A surge in cloud computing and other aspects of the digital world has created significant challenges in the ethical handling of data, As companies continue to gather data, even while you read this article, concerns are raised when it comes to ensuring the privacy, confidentiality, and security of their user’s personal information.
Users are more aware of how their data is being processed in companies after major data breaches in some of the leading tech companies. To rebuild trust and confidence in users, regulatory bodies have developed security standards that help maintain the integrity of companies.
All users have sought compliance certifications such as GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and PCI to ensure that the services they are dealing with care about THEIR data. However, it has been quite tedious for organizations to manage these varying compliance regulations, with so many available in the industry today.
A quick read through this article will give you all the information you need and a detailed comparison of these four popular compliance regulations: GDPR vs. HIPAA vs CCPA vs PCI.
Why Is Compliance Important In Cybersecurity?
Before we explore the four compliance standards mentioned above, it is best to understand why exactly we need compliance. Compliance is necessary for several reasons. It establishes a framework of standards and practices that organizations must adhere to, helping to ensure a base level of security. Compliance frameworks, such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, CCPA, or GDPR, provide guidelines that help protect sensitive information and reduce the risk of data breaches.
According to the Identity Theft Resource Center, about 1802 data breaches occurred back in 2022, resulting in more than 422 Million people being exposed. Acts like these deter consumers from trusting companies with their data. This is something that Compliance helps to solve as well.
Compliance helps build trust among stakeholders, including customers, partners, and regulatory authorities. Demonstrating adherence to recognized cybersecurity standards reassures customers that their data is handled responsibly, fostering a positive reputation for the organization. Which in turn helps to boost business for the company as well.
What is GDPR in cyber security?
General Data Protection Regulation, more popularly known as GDPR, is a compliance standard that was created for companies handling European Union residents’ data. Implemented on the 25th of May 2018, GDPR was designed by the European Parliament and Council of the European Union.
GDPR is widely known to be very strict with its data protection policies, allowing consumers to decide how their data is handled. It also stresses a company’s ability to ensure enough security to protect these data. Companies that deal with GDPR need to maintain themselves in accordance with its rules continually. Non-compliance would have the company face a hefty fine of 4% against its annual global revenue, which is a lot!
Who needs to be GDPR Compliant?
According to GDPR, any company in the globe that is collecting or processing the data of European Union residents must stay compliant with it. A range of companies, like data processors, data controllers, and even other data protection authorities, must comply with GDPR.
It’s essential to note that GDPR compliance is not limited to specific industries or business sizes. Whether you’re a small e-commerce website that collects customer information or a multinational conglomerate that handles vast amounts of data, you may need to comply with GDPR if you process the personal data of EU residents.
What is HIPAA in cyber security?
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, or HIPAA, is a U.S. federal law presented on the 21st of August, 1996. While HIPAA primarily focuses on healthcare data and privacy, it significantly impacts cybersecurity in the healthcare industry.
HIPAA sets standards for protecting sensitive patient health information and establishes requirements for healthcare organizations and their business partners to ensure this information’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Healthcare organizations must implement strong measures to protect sensitive patient information, and failure to do so can lead to legal and financial consequences. Non-compliance fines for HIPAA can start from $50,000 and go up to $1.5 Million for companies.
On the other hand, threat actors can face prison time of 1 year up to 10 years for intentionally misusing protected health information (PHI).
Who needs to be HIPAA Compliant?
HIPAA compliance is necessary for companies in the United States that handle PHI. This includes healthcare providers like doctors, hospitals, clinics, pharmacies, health plans like insurance companies, healthcare clearinghouses, and third-party business associates like IT firms.
Even subcontractors of business associates, if they have access to PHI, are subject to HIPAA regulations. Compliance with HIPAA is essential to protect patient privacy and security. Covered enterprises and their business associates must establish and maintain security measures, policies, and procedures to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the patients.
What is CCPA in cyber security?
