What Is Cyber Security Policy?
A cybersecurity policy is a structured framework that defines an organization’s approach to protecting its information systems, networks, and digital assets from cyber threats. It includes documented guidelines, procedures, and security controls that align with the organization’s security objectives.
Cybersecurity policies outline roles, responsibilities, methods, and technical safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. They also address key security attributes such as authenticity, accountability, and non-repudiation, ensuring that all digital interactions are verifiable and secure.
These policies vary based on an organization’s needs. Some are high-level strategic guidelines, while others include detailed technical procedures, such as Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) protocols, risk management frameworks, and incident response plans.
Key Components of a Cybersecurity Policy
A strong cybersecurity policy is essential for protecting our organization’s sensitive data, systems, and networks from threats. It provides guidelines and measures to protect our digital assets and meet regulatory requirements. An effective policy addresses key areas like access controls, incident response, and employee training. Here’s an overview of the main components for a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy:
- Security Objectives and Scope: Defines the organization’s security goals and the systems, data, and processes covered under the policy.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Assigns responsibilities to employees, IT teams, and leadership for maintaining cybersecurity measures and responding to incidents.
- Access Control and Authentication: Establishes guidelines for user authentication, password management, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and access permissions.
- Data Protection and Privacy: Outlines encryption standards, data handling procedures, and policies to ensure confidentiality and compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Network Security Measures: Specifies firewall configurations, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and monitoring tools to safeguard the network.
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) Policies: Defines rules for employees using personal devices for work, including security software requirements and access limitations.
- Incident Response Plan: Details the steps to be taken in case of a cyberattack, including detection, containment, recovery, and reporting procedures.
- Security Awareness and Training: Educates employees on best practices, phishing awareness, and social engineering threats to reduce human error-based vulnerabilities.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Ensures adherence to industry-specific security regulations such as ISO 27001, NIST, SOC 2, PCI DSS, GDPR, and HIPAA.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Implements regular security assessments, vulnerability scans, and audits to identify and address weaknesses in the security framework.
Who Should Write The Cyber Security Policy?
A cybersecurity policy should be developed by a collaborative team involving key stakeholders within an organization. The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or IT security leadership typically spearheads the process, ensuring alignment with security best practices and regulatory requirements.
Other contributors include IT teams, legal and compliance officers, risk management professionals, and executive leadership to address technical, legal, and business considerations. Additionally, HR and department heads provide input on employee access and usage policies.
A well-structured cybersecurity policy requires a multi-disciplinary approach to ensure it is comprehensive, enforceable, and aligned with the organization’s overall security strategy.
Types of Cyber Security Policies
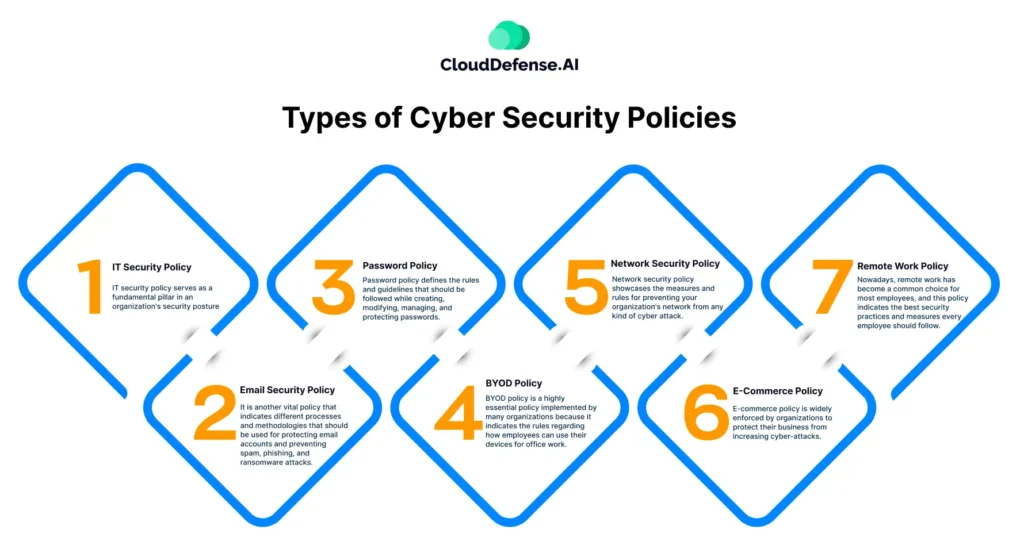
Cybersecurity policies are designed to address different aspects of security within an organization. These policies establish guidelines and controls to protect sensitive information, regulate access, and mitigate cyber risks. Below are some of the key types of cybersecurity policies:
| Policy Type | Purpose | Key Topics Covered |
| Access Control Policy | Ensures only authorized users can access information and digital assets. | Need-to-know principle, privilege management, user rights, segregation of duties. |
| Information Transfer Policy | Protects data transferred within the organization and with external parties. | Encryption during transfer, labeling, transfer agreements, traceability. |
