In recent times, the surge in cyberattacks has left many individuals and organizations grappling with a pressing question: What exactly is a zero-day exploit? Simply put, a zero-day exploit is a software vulnerability that cybercriminals discover before developers do.
This gives hackers an opportunity to exploit the vulnerability until it’s identified and patched—a scenario akin to seizing the moment while the iron is hot. The alarming frequency with which businesses are targeted by these attacks should serve as a wake-up call to all decision-makers.
In this article, we will learn more on how to prevent zero day attacks and explore effective strategies to strengthen your company’s cybersecurity defenses in challenging era.
What Is a Zero-Day Attack?
A zero-day attack exploits a newly discovered security vulnerability in software, hardware, or firmware. The term “zero-day” signifies that the vendor has zero days to fix the flaw because hackers can immediately exploit it. Malicious actors use these vulnerabilities before developers have a chance to release patches or updates.
Zero-day attacks pose significant threats to cybersecurity, as they can compromise systems, steal sensitive data, or disrupt operations. Protecting against zero-day attacks requires proactive security measures and rapid response strategies to mitigate risks and protect against potential exploits.
Systems That Are Common Targets for Zero Day Attacks
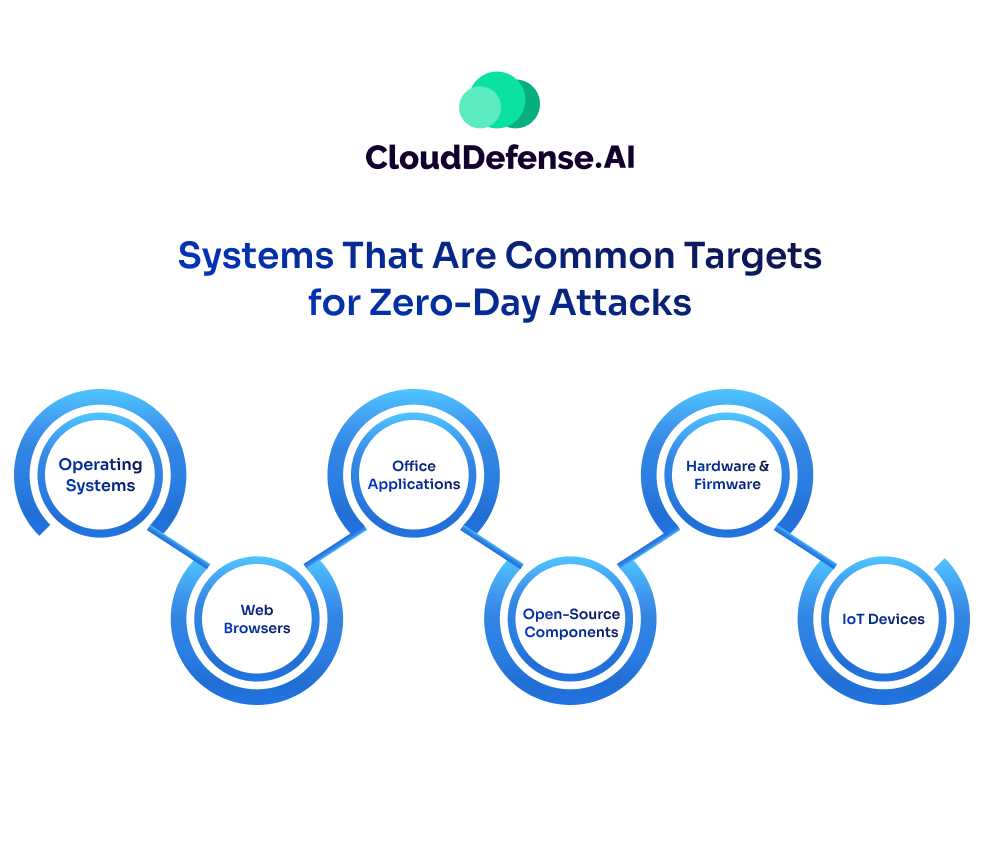
Zero-day attacks target various systems, including:
Operating Systems: Vulnerabilities in operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux are prime targets due to their widespread use across devices.
Web Browsers: Exploits in browsers such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Edge can compromise user data and lead to unauthorized access.
Office Applications: Vulnerabilities in office suites like Microsoft Office and Adobe Acrobat can be exploited to execute malicious code or steal sensitive information.
Open-Source Components: Many software applications rely on open-source libraries and frameworks, making them susceptible to zero-day attacks if vulnerabilities are discovered.