The California Consumer Privacy Act, called CCPA, is a data privacy law in California. Presented on the 21st of June, CCPA grants California residents certain rights over their personal information held by companies, including the right to know what data is collected and how it’s used, the right to opt out of data sales, and the right to have their data deleted.
Compliance with CCPA requires strong data protection measures. Businesses subject to CCPA must secure personal information to prevent data breaches, unauthorized access, and data theft. Various cybersecurity practices are outlined under CCPA for protecting consumer data and complying with CCPA requirements.
Failure to comply can lead to regulatory fines and reputational damage to the company. CCPA violation fines can become enormous, as the regulatory body requires companies to pay $2,500 to $7,500 for each user affected by a data breach.
Who needs to be CCPA Compliant?
Any business or organization collecting, processing, or sharing California residents’ personal information must be CCPA compliant. The law applies to for-profit companies with an annual gross revenue of over $25 million, those processing the personal information of 50,000 or more California consumers, or companies that generate 50% or more of their annual income from selling California consumers’ personal information.
CCPA compliance is also necessary for service providers processing personal information on behalf of businesses subject to the law. It is also important to note that even businesses based outside California that interact with California consumers are required to comply with CCPA if they meet the criteria mentioned above.
What is PCI DSS in cyber security?
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, or PCI DSS, is a compliance framework for businesses that handle payment card data. It was established back in 2004 by five leading credit card companies: Mastercard, Visa, JCB, American Express, and Discover. Its primary aim is protecting sensitive payment card information and preventing data breaches and fraud.
This standard applies to various companies that process, store, or transmit payment card data, including merchants, financial institutions, and service providers.
To comply with PCI DSS, institutions must adhere to several security requirements. These requirements include the maintenance of secure networks, effective access controls, encryption of cardholder data, regular vulnerability assessments, and establishing a solid information security policy.
A company that is non-compliant with PCI DSS is required to pay a fine, just like the other compliance regulations on this list. A fine could start from $5000 and reach $100,000, which needs to be paid monthly. The amount of fine depends on how big the company is and the severity of the non-compliance.
Who needs to be PCI Compliant?
PCI compliance is necessary for any company that handles payment card data. This includes organizations such as retailers, e-commerce websites, and payment card processing service providers. Merchants that accept payment cards and service providers that offer similar services must adhere to PCI DSS.
