As more organizations move to the cloud, protecting sensitive data has never been more important. With cyber threats on the rise, staying ahead with a strong security strategy is essential.
Cybersecurity compliance helps businesses strengthen their defenses by following key regulations and best practices. In fact, companies that prioritize compliance have saved millions by preventing costly security breaches.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know to build a solid cybersecurity framework and keep your organization safe.
What is Cybersecurity Compliance?
Cybersecurity compliance refers to an organization’s adherence to laws, regulations, and industry standards designed to protect sensitive data and digital assets from cyber threats. It ensures that businesses follow best security practices, reducing vulnerabilities and minimizing the risk of data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Compliance frameworks vary by industry and region, with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and NIST providing guidelines on data protection, risk management, and incident response. Meeting these requirements involves implementing security controls, conducting regular audits, and maintaining proper documentation.
Beyond legal obligations, cybersecurity compliance strengthens an organization’s overall security posture, enhances customer trust, and improves resilience against evolving cyber risks. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, legal consequences, and increased exposure to cyberattacks.
Why is Compliance Important in Cybersecurity?
With the growing dependence on digital infrastructure, cyberattacks are on the rise. In recent years, even top organizations have suffered major security breaches. Despite advancements in modern security technology, businesses still struggle to address evolving threats effectively.
Ransomware and other cyber threats remain a significant concern from small businesses to large enterprises and government agencies. Adhering to cybersecurity compliance frameworks has proven essential in strengthening security defenses and preventing attacks. Here’s why compliance is critical:
- Data Privacy & Protection: Compliance ensures the safeguarding of sensitive customer data, preventing exploitation by cybercriminals and reducing the risk of breaches.
- Reputation Management: Cyberattacks can severely damage an organization’s reputation, disrupt operations, and erode customer trust. Compliance helps mitigate these risks.
- Effective Risk Management: By implementing security controls and continuous monitoring, organizations can proactively identify and address vulnerabilities before they escalate.
- Preparedness Against Data Breaches: Compliance frameworks guide organizations in developing proactive strategies to detect, prevent, and respond to potential breaches.
- Business Continuity: Adhering to security standards ensures resilience during cyber incidents, minimizing disruptions and maintaining operations.
- Legal & Regulatory Compliance: Meeting industry-specific regulations helps organizations avoid legal consequences and ensures smooth global operations.
- Stronger Security Posture: Compliance requires continuous improvements in security strategies, ultimately strengthening an organization’s overall defense against threats.
Focusing on cybersecurity compliance enables organizations to safeguard their assets, sustain trust, and establish a fail-proof security framework.
Key Cybersecurity Compliance Frameworks
Cybersecurity compliance frameworks provide organizations with structured guidelines to protect their digital assets, mitigate risks, and ensure regulatory adherence. These frameworks vary by industry, region, and security needs, but all share the goal of strengthening cybersecurity resilience. Below are some of the most critical cybersecurity compliance frameworks in detail:
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
The GDPR is a comprehensive data privacy regulation established by the European Union (EU) to protect personal data and privacy rights of individuals within the EU and the European Economic Area (EEA). It applies to any organization that processes the personal data of EU citizens, regardless of location.
- Region: European Union (EU) (applies globally to businesses handling EU citizen data)
- Purpose: GDPR focuses on data privacy and security, ensuring organizations protect personal data and uphold user rights.
Key Requirements:
- Secure processing, storage, and transmission of personal data.
- Obtain explicit user consent before collecting data.
- Implement data breach notification processes (must report breaches within 72 hours).
- Allow users the “right to be forgotten” and access to their personal data.
- Impose strict fines for non-compliance (up to 4% of global annual turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher).
GDPR applies to any business dealing with EU citizens’ data, making it one of the most globally influential data protection laws.
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework
Developed by the U.S. Department of Commerce, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) provides voluntary guidelines for improving cybersecurity risk management. It is widely used across industries to enhance security postures.
- Region: United States (widely adopted globally)
- Purpose: Provides best practices to improve cybersecurity posture across industries.
Key Requirements:
- Organized into five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
- Encourages organizations to assess and mitigate cyber risks continuously.
- Focuses on implementing layered security measures, including network security, data encryption, and incident response plans.
NIST is widely used by government agencies, enterprises, and critical infrastructure organizations to enhance cybersecurity.
ISO/IEC 27001 (International Organization for Standardization)
ISO/IEC 27001 is an internationally recognized standard for information security management systems (ISMS). It provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company and customer data.
