If you are a company storing your clients’ sensitive health information, you should be prepared to deal with the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) at any moment to protect your company’s interest. Yes, we are talking about the HIPAA audit process.
As the healthcare industry shifts to the digital world, navigating the fine line between innovation and the ethical duty to protect privacy has become very important. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) indeed works on presenting strict regulations that help maintain the security of Protected Health Information (PHI)
Join us as we explore the HIPAA audit process and provide you with a HIPAA compliance checklist, where the company’s commitment to data security faces scrutiny in an era where trust is irreplaceable.
What is HIPAA Compliance?
HIPAA compliance refers to adhering to the regulations set by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) to protect the privacy, security, and accessibility of PHI. It applies to healthcare providers, insurers, and business associates handling PHI.
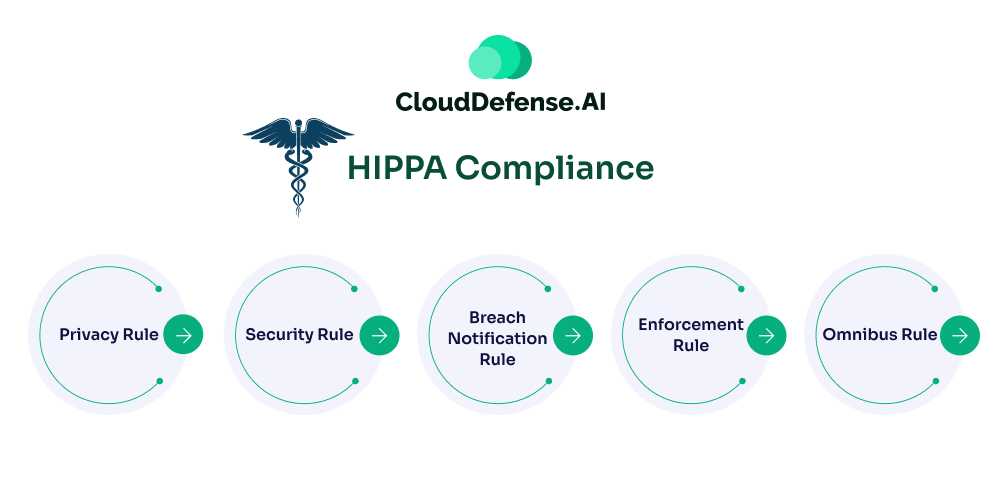
5 Key Components of HIPAA Compliance
- Privacy Rule: Protects patients’ health information and grants rights to access and control their data.
- Security Rule: Requires protection measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic PHI (ePHI).
- Breach Notification Rule: Obligates organizations to notify individuals and authorities of data breaches involving PHI.
- Enforcement Rule: Details investigation processes and penalties for non-compliance.
- Omnibus Rule: Extends HIPAA requirements to business associates and strengthens breach reporting standards.
Together, these components ensure the secure handling of sensitive health data.
Who Does HIPAA Apply To?