| Secure Configuration & Endpoint Security Policy | Secures user endpoint devices to prevent security risks. | Device registration, software restrictions, updates, storage encryption, network security. |
| Network Security Policy | Safeguards networks and information processing facilities from cyber threats. | Firewall management, intrusion detection, traffic filtering, network segmentation, logging. |
| Incident Management Policy | Provides structured response to information security incidents. | Incident classification, escalation, evidence handling, reporting procedures. |
| Backup & Data Recovery Policy | Ensures business continuity through data backup and recovery. | Backup frequency, storage locations, retention policies, encryption, testing. |
| Cryptography & Key Management Policy | Protects data confidentiality and integrity using encryption. | Key management, encryption standards, cryptographic provider security. |
| Information Classification & Handling Policy | Defines how sensitive data should be classified and handled. | Data labeling, handling procedures, storage security requirements. |
This structured approach helps organizations establish strong cybersecurity measures tailored to their security needs and regulatory requirements.
Updating and Auditing Cyber Security Procedures
Regularly updating and auditing cybersecurity procedures is essential to maintaining a strong security posture and ensuring protection against evolving cyber threats. Cybersecurity threats and compliance requirements are constantly changing, making it crucial for organizations to review, enhance, and test their security policies and procedures.
Why Updates and Audits Are Important
- Keeps Security Measures Up to Date: Cyber threats evolve rapidly, and outdated security policies can leave organizations vulnerable to new attack methods.
- Ensures Compliance: Industry regulations like ISO 27001, NIST, GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require regular security audits to maintain compliance.
- Identifies Weaknesses: Routine audits help detect vulnerabilities and gaps in security controls before they can be exploited.
- Improves Incident Response: Reviewing security procedures ensures that response plans remain effective and aligned with emerging threats.
Best Practices for Updating and Auditing Cybersecurity Procedures
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits help organizations assess their cybersecurity and identify vulnerabilities. Internal and external audits provide a thorough evaluation of security measures. Additionally, penetration testing and vulnerability assessments simulate attacks to uncover weaknesses before malicious exploitation.
- Review and Update Policies Periodically: Cybersecurity policies require regular reviews and updates to tackle evolving threats, regulatory changes, and technological advancements. Organizations should review them annually or after major incidents, ensuring updates include new security technologies, compliance needs, and business operation changes for continuous protection.
- Monitor Security Controls and Logs: Continuous monitoring of security controls helps detect unauthorized access and anomalies. Organizations should use automated monitoring tools for real-time alerts on suspicious activities. Regular log analysis enables security teams to identify and respond to threats proactively, preventing cyber incidents before escalation.
- Test Incident Response and Disaster Recovery Plans: Organizations must routinely test incident response and disaster recovery plans to ensure they are effective during security breaches. Simulations and drills identify weaknesses in response strategies, refining recovery plans for coordinated responses to cyber incidents.
- Ensure Employee Awareness and Compliance: Human error poses a significant cybersecurity risk, making employee training crucial. Organizations should conduct regular security training to update employees on policies and phishing threats. Phishing simulations and awareness campaigns foster a security-aware culture and reduce the risk of social engineering attacks.
- Engage Third-Party Auditors: Third-party security audits objectively assess an organization’s cybersecurity posture. External auditors identify blind spots and compliance gaps internal teams might miss. Engaging independent experts ensures industry standards and regulatory requirements are met, strengthening the overall security framework with unbiased recommendations.