The required compliance level can differ based on the volume of transactions and the specific payment card brands processed. PCI compliance involves implementing security measures like data encryption, network protection, access control, and regular security checks.
GDPR vs HIPAA vs CCPA vs PCI: Compliance Differences
GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and PCI are very different from each other. Refer to the table below to understand all the different regulations they have.
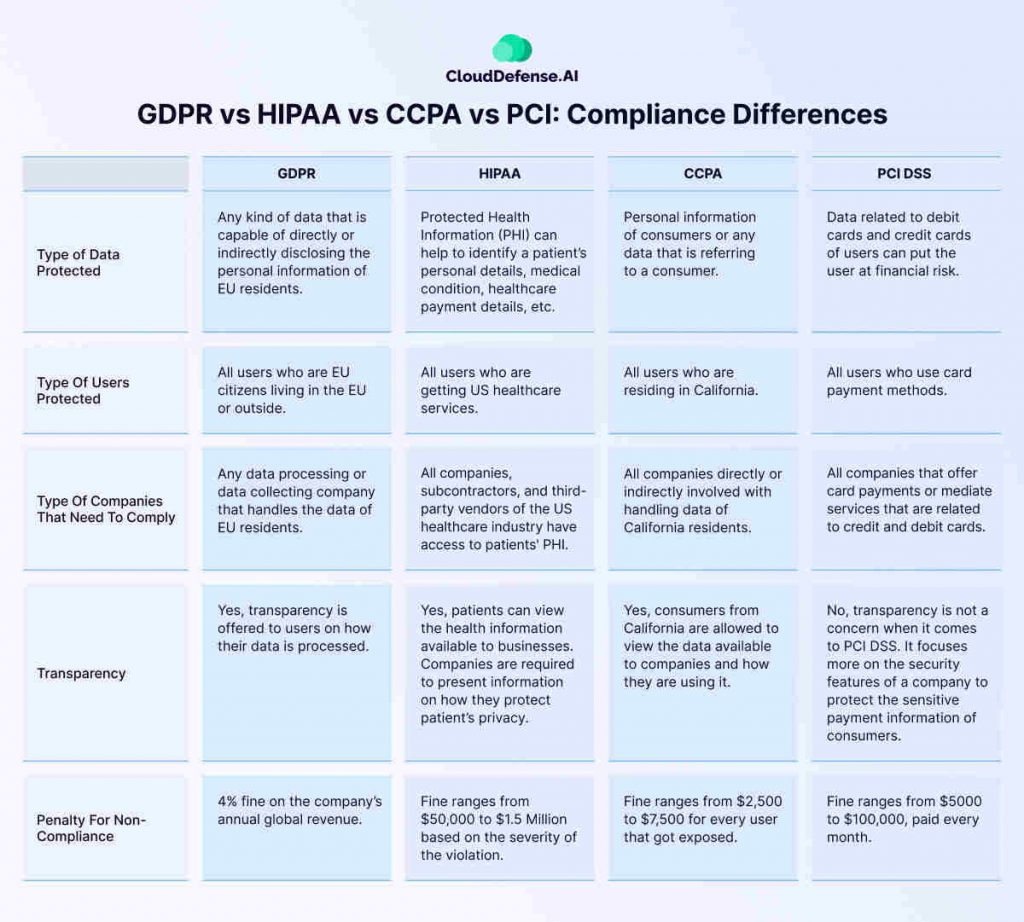
Similarities Between GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and PCI Compliance
GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and PCI DSS do share some common principles. They all stress the importance of protecting sensitive information, controlling who accesses the data, and conducting regular audits to identify vulnerabilities. Also, these regulations require organizations to notify authorities and affected individuals in the event of a data breach.
Data minimization, consent, opt-out rights, compliance documentation, and the imposition of penalties for non-compliance are some similarities between all four compliance frameworks. Despite these similarities, each regulation has different requirements and compatibility, requiring varying compliance goals.
FAQ
Here are a few queries that people have regarding GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and PCI.
What type of information is protected by GDPR?
GDPR protects any information that can directly or indirectly link to any certain individual who is a citizen of the European Union. According to Art. 4 (1). According to GDPR laws, personal data is any information that is related to an identified or identifiable natural person.
How does the HIPAA compare to the CCPA and GDPR?
HIPAA has been created to safeguard the Protected Health Information (PHI) of anyone receiving US healthcare services. On the other hand, CCPA and GDPR are established to protect the personal information of residents living in California and the EU, respectively. They have different scopes of data that they protect.
Is GDPR the same as PCI?
No, PCI is focused on protecting the payment details of consumers. While GDPR is focused on protecting the personal information of EU residents. They are very different from each other based on the type of data they protect and the users they protect.
Does GDPR cover privacy?
Yes, in fact, GDPR is known as the strongest privacy protection law in the world. It was built to improve the originally made 1995 data protection directive.
Conclusion
The goal of getting users to trust sharing their personal data on the internet has been made possible again due to the many compliance frameworks that have been developed so far. However, we can’t ignore the range of complexity and other issues that companies face when it comes to pleasing these regulatory bodies to stay relevant.
As hard as it may seem, a clear understanding of the compliance frameworks and their goals is surely a good starting point to kickstart your compliance journey. When it comes to GDPR vs. HIPAA vs. CCPA vs. PCI discussions, you should know by now that they are very different from one another, even though they share the mutual goal of data protection.







