Cost Management
Although SaaS eliminates upfront infrastructure investments, subscription fees can accumulate over time, particularly for organizations using multiple services. Scaling usage without proper monitoring can lead to unexpected expenses. Additionally, businesses must ensure they’re not paying for features they don’t use or underutilized licenses.
Limited Customization
SaaS solutions are typically designed for broad audiences, which means they may not fully cater to the unique requirements of every organization. Customization options can be limited, and modifying the software to meet specific needs often requires collaboration with the provider or third-party developers.
What’s the Difference Between SaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS?
SaaS (Software as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) represent different layers of cloud computing, each catering to distinct needs. Here’s how they differ:
Level of Service Provided
- SaaS: Provides ready-to-use applications for end-users. The software is managed entirely by the provider, with users accessing it via a browser or app.
- PaaS: Offers a development platform where developers can build, test, and deploy applications. The provider manages infrastructure and middleware, while developers focus on their code.
- IaaS: Supplies virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, giving businesses full control over their operating systems and applications.
Target Audience
- SaaS: Designed for end-users who need ready-to-use tools like email, CRM, or project management software.
- PaaS: Tailored for developers who need an environment for creating and deploying applications without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- IaaS: Aimed at IT administrators and businesses that require complete control over infrastructure and scalability.
Management Responsibility
- SaaS: Provider manages everything, including infrastructure, software, and data. Users only handle basic configurations.
- PaaS: Provider manages the infrastructure and runtime environment, while users handle application development and data.
- IaaS: Provider manages only the infrastructure, such as servers and storage. Users control operating systems, applications, and data.
Customization and Control
- SaaS: Minimal customization and control; users work within the software’s pre-defined framework.
- PaaS: High customization for applications but limited control over the underlying environment.
- IaaS: Maximum control, allowing businesses to configure servers, operating systems, and applications to their exact requirements.
Examples
- SaaS: CloudDefense.AI, Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox.
- PaaS: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, Heroku.
- IaaS: Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine.
Cost Structure
- IaaS: Pay-as-you-go model for infrastructure resources like virtual machines, storage, and networking.
- SaaS: Subscription-based, with costs dependent on the number of users and tiers of service.
- PaaS: Pay-per-use model for resources consumed, such as storage and development tools.
Conclusion
Software as a Service (SaaS) revolutionizes software access and management. Its subscription model, cloud accessibility, and automatic updates offer cost-efficiency, scalability, and rapid deployment. Despite clear benefits, challenges like data integration and hybrid infrastructure management exist.
However, we can say the benefits clearly outweigh the challenges involved. As SaaS reshapes how we interact with technology, embracing it helps in unleashing the powers of cloud computing. We hope this article has enabled you to understand what Software as a Service is.
FAQs
Are SaaS Apps Secure?
The security of SaaS applications depends on the SaaS provider. Since sensitive information from the company might need to be stored off-premise, it raises security concerns about the data. Therefore, before selecting a SaaS provider, it is best to check if they follow industry security standards.
What is the Difference Between SaaS and Cloud computing?
SaaS is a part of cloud computing. It is a concept where ready-to-use applications are provided for companies without the hassle of making their own applications.
What Is An Example of SaaS?
Various SaaS subscription services are available on the internet. Google Drive is a good example of SaaS that we use daily. Google Drive allows its users to store, share, and view data without the need to store it locally.
- Shared Database with Tenant Segmentation: A single database instance serves multiple customers with logical separation using unique identifiers.
- Isolated Database Per Tenant: Each customer gets a separate database instance, improving security at the cost of higher resource consumption.
Multi-tenancy enables cost efficiency, scalability, and streamlined maintenance.
API-Driven and Microservices Architecture
Modern SaaS platforms are built using microservices—independent, loosely coupled services that communicate via APIs. This approach offers:
- Scalability: Services scale independently based on demand.
- Fault Isolation: A failure in one service doesn’t impact the entire system.
- Faster Updates: Individual services can be updated without affecting the entire application.
APIs enable seamless integrations with third-party services, extending functionality (e.g., payment gateways, CRM tools, or security solutions).
Elastic Load Balancing & Auto-Scaling
SaaS providers use cloud-native services for automatic scaling and load distribution:
- Load Balancers: Distribute incoming traffic across multiple instances to prevent bottlenecks.
- Auto-Scaling Groups: Dynamically adjust resources based on real-time demand.
- Edge Computing & CDNs: Improve performance by caching static content closer to users.
This ensures high availability, even during peak traffic.