Importance of a Cyber Security Policy
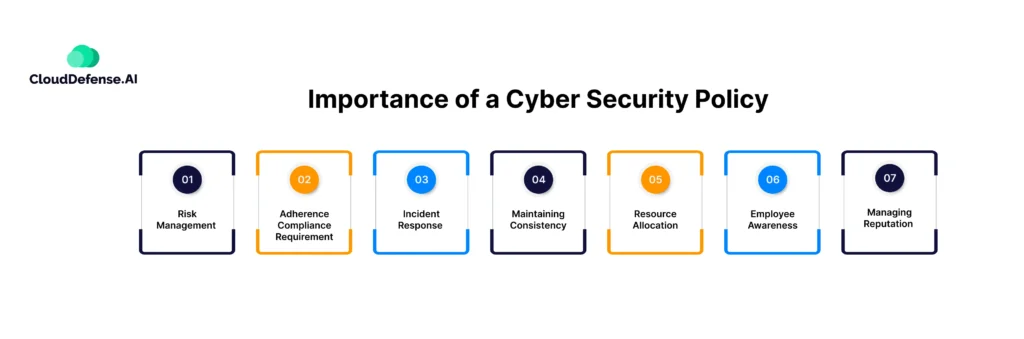
Importance of a Cyber Security Policy
Cybersecurity policies establish the guidelines and rules that an organization must follow to maintain an optimal security posture. The significance of such a policy is unparalleled within an organization. Here are the key reasons that highlight the importance of cybersecurity policies:
Risk Management
One of the primary importance of cyber security policies is the robust risk management capabilities they offer. A well-defined policy will help identify risks and vulnerabilities in the infrastructure and mitigate them by enforcing the appropriate security protocols and measures.
Adherence Compliance Requirement
Every organization must follow specific regulations and compliance requirements to ensure optimal protection of data and other sensitive information. A clearly defined policy aids the organization in adhering to all regulations and laws concerning data protection.
Incident Response
Having a strong cybersecurity policy in place in your organization will help you develop an effective incident response framework. This policy will outline all the reporting procedures, quarantine methods, and recovery processes that must be adhered to for appropriate incident response and damage reduction.
Maintaining Consistency
A cybersecurity policy helps you maintain consistent security practices across your organization. It offers a defined set of rules and a standard approach, making it easier to uphold a secure posture in various departments.
Resource Allocation
Cybersecurity policy is a crucial component in effectively allocating resources for an organization’s cybersecurity. It enables your team to identify areas of concern, prioritize sectors, and distribute resources efficiently.
Employee Awareness
Enforcing a cybersecurity policy also helps define the roles and responsibilities of employees and teams in maintaining the security of all the organization’s digital assets. A cybersecurity awareness policy is vital for every organization, as it enables employees to understand different cyber attacks and the procedures they can follow to prevent common threats.
Managing Reputation
Your organization’s reputation among investors, stakeholders, and consumers largely depends on your cyber security practices. Implementing a strong cyber security policy demonstrates your commitment to protecting sensitive data and preventing cyber attacks. It also enhances your reputation in the industry and gives you an edge over competitors.
How to Create A Cyber Security Policy?
Creating a cybersecurity policy is a crucial step in establishing a strong security framework for your organization. A well-defined policy safeguards critical assets, ensures regulatory compliance, and enhances overall security awareness. Follow these key steps to develop an effective cybersecurity policy:
Identify the Threat
Before drafting a cybersecurity policy, assess the systems, processes, and data that need protection. Different policies address different security concerns, such as data privacy, access control, or incident response. Clearly define which areas require regulation to mitigate cyber threats effectively.
Define Security Goals and Compliance Requirements
Establish clear security objectives aligned with your organization’s needs and regulatory obligations. Depending on your industry, compliance requirements may include:
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) for healthcare data protection
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) for payment security
- SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2) for cloud security compliance.
Ensure that your cybersecurity policy meets these standards to prevent regulatory violations and security breaches.
