Data has been the most valuable and precious commodity in the business for the last two decades. Every organization, whether in Europe or the US, has been utilizing data to gain real insight into their business to drive growth and sales.
Since 1998, businesses in the EU have stayed compliant with the EU directive designed for data privacy and protection. However, as cyber-attacks on data have evolved EU member countries sought to bring a harmonized data privacy law.
Thus, on May 25, 2018, EU member countries enforced the General Data Protection Regulation and made a giant step toward a more data privacy and protection framework. GDPR audit can be a time-consuming process, and it lasts between a few weeks to a few months, depending upon multiple factors.
However, to reduce the duration, we have come up with this article that will navigate you through the GDPR audit process.
What is a GDPR Audit?
The General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, is a legal framework set by European Union law period. It provides regulations and laws for organizations concerning the collection and processing of personal information.
It can also be described as a data privacy regulation that provides control and rights regarding personal data to individuals residing in EU countries. The European Union approved GDPR in 2016, but it formally came into effect in May 2018.
The regulation and principle apply to every organization and website handling the personal data of individuals residing in European countries. According to the law, businesses must inform users how they are handling consumer data, what they do with it, and whenever there is a breach.
The GDPR audit is a systematic assessment process that helps organizations assess their compliance with GDPR laws and regulations. It also identifies the vital security gaps and risks in the organization’s security, policies, and processes. After the audit, it provides the organization with the guidelines and implementations needed to mitigate the risk and close the security gaps.
The recommendation also includes implementing appropriate policies for monitoring personal data, security controls for PIs (performance indicators), and enforcing GDPR-compatible consent management solutions.
Key Components of GDPR
The GDRP includes many vital components to ensure the safeguarding of users data privacy and the responsibility to handle personal information appropriately. These key components are:
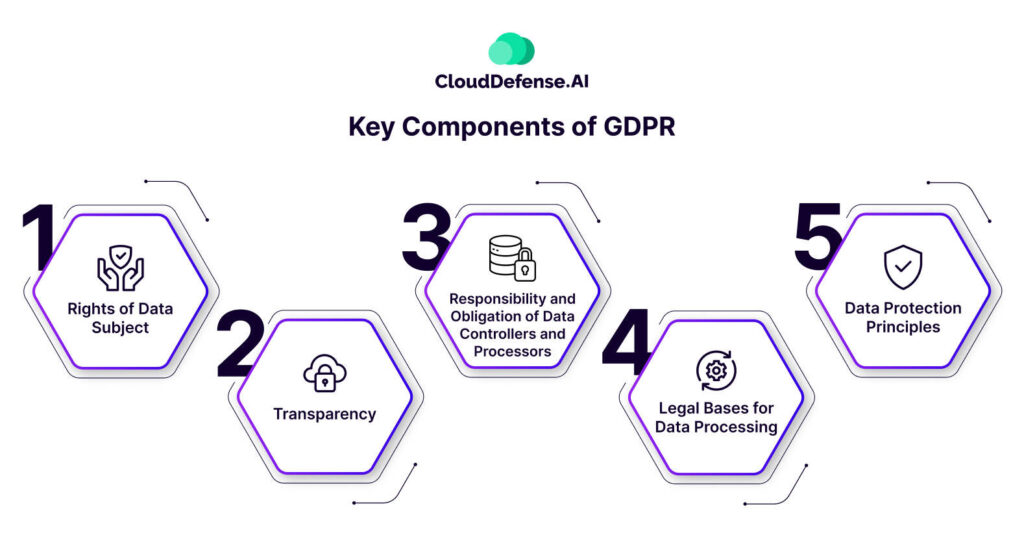
Rights of Data Subject
The GDPR regulation empowers users to possess a set of rights regarding all the personal data stored by businesses. GDPR provides users the right to access, assess, erase, govern, and restrict the processing of their personal data by every organization. GDPR also provides rights to the individual with regard to rectification and the right for automated decision-making and profiling.
Transparency
Organizations collecting personal information of EU residents must inform them about the collection and purpose for which they are collecting it.
Organizations must create policies requiring them to notify users how they will be collecting the user data whenever they visit the site. During sign-up for the accounts, the organization must mention all the consent and how the organization will process and use the data for the visitors.
Responsibility and Obligation of Data Controllers and Processors
When it comes to the processing of personal data, GDPR clearly outlines the roles of data controllers and processors. Both data controllers and processors have specific responsibilities and obligations that they need to follow to ensure secure processing of all personal information.