Security & Data Protection
Since SaaS applications operate in a shared environment, security is a top priority. Key measures include:
- End-to-End Encryption: TLS (for data in transit) and AES (for data at rest).
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Role-based access control (RBAC) and Single Sign-On (SSO).
- Threat Detection & Compliance: Advanced security tools like CloudDefense.AI help detect misconfigurations, enforce compliance, and monitor runtime threats.
SaaS providers must comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 to maintain trust.
Continuous Deployment & CI/CD Pipelines
Unlike traditional software, SaaS applications receive frequent updates without user intervention. This is made possible through:
- CI/CD Pipelines: Automate testing, deployment, and rollback mechanisms. Learn more about CI/CD here.
- Feature Flags: Gradually roll out new features without affecting all users at once.
- Blue-Green & Canary Deployments: Minimize downtime by deploying updates in controlled stages.
These strategies ensure reliability, quick bug fixes, and seamless feature enhancements.
Subscription & Billing Management
SaaS platforms typically operate on a subscription model with automated billing, including:
- Usage-Based Pricing: Charges based on API calls, storage, or active users.
- Tiered Plans: Different pricing levels with varying feature sets.
- Automated Invoicing: Integrated payment gateways handle recurring billing.
Advanced SaaS platforms use AI-driven analytics to optimize pricing and predict customer churn.
Software as a Service (SaaS) Characteristics and Features
SaaS has a tonne of unique features that help it to stand out. Here are some SaaS characteristics and features for you to check out.
Characteristics of SaaS:
- Multi-Tenancy: SaaS applications are multi-tenant, meaning a single software instance serves multiple customers. Each customer’s data is isolated and secure, and they can customize certain aspects of the application to suit their specific needs.
- Accessibility via the Internet: SaaS applications are hosted on a cloud infrastructure and can be accessed through a web browser. This eliminates the need for users to install, maintain, and update software locally.
- Subscription-Based Pricing: SaaS is typically offered on a subscription basis, where users pay a recurring fee to access the software. This pricing model often includes updates, support, and maintenance costs, making it a cost-effective solution for users.
- Centralized Updates and Maintenance: SaaS providers centrally handle software updates, patches, and maintenance. Users do not need to worry about installing updates or managing the underlying infrastructure, as the service provider performs these tasks.
- Scalability: SaaS applications are designed to scale easily, allowing users to adjust their subscription levels based on their needs. This scalability makes it convenient for businesses to adapt to changing requirements, whether scaling up or down.
SaaS Features:
- User Authentication and Authorization: SaaS applications typically include robust user authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized individuals can access the system. Role-based access controls (RBAC) are often employed to manage permissions based on user roles.
- Data Storage and Management: SaaS applications provide a centralized and secure storage system for user data. This includes features for creating, updating, deleting, retrieving data and organizing and structuring information effectively.
- Collaboration Tools: Many SaaS applications are designed to facilitate collaboration among users. This may include features such as real-time document editing, commenting, file sharing, and communication tools like chat and messaging.
- Integration Capabilities: SaaS applications often offer integration with other third-party services and applications. This allows users to connect their SaaS tools with existing software and services to streamline workflows and enhance functionality.
- Customization and Configuration: Users often have the ability to customize and configure certain aspects of the SaaS application to meet their specific needs. This may include settings, preferences, and branding options.
- Scalability: SaaS applications are designed to scale easily to accommodate changes in user load and data volume. This scalability ensures that the software can grow or shrink based on user needs.
- Reporting and Analytics: SaaS applications often include built-in reporting and analytics tools. Users can generate various reports and analyze data to gain insights into their activities, performance, and trends.
Different types of SaaS (Software as a Service)

SaaS solutions span a wide range of industries, providing businesses with cloud-based tools to enhance efficiency, collaboration, and security. Here are some of the most common SaaS categories:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM solutions help businesses manage customer interactions, track sales leads, automate marketing campaigns, and improve customer service. Popular CRM platforms centralize customer data, providing actionable insights to boost sales and retention.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP SaaS solutions integrate business operations such as finance, supply chain management, HR, and inventory control. They streamline workflows, enhance decision-making, and ensure smooth business operations across departments.
Human Resources (HR) Management
SaaS HR platforms offer employee onboarding, payroll processing, benefits administration, and performance tracking. They help organizations automate HR tasks, ensuring compliance and improving workforce management.