Draft the Cybersecurity Policy
Develop the policy with input from key stakeholders, including IT, security, legal, HR, and management teams. The policy should cover:
- Data protection and classification rules
- User access control and authentication measures
- Incident response protocols
- Acceptable use policies for IT resources
- Monitoring and auditing requirements
Gather Employee Feedback
A cybersecurity policy is only effective if employees can understand and implement it. Share the draft with employees and seek feedback to ensure clarity and practicality. Address any concerns or confusion to improve policy adherence.
Conduct Employee Training
Educate employees on cybersecurity best practices and policy requirements. Training should cover:
- Recognizing phishing attempts and social engineering attacks
- Proper data handling and secure password management
- Incident reporting and response procedures
Regular training sessions help reinforce security awareness and prevent human errors that could lead to breaches.
Regularly Review and Update the Policy
Cyber threats and regulatory requirements evolve constantly. Conduct periodic reviews of your cybersecurity policy to ensure it remains relevant and effective. Update policies as needed to address emerging threats and organizational changes.
A well-structured cybersecurity policy serves as the backbone of an organization’s security strategy. By following these steps, businesses can proactively protect their systems, data, and employees while ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Cyber Security Goals
The primary objective of cybersecurity for any organization is to safeguard sensitive data and digital assets from malicious threats. Cybersecurity ensures secure access control, safe data storage, and protection against unauthorized access.
The Core Cybersecurity Goals: The CIA Triad
Every cybersecurity strategy revolves around three fundamental goals:
- Confidentiality – Protecting sensitive and confidential data from unauthorized access.
- Integrity – Ensuring data remains accurate, consistent, and unaltered by unauthorized users.
- Availability – Guaranteeing authorized users have continuous and reliable access to critical data and systems.
These three principles form the CIA Triad—a widely used security model that serves as the foundation for creating cybersecurity policies and frameworks. Organizations handling sensitive data, such as financial institutions, healthcare providers, and tech companies, rely on the CIA Triad to ensure data security.
Each of the elements in the CIA triad has different tools that help in upholding and achieving the goal.
Confidentiality Tools
To maintain confidentiality and prevent unauthorized access, organizations implement:
- Encryption – Converts sensitive data into a secure format, readable only by authorized users.
- Access Control – Restricts data access based on user roles and permissions.
- Authentication – Verifies user identity through passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Authorization – Determines which users have access to specific resources.
- Physical Security – Secures data centers and hardware through controlled access, surveillance, and security protocols.
Integrity Tools
Ensuring data integrity prevents unauthorized modifications or corruption. Common tools include:
- Backups – Regular copies of critical data to prevent loss or tampering.
- Checksums – Algorithms that verify data accuracy and detect changes.
- Data Correcting Codes – Mechanisms that identify and correct errors in data transmission.
Availability Tools
To ensure continuous access to critical systems, organizations deploy:
- Physical Protection – Defending infrastructure from physical threats such as theft, fire, or natural disasters.
- Computational Redundancies – Implementing backup servers, load balancing, and failover systems to minimize downtime.
Implementing Cloud Security Policies with CloudShield.AI
Keeping your cloud secure and compliant can be a challenge, but it doesn’t have to be. CloudShield.AI by CloudDefense.AI takes the stress out of security by automatically enforcing policies and protecting your infrastructure—so you can focus on what really matters!
Why Choose CloudShield.AI?
- Proactive Policy Enforcement: Automate policy enforcement with real-time remediation to prevent security risks before they occur.
- Real-Time Violation Detection: Identify policy violations across your cloud infrastructure as they happen, ensuring immediate response to potential threats.
- Multi-Cloud Compatibility: Manage and enforce policies seamlessly across multiple accounts and cloud platforms, including AWS, Azure, and GCP.
- Comprehensive Compliance Management: Support for over 20 compliance frameworks with 300+ pre-built security policies, enabling one-click audit-ready reporting.
- Centralized Security Management: Gain a holistic view of threats and streamline security operations, reducing the complexity of managing multiple tools.
Experience CloudShield.AI in Action
Elevate your cloud security posture with CloudShield.AI’s advanced policy enforcement capabilities. To see how CloudShield.AI can transform your organization’s cloud security, book a free live demo today.







