You might have come across the terms cybersecurity and information security and think that they are the same. While both fields aim to protect sensitive data and systems, their focus and implementation largely vary.
Cybersecurity primarily addresses the protection of internet-connected systems from cyber threats, while information security involves a broader scope, protecting all forms of data, whether digital or physical. If you are a company looking to protect yourself from the threats that the internet has to offer to you then it is highly important that you understand the differences between these two terms.
This article will explore the unique functions of cybersecurity vs information security, highlighting their similarities as well as their differences, to provide clarity for companies that are looking to invest in protection strategies. Keep reading to get started with your security journey!
What Is Information Security?
Information security is the methodology of defending data in all variations of it from unauthorized access, usage, disruption, disclosure, destruction, or alteration. Commonly known as InfoSec, this discipline is integral to maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, whether it is stored digitally, physically, or in any other medium.
At its core, information security aims to protect valuable and sensitive data from threats that could compromise its integrity, confidentiality, or availability. Here’s a breakdown of the three terms for you to understand them better.
Key Components of Information Security
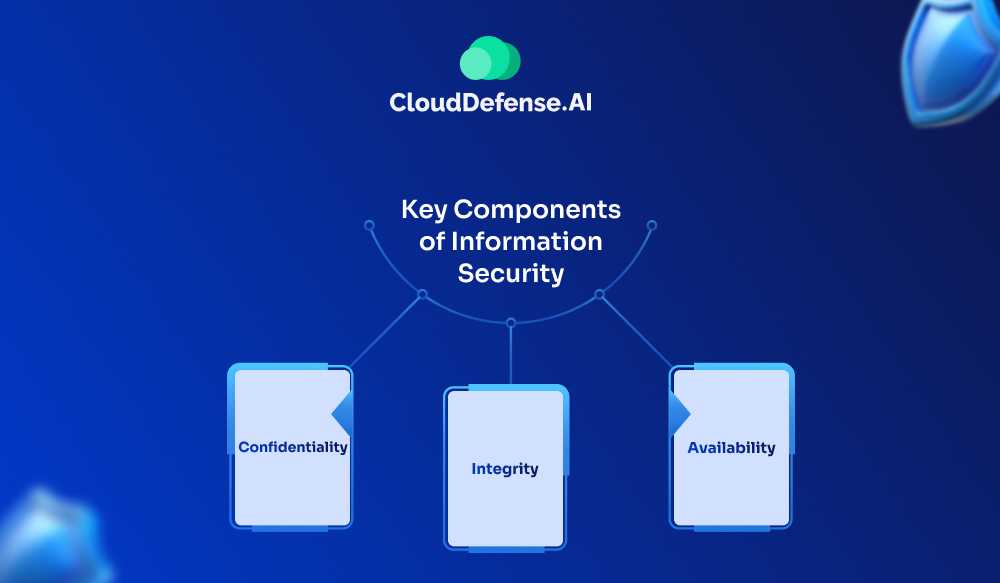
Confidentiality
Confidentiality ensures that information is accessible only to those with authorized access, protecting personal privacy and proprietary information from unauthorized disclosure.
Integrity
Integrity involves maintaining the accuracy and completeness of data, ensuring that it remains unaltered and trustworthy throughout its lifecycle.
Availability
Availability ensures that information and systems are accessible and usable when needed, supporting uninterrupted business operations and decision-making.
Governance Framework in Information Security
A strong governance framework can help you to manage information security effectively within an organization. The Information Security and Governance Framework provides guidelines and best practices for identifying, classifying, and protecting sensitive information. This framework encompasses security controls, procedures, incident response strategies, and disaster recovery plans.
The ISGF is aligned with international standards such as ISO/IEC 27001:2013, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and regulations like the EU GDPR. It is designed to be flexible, accommodating the specific needs of various organizations across different industries.
The Importance of Information Security
Information security is a rapidly evolving domain. With the increasing frequency and complrxity of cyber threats, organizations are required to upgrade their security measures to protect against breaches that could result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties. Effective information security practices not only protect data but also support the overall resilience and trustworthiness of an organization.
By implementing comprehensive information security measures, organizations can protect their valuable assets, ensure regulatory compliance, and maintain the trust of their clients and stakeholders. The ongoing development of policies, procedures, and technologies in information security is essential for reducing risks and responding effectively to newer threats.
What Is Cyber Security?
Cybersecurity is the practice of defending computer systems, networks, devices, and applications from a wide array of cyber threats. As digital transformation accelerates globally, the incidence of cyber attacks has surged, posing significant risks to sensitive data. Consequently, cybersecurity has become a critical concern for both corporations and national governments, interwoven with geopolitical complexities and increasingly sophisticated attack methodologies.