Collaboration and Productivity Tools
Remote and hybrid work environments rely on SaaS collaboration tools, including project management software, document sharing platforms, and video conferencing apps. These solutions enhance communication, task management, and real-time collaboration.
Accounting and Financial Management
SaaS accounting tools simplify bookkeeping, invoicing, expense tracking, and financial reporting. They provide businesses with real-time financial insights, ensuring compliance with tax regulations and industry standards.
Security as a Service (SECaaS)
With the rise of cyber threats, businesses turn to Security as a Service (SECaaS) for cloud-based protection. This category includes SaaS solutions for identity and access management (IAM), antivirus, threat intelligence, and compliance monitoring.
CloudDefense.AI: A Next-Gen Security SaaS
Among leading SECaaS providers, CloudDefense.AI stands out with its AI-powered CNAPP. Offering CSPM, CIEM, and other cloud security solutions, CloudDefense.AI helps businesses secure their cloud environments with real-time risk mitigation and policy enforcement.
SaaS has revolutionized industries by offering scalable, cloud-based solutions for various business needs. From CRM to security, these tools enhance efficiency, drive innovation, and ensure better operational control in an increasingly digital world.
SaaS vs. On-Premise Software
Before SaaS’s inception, companies heavily relied on on-premise software. The word “On-premise” is used to refer to infrastructure that is hosted locally in a company. Check below for a detailed comparison of SaaS benefits over on-premise software.
| On-premise Software | Software as a Service | |
Deployment |
Software is installed and runs on local servers and infrastructure. | It is hosted in the cloud and does not require local installations or on-site servers. |
Accessibility |
Access is limited to the physical location where the software is installed and cannot be accessed from off-premise. | Accessible from any location with an internet connection. Often supports various devices (laptops, tablets, smartphones), allowing easy access. |
Maintenance |
The in-house IT team is responsible for updates, patches, and maintenance. Updates may cause downtime and require manual intervention. | The SaaS provider manages and applies updates centrally. Users typically receive the latest features automatically without worrying about tedious maintenance. |
Scalability |
Scalability may require additional hardware and resources. IT team is responsible for scaling infrastructure. | Easily scalable to accommodate changes in user load. Providers handle infrastructure scaling. |
Cost |
Upfront capital is required for software licenses and hardware. Additional costs for maintenance, updates, and support. | Subscription-based pricing with recurring fees. Costs often include updates, maintenance, and support. |
The Benefits of Using SaaS (Software as a Service)

SaaS has many benefits that companies scramble to move from on-premise options. We’ve discussed some of these throughout the article, but here is a summary of all the benefits.
Access to Sophisticated Applications
SaaS provides access to advanced enterprise applications, such as ERP and CRM, without requiring significant upfront investment in hardware, middleware, or software. This makes sophisticated tools affordable and accessible for organizations with limited resources, allowing them to benefit from capabilities they might not otherwise afford.
Cost-Efficiency with Pay-as-You-Go
SaaS operates on a subscription-based model, where businesses pay only for what they use. This scalability ensures cost savings, as the service can adjust dynamically based on usage levels, reducing the need for overprovisioning or underutilization.
Elimination of Special Client Software
Most SaaS applications can be run directly from a web browser, eliminating the need for downloading, installing, or purchasing additional software. This simplifies onboarding and reduces compatibility concerns, though some apps may require minimal plugins.
Workforce Mobility
SaaS supports easy mobilization of teams by enabling access to applications and data from any internet-connected device. Since service providers handle cross-platform compatibility and device security, businesses save time and resources on developing platform-specific apps or addressing mobile security issues.
Anytime, Anywhere Data Access
With SaaS, data is stored securely in the cloud, enabling users to access their information from any location or device with an internet connection. This also safeguards against data loss in cases where user devices are damaged or fail.
Automatic Maintenance and Upgrades
SaaS providers handle all updates, security patches, and maintenance tasks, ensuring users always have access to the latest software version without the need for manual interventions or costly upgrades.
Simplified Collaboration
By centralizing data and applications in the cloud, SaaS facilitates seamless collaboration among team members. Real-time updates and shared access ensure smooth workflows and improved productivity.
Enhanced Security
Reputable SaaS providers prioritize data security, implementing robust measures such as encryption, regular audits, and compliance with industry standards. This ensures the protection of sensitive data without requiring in-house expertise.
Challenges of SaaS (Software as a Service)
While SaaS provides numerous benefits, organizations must also address certain challenges associated with its adoption and implementation.