HIPAA’s Administrative Simplification provisions primarily apply to health plans, healthcare clearinghouses, and healthcare providers that electronically transmit health information related to transactions governed by HIPAA standards. Here’s a breakdown of the key entities:
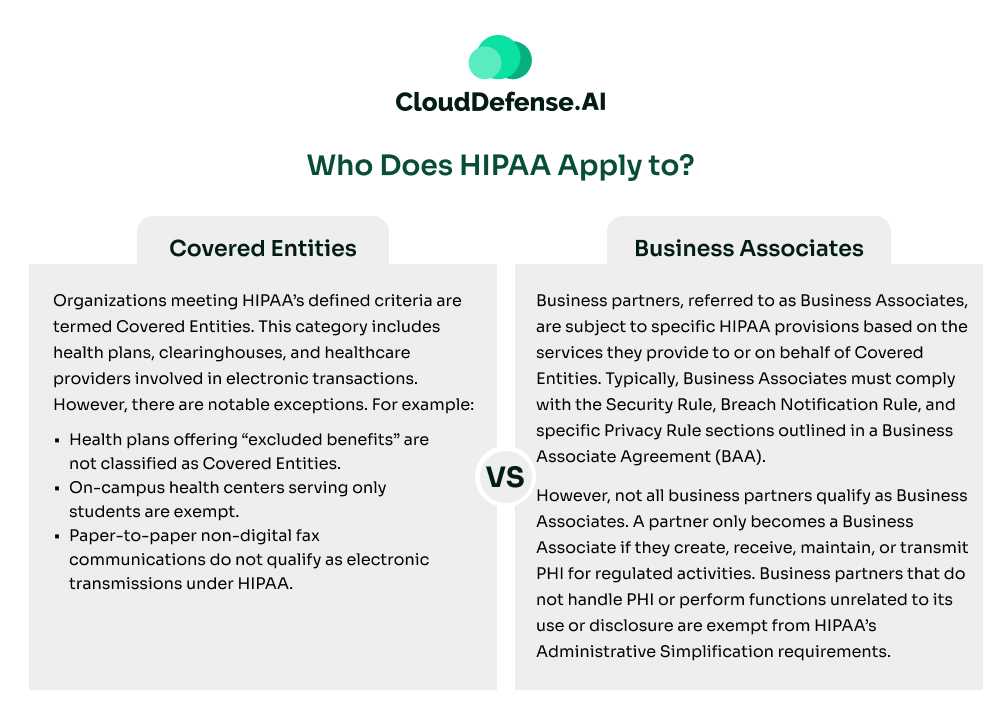
Covered Entities
Organizations meeting HIPAA’s defined criteria are termed Covered Entities. This category includes health plans, clearinghouses, and healthcare providers involved in electronic transactions. However, there are notable exceptions. For example:
- Health plans offering “excluded benefits” are not classified as Covered Entities.
- On-campus health centers serving only students are exempt.
- Paper-to-paper non-digital fax communications do not qualify as electronic transmissions under HIPAA.
Business Associates
Business partners, referred to as Business Associates, are subject to specific HIPAA provisions based on the services they provide to or on behalf of Covered Entities. Typically, Business Associates must comply with the Security Rule, Breach Notification Rule, and specific Privacy Rule sections outlined in a Business Associate Agreement (BAA).
However, not all business partners qualify as Business Associates. A partner only becomes a Business Associate if they create, receive, maintain, or transmit PHI for regulated activities. Business partners that do not handle PHI or perform functions unrelated to its use or disclosure are exempt from HIPAA’s Administrative Simplification requirements.
What is a HIPAA compliance audit?
A HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) compliance audit reviews an organization’s adherence to HIPAA regulations. HIPAA is a set of federal standards in the United States designed to protect the privacy and security of individuals’ health information. The law has several components, but two primary rules related to audits are the Privacy Rule and the Security Rule.
The Privacy Rule sets national standards for protecting individuals’ medical records and other personal health information (PHI). It establishes patients’ rights regarding their health information and imposes certain obligations on healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses.
The Security Rule focuses on protecting electronic PHI (ePHI). It outlines security standards that must be implemented to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ePHI. Covered entities, such as healthcare providers and health plans, must implement security measures to protect this information.
A HIPAA compliance audit is typically conducted by an independent auditor or the Office for Civil Rights (OCR), who is responsible for enforcing HIPAA. The audit aims to analyze whether an organization complies with the various provisions of the Privacy and Security Rules.
How to Conduct HIPAA Compliance Audits?
The best way to pass a HIPAA compliance audit is to always be prepared for one. HIPAA audits aren’t a one-time occurrence but are carried out annually. To assist you with your HIPAA audit journey, you should appoint a dedicated HIPAA security and privacy officer who emphasizes expertise, communication skills, and the ability to liaise effectively during audits.