Cyber Security Threats and Attacks
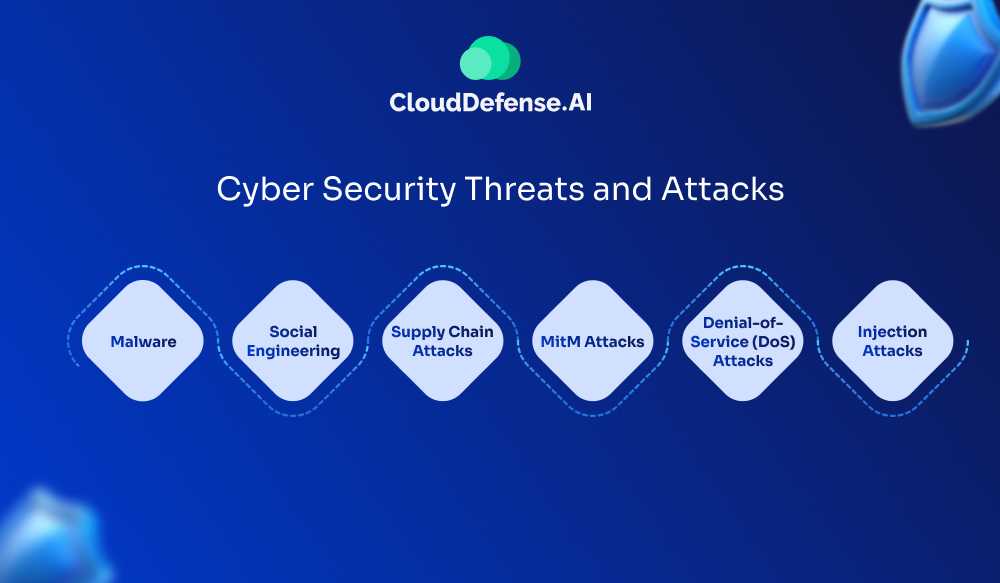
Cybersecurity threats pose significant risks to individuals and organizations alike. These threats include a wide range of malicious activities aimed at compromising the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data and systems. Let’s check out some of these cyber threats and attacks below.
Malware: The All-Inclusive Threat
Malware, a term that is derive from “malicious software,” consists of a variety of harmful software such as viruses, trojans, worms, ransomware, and spyware. Malware typically infiltrates systems through deceptive links, email attachments, or untrusted software downloads, leading to unauthorized data access, manipulation, and potential destruction.
Social Engineering: Manipulating Human Behavior
Social engineering attacks exploit human psychology to gain illegitimate access to systems or data. These attacks often involve deception and manipulation, tricking individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security. Common social engineering tactics include:
Supply Chain Attacks: Targeting the Source
Supply chain attacks involve compromising the software development process or distribution channels to inject malicious code into legitimate applications. These attacks can be particularly severe as they exploit trusted software updates or pre-installed components, allowing malware to operate with the same privileges as the legitimate application. Types of supply chain attacks include:
MitM Attacks: Intercepting Communications
MitM, or Man-in-the-Middle, attacks involve intercepting and possibly modifying communications between two parties. This allows attackers to eavesdrop on conversations, steal sensitive data, and impersonate the involved parties. Examples include:
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Overwhelming Systems
DoS attacks aim to disrupt normal system functionality by overwhelming it with excessive traffic. When multiple devices are involved, it becomes a distributed denial-of-service attack.
Injection Attacks: Exploiting Code Vulnerabilities
Injection attacks involve inserting malicious code into a web application, often exploiting vulnerabilities in the code. These attacks can expose sensitive data, disrupt services, or compromise entire systems. Common injection attacks include SQL injection, where attackers manipulate database queries to gain unauthorized access.
CyberSecurity vs Information Security
| Aspect | Cybersecurity | Information Security |
| Focus | Protecting electronic data and systems from cyber attacks | Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of all data, whether electronic or physical |
| Scope | Electronic data, networks, devices, applications, and servers | All forms of data, including electronic, physical, and paper |
| Primary Concern | Preventing unauthorized access, cyber threats, and data breaches | Protecting data from unauthorized access, ensuring data accuracy, and making sure data is available when needed |
| Threats Addressed | Malware, phishing, DDoS attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and other cyber threats | Data breaches, loss of data integrity, and unauthorized data access |
| Methodology | Identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in digital systems, implementing firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems | Implementing policies, procedures, and controls to manage and protect data in all forms |
| Overlap | Often overlaps with information security when it comes to protecting electronic data | May involve cybersecurity measures to protect electronic data but also includes physical and procedural protections |
| Teams Involved | Cybersecurity teams focusing on technical defenses and response to cyber incidents | Information security teams focusing on data classification, risk management, and policy enforcement |
| Key Activities | Penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, monitoring network traffic, and responding to cyber incidents | Data classification, risk assessments, creating data protection policies, and managing data access controls |
| Example | A cybersecurity team might use firewalls and encryption to protect data on a network | An information security team might establish data access policies and ensure sensitive documents are stored securely |
Partner with CloudDefense.AI for Kickstarting your Information and Cyber Security
With the growing interconnectivity and evolving cyber threats, CloudDefense.AI offers comprehensive solutions to boost both information security and cybersecurity for businesses. CloudDefense.AI enhances information security by continuously monitoring data integrity and ensuring compliance with strict data protection policies. It protects critical information through strong encryption and access control mechanisms, reducing risks of data breaches and unauthorized access.
On the cybersecurity front, CloudDefense.AI Strengthens your organization by identifying and patching vulnerabilities in real-time, deploying advanced threat detection systems, and monitoring dark web activities to preempt potential cyber attacks. Its proactive approach includes automated risk assessments and instant alerts to any suspicious activities, ensuring your digital assets remain secure.
By integrating both cybersecurity and information security measures, CloudDefense.AI provides a unified platform that not only protects data but also maintains the resilience of your IT infrastructure, ensuring your business remains secure and compliant. Book a free demo now to get firstand experience of CloudDefense.AI