Data Integration Across Applications
One of the most significant challenges with SaaS is integrating data across multiple cloud applications, especially when working with solutions from different providers. Seamless data sharing often requires custom workflows built using APIs (application programming interfaces). For organizations without in-house developers skilled in API integration, achieving smooth interoperability can become a time-consuming and resource-intensive task.
Managing Hybrid Environments
The transition to a fully SaaS-based IT ecosystem is rarely immediate. Many organizations operate in a hybrid environment, blending cloud-based and on-premise applications. Managing this dual-state infrastructure can lead to higher maintenance costs and increased complexity, as IT teams must ensure compatibility, performance, and security across diverse systems.
Dependency on Service Providers
SaaS solutions place a significant portion of infrastructure, data, and updates under the control of the service provider. Any downtime, outages, or disruptions on the provider’s end can directly impact business operations. Additionally, organizations may face challenges when switching providers due to data migration complexities and potential vendor lock-in.
Security and Data Privacy Concerns
While SaaS providers implement robust security measures, organizations must trust third parties with their sensitive data. Compliance with regional regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) and concerns over data breaches or unauthorized access require careful evaluation of the provider’s security standards and data handling practices.
Cost Management
Although SaaS eliminates upfront infrastructure investments, subscription fees can accumulate over time, particularly for organizations using multiple services. Scaling usage without proper monitoring can lead to unexpected expenses. Additionally, businesses must ensure they’re not paying for features they don’t use or underutilized licenses.
Limited Customization
SaaS solutions are typically designed for broad audiences, which means they may not fully cater to the unique requirements of every organization. Customization options can be limited, and modifying the software to meet specific needs often requires collaboration with the provider or third-party developers.
What’s the Difference Between SaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS?
SaaS (Software as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) represent different layers of cloud computing, each catering to distinct needs. Here’s how they differ:
Level of Service Provided
- SaaS: Provides ready-to-use applications for end-users. The software is managed entirely by the provider, with users accessing it via a browser or app.
- PaaS: Offers a development platform where developers can build, test, and deploy applications. The provider manages infrastructure and middleware, while developers focus on their code.
- IaaS: Supplies virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, giving businesses full control over their operating systems and applications.
Target Audience
- SaaS: Designed for end-users who need ready-to-use tools like email, CRM, or project management software.
- PaaS: Tailored for developers who need an environment for creating and deploying applications without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- IaaS: Aimed at IT administrators and businesses that require complete control over infrastructure and scalability.
Management Responsibility
- SaaS: Provider manages everything, including infrastructure, software, and data. Users only handle basic configurations.
- PaaS: Provider manages the infrastructure and runtime environment, while users handle application development and data.
- IaaS: Provider manages only the infrastructure, such as servers and storage. Users control operating systems, applications, and data.
Customization and Control
- SaaS: Minimal customization and control; users work within the software’s pre-defined framework.
- PaaS: High customization for applications but limited control over the underlying environment.
- IaaS: Maximum control, allowing businesses to configure servers, operating systems, and applications to their exact requirements.
Examples
- SaaS: CloudDefense.AI, Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox.
- PaaS: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, Heroku.
- IaaS: Amazon EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine.
Cost Structure
- IaaS: Pay-as-you-go model for infrastructure resources like virtual machines, storage, and networking.
- SaaS: Subscription-based, with costs dependent on the number of users and tiers of service.
- PaaS: Pay-per-use model for resources consumed, such as storage and development tools.
Conclusion
Software as a Service (SaaS) revolutionizes software access and management. Its subscription model, cloud accessibility, and automatic updates offer cost-efficiency, scalability, and rapid deployment. Despite clear benefits, challenges like data integration and hybrid infrastructure management exist.
However, we can say the benefits clearly outweigh the challenges involved. As SaaS reshapes how we interact with technology, embracing it helps in unleashing the powers of cloud computing. We hope this article has enabled you to understand what Software as a Service is.
FAQs
Are SaaS Apps Secure?
The security of SaaS applications depends on the SaaS provider. Since sensitive information from the company might need to be stored off-premise, it raises security concerns about the data. Therefore, before selecting a SaaS provider, it is best to check if they follow industry security standards.
What is the Difference Between SaaS and Cloud computing?
SaaS is a part of cloud computing. It is a concept where ready-to-use applications are provided for companies without the hassle of making their own applications.
What Is An Example of SaaS?
Various SaaS subscription services are available on the internet. Google Drive is a good example of SaaS that we use daily. Google Drive allows its users to store, share, and view data without the need to store it locally.