Conduct comprehensive HIPAA training for all employees, covering the law’s fundamentals, procedures, and consequences of non-compliance. Develop a robust risk management plan, including a thorough risk analysis, to identify vulnerabilities, threats, and necessary security measures.
Carry out regular reviews and refine policies and procedures, demonstrating a commitment to continuous improvement. Conduct internal audits to address potential risks and non-compliance instances efficiently. Lastly, an internal recovery plan should be established outlining steps to rectify breaches promptly and prevent future occurrences.
Types of HIPAA Violations that Can Cause HIPAA Audit
To comply with HIPAA, you must understand what can cause a violation of the law. Consider checking out some significant types of HIPAA violations listed below that will help you grasp some of the HIPAA audit requirements as well.
Revealing Protected Health Information through Unauthorized Access
Unauthorized access to Protected Health Information, or PHI, is a serious breach of HIPAA regulations. It involves improperly disclosing sensitive patient data, posing significant risks to privacy and security.
Such actions undermine the trust in healthcare systems and may result in legal consequences for those responsible. HIPAA mandates strict measures to prevent unauthorized disclosures of patient data. Unauthorized disclosures might occur through an internal error or inadequate access control measures.
Patient Not Being Able to Authorize the Use of Their Data
HIPAA specifies that patients should possess the right to authorize the use of their personal health data. Any infringement of this right can constitute a breach of privacy standards.
Ensuring patients can control the use of their health information not only upholds ethical standards but also builds a relationship of trust between healthcare providers and individuals seeking medical care. Upholding these rights is critical in maintaining the integrity and foundation of ethical healthcare practices.
Security Measures Not in Place
HIPAA regulations mandate strict security measures for protecting PHI. If enough data security is not ensured, it can result in a violation. Businesses or other entities handling patient data must implement administrative, physical, and technical security measures.
Administrative security measures require the appointment of a security officer and workforce training. Physical security measures involve controlling access to facilities and securing workstations. Technical security measures enforce authorized PHI access, audit controls, data integrity, and secure transmission.
Inadequate Disposal Measures of Data
HIPAA regulates the secure disposal of Protected Health Information (PHI). Physical records must be shredded, and electronic media sanitized. Your company is required to establish clear disposal policies so that you comply with HIPAA. Disposed PHI should not be able to be reconstructed or read.
Failing to Communicate a Breach
In case of a breach, HIPAA strictly requires the associated businesses or other third-party entities to notify the patient immediately if their PHI is compromised. According to HIPAA, a breach comprises the unauthorized use or disclosure of sensitive patient health information.
Steps to HIPAA Compliance
Ensuring HIPAA compliance requires a systematic approach to meet its regulatory demands effectively. Here’s a step-by-step guide to streamline the process:
- Understand Your HIPAA Obligations: Determine whether your organization is classified as a covered entity or business associate under HIPAA. This assessment is crucial for understanding your compliance responsibilities.
- Designate Responsible Officers: Appoint a Privacy Officer to oversee compliance with HIPAA’s Privacy Rule. If applicable, assign a Security Officer to manage the Security Rule requirements, ensuring ePHI is safeguarded.
- Identify and Secure PHI: Comprehend the scope of Protected Health Information (PHI) and where it resides within your organization. Minimize the number of systems and records containing PHI to reduce exposure risks.
- Implement the Security Rule Safeguards: Develop robust Administrative, Physical, and Technical Safeguards. These measures should secure ePHI against unauthorized access, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Address HIPAA Violations Proactively: Identify potential causes of non-compliance, mitigate risks, and train staff to prevent breaches. Establish a culture of vigilance to avert unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Maintain Detailed Documentation: Record all HIPAA-related activities, from audits to training sessions, and retain documentation for at least six years. Accurate record-keeping reinforces compliance and prepares your organization for potential audits.
- Establish Breach Notification Procedures: Set clear protocols for addressing data breaches, including timely notifications to affected individuals and relevant authorities, ensuring transparency and swift response.