- Region: Global
- Purpose: Provides a systematic approach to managing information security risks.
Key Requirements:
- Establishes an Information Security Management System (ISMS) to manage data security.
- Requires risk assessment, continuous monitoring, and improvement of security controls.
- Covers areas such as asset management, access control, cryptography, and incident management.
- Certification demonstrates an organization’s commitment to cybersecurity best practices.
ISO 27001 certification is a global standard that helps businesses build trust with customers and partners.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA is a U.S. federal law that sets national standards for protecting sensitive patient health information (PHI). It applies to healthcare providers, insurers, and any entity handling PHI.
- Region: United States
- Purpose: Protects sensitive healthcare data (Protected Health Information – PHI).
Key Requirements:
- Organizations handling patient data (hospitals, insurers, and healthcare providers) must ensure data security and privacy.
- Requires implementation of administrative, physical, and technical safeguards.
- Enforces strict access controls, encryption, and secure data transmission.
- Non-compliance can result in severe fines and legal consequences.
HIPAA compliance is crucial for healthcare organizations and business associates handling PHI.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
PCI DSS is a global security standard that protects credit card transactions by ensuring businesses securely process, store, and transmit payment data.
- Region: Global
- Purpose: Ensures secure handling of credit card transactions and protects cardholder data.
Key Requirements:
- Businesses processing, storing, or transmitting payment card information must comply.
- Requires encryption of cardholder data, strong access controls, and regular security testing.
- Enforces network segmentation to isolate cardholder data environments.
- Annual compliance validation through assessments or audits.
PCI DSS helps businesses prevent fraud, reduce financial risks, and maintain trust with customers.
Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP)
FedRAMP is a U.S. government program that standardizes security requirements for cloud service providers (CSPs) working with federal agencies.
- Region: United States
- Purpose: Standardizes security requirements for cloud service providers (CSPs) working with federal agencies.
Key Requirements:
- Cloud providers must undergo a rigorous security assessment process.
- Requires continuous monitoring and reporting of cloud security posture.
- Ensures compliance with federal data security standards, including encryption and access control.
FedRAMP is essential for cloud vendors serving the U.S. government.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
SOX is a U.S. federal law that enforces financial transparency and security in publicly traded companies.
- Region: United States
- Purpose: Ensures financial transparency and protects against corporate fraud.
Key Requirements:
- Establishes controls for secure financial reporting.
- Requires IT systems that store financial data to implement security measures.
- Enforces accountability through regular audits and compliance reporting.
SOX compliance is crucial for publicly traded companies and financial institutions.
Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC)
CMMC is a cybersecurity certification framework created by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) to protect sensitive defense-related data within the supply chain.
- Region: United States
- Purpose: Ensures cybersecurity in the defense supply chain.
Key Requirements:
- Required for all U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) contractors and suppliers.
- Includes five maturity levels, from basic cyber hygiene to advanced security practices.
- Organizations must undergo third-party assessments to obtain certification.
CMMC enhances national security by protecting defense-related information.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
CCPA is a California state law that enhances consumer privacy rights and gives residents control over their personal data.
- Region: United States (California, with global impact)
- Purpose: Enhances consumer privacy rights and data transparency.
Key Requirements:
- Grants California residents rights to access, delete, and control their personal data.
- Requires businesses to disclose data collection practices and allow users to opt out.
- Imposes penalties for non-compliance, similar to GDPR.
CCPA applies to companies handling personal data of California residents, regardless of location.
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA)
GLBA is a U.S. law that mandates financial institutions to protect consumers’ personal financial information.
- Region: United States
- Purpose: Regulates financial institutions to protect customer data.
Key Requirements:
- Requires financial organizations to develop security policies for customer information.
- Mandates disclosure of data collection and sharing practices.
- Imposes penalties for failure to protect financial data.
GLBA compliance is crucial for banks, insurance companies, and investment firms.
Cybersecurity compliance frameworks are essential for protecting sensitive data, ensuring regulatory adherence, and mitigating security risks. Organizations must carefully evaluate which frameworks apply to their industry and region, implementing the necessary controls to maintain compliance and safeguard their digital assets.