The data controller provides the purpose and means of processing the data, as well as all the legal bases for processing the data. The data controller collects only the amount of data needed and no more.
The data processors, on the other hand, work alongside data controllers period. They should process personal data according to the controller’s instructions. The data processors are tasked with maintaining the confidentiality and security of the personal data they process.
Legal Bases for Data Processing
Organizations complying with the GDPR framework must have legal bases for processing the personal data of European citizens. GDPR has outlined different legal bases for the data processing period. Every organization must identify the lawful bases when processing personal information.
The legal bases outlined by GDPR include contractual necessity, consent, legal obligation, protection of vital interests, and various others. Organizations that rely on legal bases for data processing must perform a balancing test that will demonstrate the organization’s processing interest won’t impact the rights of the data subjects (users).
Data Protection Principles
GDPR principles for the protection of individuals’ data rights and privacy, leverages seven core principles. Every organization must adhere to these principles when processing the data. These principles ensure all the data processing is done fairly and securely while protecting the rights of the users.
Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency are the most vital principles of GDPR forcing every organization to maintain lawful, transparent, and fair data collection. Organizations must also follow purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, accountability, integrity, and confidentiality principles when processing users’ personal information.
Adhering to all these principles allows organizations to protect privacy rights and helps them adhere to GDPR compliance.
How to Perform a GDPR Audit?
Performing a GDPR audit is an overwhelming period. It not only consumes many resources but also time. However, if you follow the following steps, the process will become more straightforward. Here are the steps you need to follow:
Understand the GDPR Requirement
First, you must understand the GDPR principles, requirements, and provisions before you begin the auditing process. Familiarize yourself with all the rights of EU users, the responsibility of data controllers and processors, and the laws associated with data processing. Familiarity with the requirements helps simplify and expedite the audit process.
Determine the Scope of GDPR Compliance
To begin the GDPR audit, you will first have to understand the scope of GDPR compliance. You need to identify the personal information databases of EU citizens and the location of all stored personal data. In addition, you must identify all the data processing activities, including cross-border activity, performed by the data processor and controller.
Evaluate the Personal Collection and Processing Activity
The next thing you must do is evaluate how your organization collects and processes all EU citizens personal data. You also need to categorize the type of personal data you collect, the legal basis for processing it, and why you collect it.
During the audit, you will must provide proper documentation mentioning the legal reason for processing each data type and that you have obtained consent from the user. You should also conduct data mapping as it will highlight the flow of personal data and who has access.
Appoint a Data Protection Officer
When commencing your GDPR audit process, it is vital to appoint a Data Protection Officer, or DPO, who has extensive knowledge regarding data protection regulations and requirements.
DPO will help the organization throughout the audit process, beginning with demonstrating compliance and monitoring internal compliance to offering advice on DPIAs and data protection obligations.
Develop Policies and Procedures
You must also establish policies and procedures to satisfactorily complete the GDPR audit process. However, to establish them, you must first understand the regulation and its requirements. Developing policies and procedures in accordance with the requirements will help your organization implement the proper security controls and provide a uniform measurement for the protection of all personal information.
When developing policies and procedures, it is also important to involve all the proper team members so that the business goals are not jeopardized and compliance with the framework is ensured.
Define the Roles and Responsibilities
Once you have created policies and procedures, it is time for your organization to create roles and responsibilities for every team member tasked with data protection. To ensure everyone clearly understands their roles, your organization should conduct training programs at regular intervals. Training programs will also make members aware of current scenarios and what needs to be done to ensure an accelerated GDPR audit process.
Conduct Data Protect Impact Assessment
The next task in the GDPR audit process is to conduct DPIA (Data Protect Impact Assessment) by consulting with the DPO. Leveraging DPIA will help the organization identify and mitigate all risks associated with personal information processing activities. DPIA will also help the organization evaluate the effectiveness of all security policies, procedures, and measures implemented to protect users’ personal data.
Implement Process to Ensure Data Subject Rights
The GDPR framework provides users with various rights regarding their personal data. To ensure all the data subject rights are met, your organization must implement processes and procedures to facilitate and respond to individuals exercising their rights as defined by GDPR. You also need to ensure these procedures respond to all the requests within a given time frame.
Assess Data Processing Agreements with Vendors
Nowadays, many organizations work with various third-party processors for data processing. So, it is important for your organization to assess the data processing agreement during the GDPR audit.