- Implement Physical Security Measures: Restrict physical access to PHI and critical systems through policies and controls. Secure workstations, storage media, and facility access to prevent unauthorized entry.
- Enhance Technical Safeguards: Define clear access controls, integrate emergency response plans, and use encryption and secure data transmission methods to meet HIPAA’s technical requirements effectively.
HIPAA Compliance Checklist
The following tables outline a comprehensive HIPAA compliance checklist to help assess your organization’s readiness.
Audit Checklist
| Audit Requirements |
| Have you performed a comprehensive security risk assessment? |
| Have you conducted a privacy compliance assessment? |
| Have you completed an administrative compliance audit? |
| Have you documented all deficiencies identified in the audits? |
| Have you audited business associates to ensure HIPAA compliance? |
Personnel Checklist
| People and Training |
| Have you communicated all security and privacy policies to employees? |
| Have all employees received training on basic HIPAA requirements? |
| Have you documented all training sessions? |
| Have you assigned a designated HIPAA Compliance Officer? |
| Have you restricted access to PHI to employees with job-related needs? |
| Have you limited physical access to facilities with PHI to authorized personnel? |
Policies and Procedures Checklist
| Policy Requirements |
| Do you have documented security and privacy policies? |
| Is there a risk management policy in place? |
| Is all PHI encrypted before being shared over public networks? |
| Do you have policies for securely disposing of PHI? |
| Are there procedures to document and account for PHI violations? |
| Are breach notification policies established and tested? |
| Have all business associates been identified and agreements signed? |
| Is there a process for employees to anonymously report HIPAA violations? |
| Do you have a contingency plan for emergencies affecting PHI systems? |
Remediation Checklist
| Remediation Plans |
| Have you created a remediation plan for risk assessment deficiencies? |
| Have you developed a plan for resolving privacy audit deficiencies? |
| Are there remediation steps for addressing administrative audit deficiencies? |
Reporting and Investigations Checklist
| Reporting Requirements |
| Do you have reports demonstrating HIPAA compliance efforts? |
| Is there a system to track and manage HIPAA violation investigations? |
| Are processes in place to report breaches within HHS timeframes? |
| Are breach violations reported annually to HHS by fewer than 500 individuals? |
| Have policies and procedures been reviewed and updated annually? |
These tables simplify the compliance process, helping you address key requirements efficiently while maintaining thorough documentation.
5 Tips to Expedite the HIPAA Audit Process
Are you worried about your HIPAA audit process? We will give you 5 tips to help expedite your HIPAA audit process. Adopting these tips can enhance overall HIPAA compliance and contribute to a more efficient audit experience.
Documentation Readiness
Documentation is crucial for companies to comply with HIPAA regulations. Develop comprehensive policies covering privacy, security, and breach notification. Document employee training on PHI handling regularly. Conducting and documenting risk assessments and outlining security measures are essential to expedite your HIPAA audit process.
Record all security incidents, maintain up-to-date business associate agreements, and retain documentation per HIPAA guidelines. Also, consider seeking legal consultation to align documentation with current regulations.
Training and Awareness
Businesses collecting PHI should construct a thorough training program for all staff levels to make it easier to attain HIPAA compliance. Customized modules tailored to specific roles clarify responsibilities in handling patient data. This also reduces the chances of any internal errors that could result in unauthorized access or disclosures.
Engage Legal and Compliance Experts
Engaging legal and compliance experts possess the expertise to break down complex HIPAA regulations and ensure that organizational policies align with legal requirements. To streamline the audit process, collaborate with legal counselors who are well-versed in healthcare law to assess and enhance policies and procedures.
Compliance experts can conduct internal audits, identifying potential vulnerabilities and providing guidance on remediation. Additionally, legal support becomes invaluable if audit findings lead to regulatory action.