Hardware and Firmware: Flaws in hardware components and firmware, including CPUs, BIOS, and device drivers, can be exploited to gain unauthorized access or disrupt device functionality.
IoT Devices: Connected devices like smart home appliances, wearables, and industrial IoT systems are increasingly targeted by zero-day attacks due to their use recently and often lax security measures.
The Zero-Day Exploit Timeline
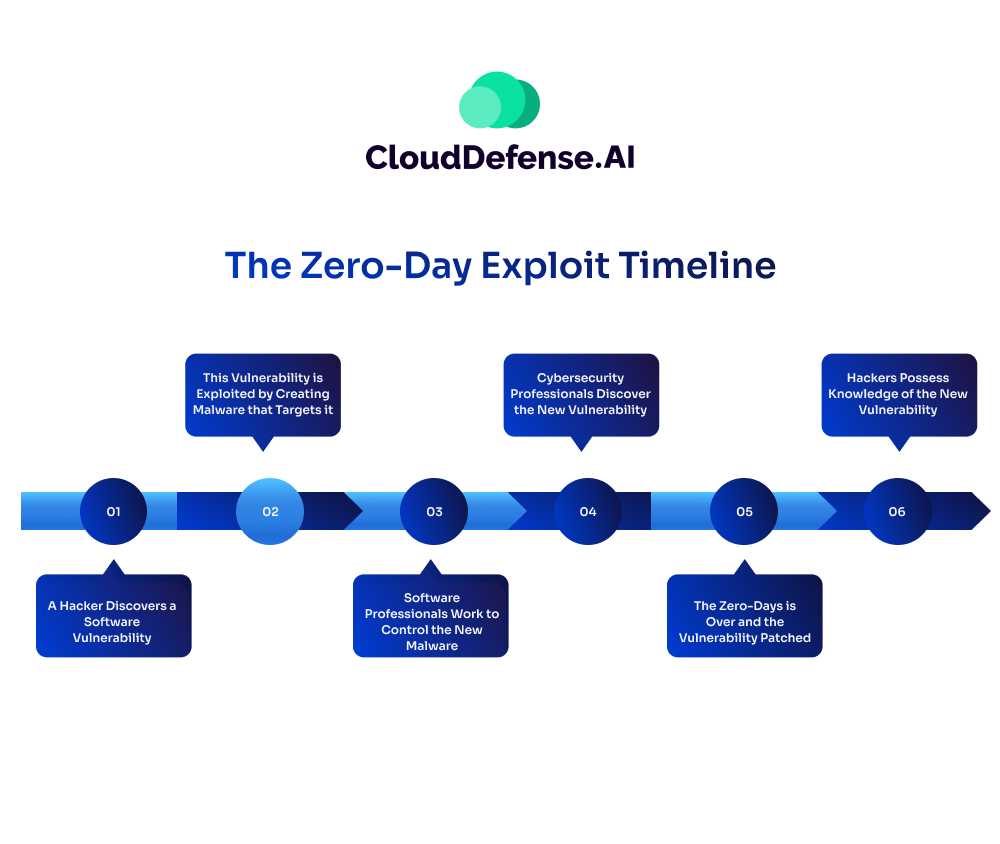
The timeline of a zero-day exploit begins with the discovery of a previously unknown vulnerability in software, hardware, or firmware. Once identified, hackers exploit this flaw to launch attacks on vulnerable endpoints, such as computers, servers, or IoT devices. Due to the increased number of endpoints within businesses, these attacks can quickly spread, leading to widespread compromise and potential data breaches.
- A Hacker Discovers a Software Vulnerability
Cybercriminals give hidden exploits extra value as security systems are not well prepared to prevent zero day threats. - This Vulnerability is Exploited by Creating Malware that Targets it
Criminals use exploit kits, watering hole attacks, and phishing methods to spread the malware they’ve created as soon as possible. - Hackers Possess Knowledge of the New Vulnerability
Hackers keep using the newly found vulnerability for their profit as long as it stays hidden from companies. - Cybersecurity Professionals Discover the New Vulnerability
The malware exploiting their system has been detected. This is when the security team rings the emergency alarm. - Software Professionals Work to Control the New Malware
Once the security team is aware of the new malware, they work round the clock to patch the exploit. The patched version is rolled out for their customers. - The Zero-Days is Over and the Vulnerability Patched
The exploit has been taken care of by the able security team, and it cannot be misused anymore. Now the team waits for the next zero day attack.