During the audit steps, you must make sure all the agreements adhere to the GDPR requirement. You must also ensure all the security measures are in place for all the personal data that the third-party processors handle on your behalf.
Implementing a Personal Information Management System
GDPR requires an organization to maintain a lot of documentation to ensure that your organization is appropriately adhering to GDPR compliance requirements.
However, to ease the documentation process and GDPR auditing, it is best to implement a PIMS (Personal Information Management System). Implementing PIMS will help the organization document all data protection policies, data breach notification procedures, consent forms, access request forms, and other essential activities.
Implementing an Information Security Management System
Along with PIMS, your organization should also implement an Information Security Management System to ensure you have all necessary security measures to protect the personal data in hard copy or electronic form.
4 Tips to Expedite the GDPR Audit Process
Expediting the GDPR audit process is not only about preparing for the audit beforehand but also involves efficient planning and a systematic approach. You should follow a checklist to expedite your GDPR audit process. Here are four tips to accelerate the GDPR compliance audit process:
Learn About All Your Data
When you plan to expedite the GDPR audit process, the first thing you need to do is learn about all your data, especially fluid assets. For GDPR, it is important for the organization to learn about the flow of information and how it is processed.
Learning about your organization’s data flow and processing will help the organization document everything and present it effectively during the audit. Documentation of all the data will also help you demonstrate compliance with GDPR and answer all relative questions during the audit process.
Consider the GDPR Enforcement as an Investment
According to experts, every organization should consider GDPR enforcement as an investment that will provide them with good returns in the future. Organizations should make an effort to stay compliant with GDPR for the long term because it will benefit them in many ways.
Not only will it help them address regulatory and data management risks, but it will also help them seize multiple opportunities in the market. It is important for organizations to invest in modern privacy technology helping organizations automate processes required for GDPR compliance and other regulatory frameworks.
Privacy technologies are also helping organizations showcase privacy by design as an integral part of the IT process, thus adhering to the best practices for GDPR. Demonstrating privacy by design factor also provides a chance to promote data minimization, which is vital for organizations to prevent compliance issues and curb compliance costs.
Leverage Control Objective Framework
Leveraging a control objective framework can greatly benefit your organization in adhering to compliance requirements and help expedite the GDPR audit process. Using a control objective framework will enable the organization to emphasize and enforce IT security and process control in the organization’s infrastructure, which will ultimately help in the compliance journey.
From vulnerability management, patching, and preventive security controls to configuration management, you must cover every aspect that is intended for data security, as it will help you in the audit process. Enforcing all the best security practices throughout will ease the audit process and help you achieve compliance quickly.
Make Changes to the Contracts with Vendors
To accelerate the GDPR audit process, you also need to make changes to contracts with vendors because vendor risk management serves as a vital aspect of compliance requirements. While revising contracts with the vendors, the organization must make necessary changes to audits that include evidence of process controls, configuration statics, and audits.
In all contracts, the organization must introduce processes through which vendors can periodically get in touch with the organization and verify they are maintaining specific controls to maintain compliance. In a proper contract, the organization will require the vendor to implement specific controls and make them equal for GDPR compliance.
FAQs
Are GDPR audits mandatory?
The GDPR audit is not mandatory for every organization storing consumer data. However, it states that any organization collecting and processing EU consumers’ personal information must adhere to GDRP compliance. The audit mandates have legal justification for storing and processing the personal data of EU customers.
What is the frequency of GDPR audits?
Although there is no official statement regarding how many times an organization must conduct a GDPR audit, it is recommended that it should be conducted once a year. Conducting annual GDPR audits is sufficient for every organization to demonstrate its compliance with GDPR requirements.
What is the purpose of the GDPR audit?
The primary purpose of the GDPR audit is to protect the EU individual’s right to protect their personal data that is collected and processed by various organizations.
The GDPR audit also aims to discover the critical security gaps and issues in the policies, procedures, and processes with regard to the GDPR requirements. Besides identifying the risks and gaps, it also provides recommendations for mitigation.
Conclusion
GDPR compliance is an essential aspect of modern organizations. Everyone must adhere to it when collecting and processing EU resident’s personal information. The GDPR audit process has a varied time that ranges from one month to a year. However, it is a systematic assessment process that helps organizations assess organizational compliance with GDPR laws and regulations.