Regular Self-Assessment
Regular self-assessment is critical when it comes to maintaining HIPAA compliance. Establish a HIPAA audit checklist to review and update policies, conduct a comprehensive risk analysis, and assess workforce training effectiveness. Map data systems, simulate incident responses, and validate physical security measures.
Thoroughly review documentation and ensure business associates comply. These assessments boost adherence to HIPAA regulations and enhance overall data security, mitigating risks associated with PHI.
Cooperate with Auditors
Collaborate openly and transparently with auditors. Provide requested information and address any concerns raised during the audit. Cooperation helps create a smoother and more efficient process. Be prepared to answer inquiries and address any concerns they may have. Collaborate proactively, offering insights into compliance measures and showcasing the organization’s commitment to safeguarding patient information.
The HIPAA Breach Notification Rule
The HIPAA Breach Notification Rule mandates that any organization handling PHI or ePHI must adhere to specific protocols in the event of a data breach. This applies not only to entities covered by the Privacy and Security Rules but also extends to others, such as:
- Vendors of Personal Health Records (PHRs)
- PHR-Related Entities (e.g., fitness trackers interfacing with PHRs)
- Third-Party Service Providers
These entities must notify affected individuals, relevant federal agencies, and, in certain circumstances, local media when a breach involving unsecured PHI or ePHI occurs.
Determining Reportable Breaches
Before initiating breach notifications, it is critical to assess whether the breach qualifies as reportable. Unnecessary reporting can trigger unwarranted investigations, causing operational disruptions and undue concern for affected individuals.
Organizations should conduct a thorough risk assessment to determine if the breach is reportable. This process involves evaluating:
- Encryption Status: Was the exposed ePHI encrypted, rendering it unreadable, unusable, or undecipherable?
- Exposed Data: What specific health information or identifiers were compromised?
- Access Details: Who (if known) accessed or viewed the PHI/ePHI without authorization?
- Risk of Misuse: What is the likelihood that the exposed data could be further used or disclosed?
- Mitigation Measures: What actions have been implemented to minimize the breach’s impact?
Organizations can use a HIPAA breach risk assessment form or decision tool to streamline this evaluation.
Notification Requirements
If a breach is deemed reportable, organizations must notify affected individuals promptly, ensuring all notifications are issued within 60 days of the breach discovery. Notifications must include:
- Details of the Breach: Specific information about the data disclosed.
- Mitigation Efforts: Actions the organization is taking to control the breach’s impact and prevent recurrence.
- Protective Steps: Guidance for individuals on how to safeguard themselves against fraud or identity theft.
Federal and Media Reporting Obligations
The reporting requirements to federal agencies and media depend on the breach’s scale:
- Breaches Affecting Fewer Than 500 Individuals: Organizations must report such breaches to the HHS OCR or the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) by the end of the calendar year in which the breach occurred.
- Breaches Affecting 500 or More Individuals: These must be reported to the OCR or FTC and relevant local media outlets within 60 days of the breach discovery. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, including fines of up to $46,517 per day for noncompliance.
Proactive Compliance Measures
To minimize risks, organizations should implement:
- Strong encryption protocols to secure PHI/ePHI.
- Training programs for staff to identify and prevent breaches.
- Regular audits to ensure ongoing compliance with HIPAA’s Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rules.
By prioritizing a structured breach response process, organizations can not only meet regulatory requirements but also protect their reputation and maintain trust with patients and stakeholders.
Conclusion
HIPAA compliance is critical for any company dealing with US citizens’ PHI. Looking at the surge in data breaches around the US, such regulations work as a standard of perfection in data security. Organizations looking to expedite this process and ensure compliance should prioritize documentation readiness, maintain comprehensive policies, and conduct regular self-assessments.
Thorough training programs for staff at all levels, engagement with legal and compliance experts, and proactive collaboration with auditors can help streamline the HIPAA audit process. These tips, together with the HIPAA compliance checklist, enhance overall HIPAA compliance and contribute to a more efficient and effective audit experience.