Steps of Zero-Day Attack Prevention
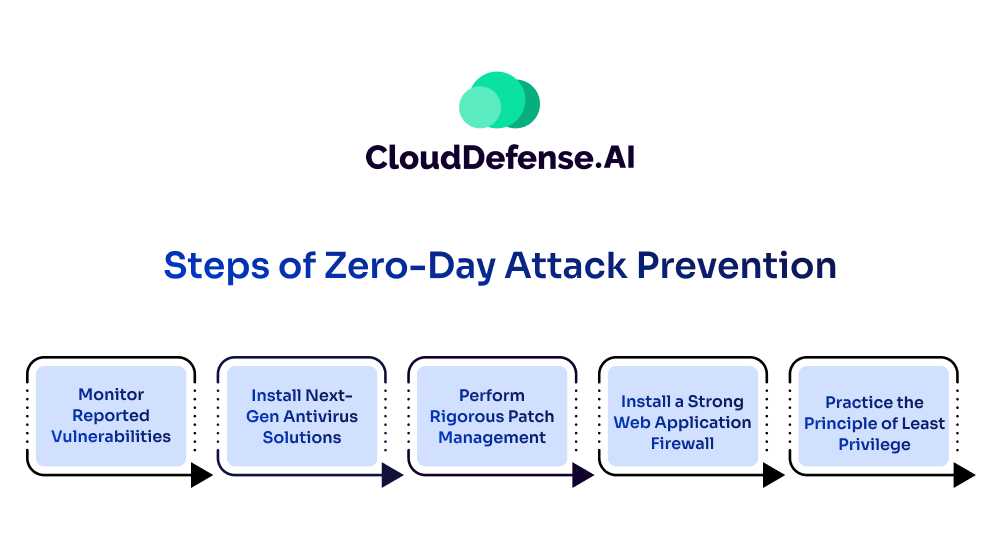
Zero-day attacks might seem the end of the road for you but that’s not the case. With careful vigilance, your security team can easily curb zero-day attacks on your business. Steps for zero-day attack prevention include:
1. Monitor Reported Vulnerabilities
Regularly monitor security databases and vendor releases for reported vulnerabilities. Stay informed about potential threats to identify and address issues before they are exploited.
2. Install Next-Gen Antivirus Solutions
Implement NGAV solutions to detect and prevent anomalous behavior, even in the absence of known malware signatures. NGAV tools can establish baselines of normal system behavior and automatically block suspicious activities.
3. Perform Rigorous Patch Management
Develop a strong patch management process to identify and address vulnerabilities promptly. Automate patch deployment wherever possible to minimize exposure windows and reduce the risk of exploitation.
4. Install a Strong Web Application Firewall
Deploy a WAF to monitor and regulate incoming and outgoing network traffic. Next-generation firewalls combine traditional firewall features with additional tools such as antivirus, intrusion prevention, and encrypted traffic inspection to enhance security.
5. Practice the Principle of Least Privilege
Enforce the principle of least privilege to limit user access rights to only those necessary for their tasks. By restricting access and privileges, organizations can minimize the potential damage caused by malicious actors and prevent lateral movement within the system.
Zero Day Attack Protection with CloudDefense.AI
CloudDefense.AI offers complete protection against zero-day attacks by using innovative solutions and a holistic approach to security. With its exclusive Hacker’s View™ feature, the platform provides insights into potential pathways of invasion and identifies weak points in infrastructure, allowing companies to anticipate and minimize threats before they materialize.
Additionally, CloudDefense.AI’s Noise Reduction technology prioritizes high-impact threats, enabling organizations to focus on critical risks and effectively reduce the likelihood of zero-day attacks. By seamlessly integrating with the development process through its “Code to Cloud” approach, CloudDefense.AI ensures that vulnerabilities are identified and addressed early on, preventing them from spreading into production environments.
With its user-friendly interface and expert support, CloudDefense.AI empowers companies to navigate complex security landscapes and protect their cloud-native applications effectively against evolving threats, including zero-day attacks.
Final Words
The current cybersecurity situation demands proactive measures to prevent zero-day attacks. As organizations adapt to remote work environments and face increasing vulnerabilities, it’s essential that companies implement strong mitigation strategies and have a detailed incident response plan in place.
By reducing the attack surface, shortening the exposure window, and limiting potential damage, companies can enhance their resilience against zero-day threats. Moreover, using advanced solutions like CloudDefense.AI can provide complete protection and peace of mind in protecting cloud-native applications and infrastructure. Book a free demo now to experience the future of cybersecurity.