9 Steps to Achieve Cybersecurity Compliance
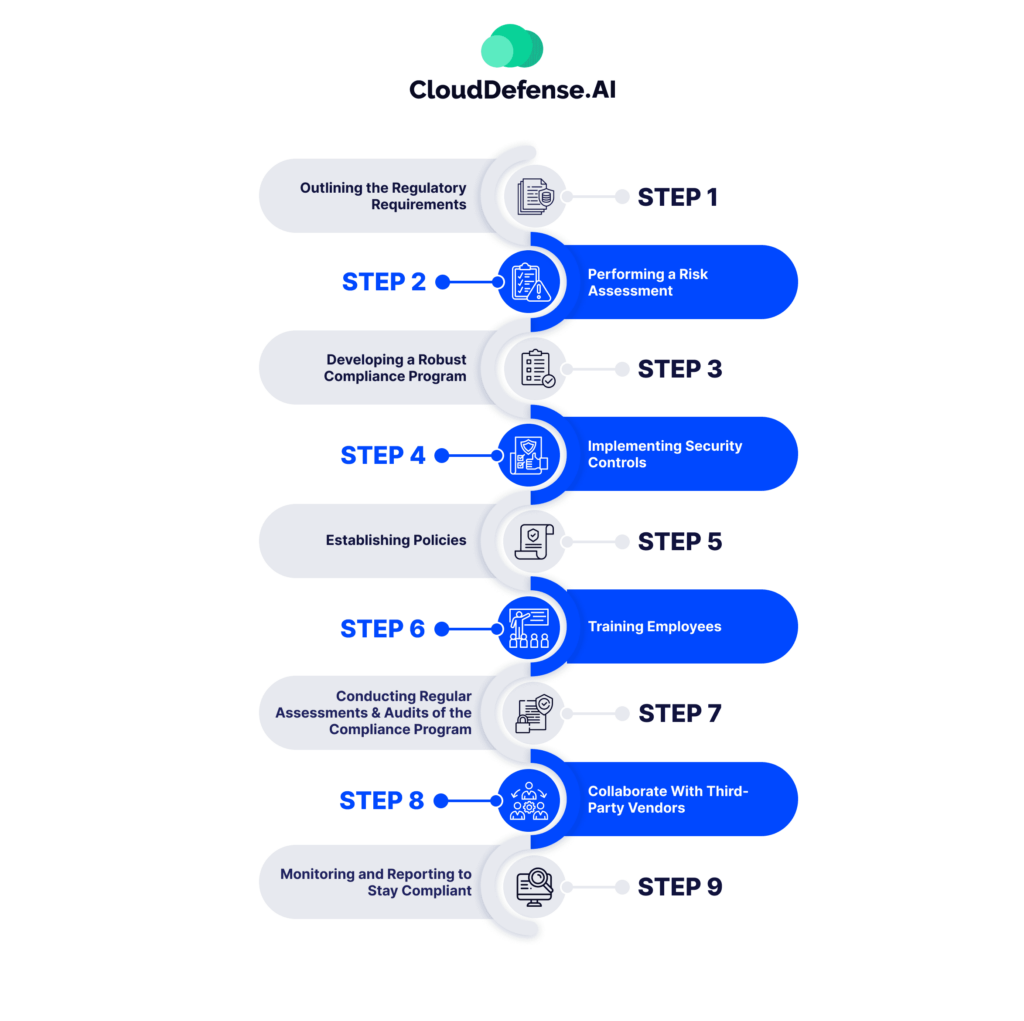
Ensuring cybersecurity compliance is a vital journey for organizations looking to safeguard sensitive data while adhering to industry regulations. It’s important to remember that compliance isn’t just a one-off task; it’s a continuous commitment to maintaining security and managing risks. Here are nine key steps to guide organizations along this important path effectively.
Step 1: Identify Applicable Regulations
Begin by researching and understanding which cybersecurity regulations and industry standards apply to your organization. Compliance requirements vary based on industry, geography, and business operations. Engaging a compliance specialist can help define the scope and critical aspects of each regulation.
Step 2: Conduct a Comprehensive Risk Assessment
Perform a detailed assessment of your IT infrastructure to identify potential vulnerabilities, internal and external threats, and areas of non-compliance. Prioritize risks based on their potential impact and take proactive steps to mitigate them.
Step 3: Develop a Strong Compliance Program
Use the insights from your risk assessment to create a structured compliance program. This program should define security policies, technical controls, incident response protocols, and risk management strategies that align with regulatory requirements.
Step 4: Implement Robust Security Controls
- Deploy security measures that align with regulatory standards and best practices, including:
- Access control and identity management
- Data encryption
- Firewalls and intrusion detection systems
- Continuous monitoring and logging
- Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) enforcement
Step 5: Establish Clear Security Policies
Develop formal policies outlining cybersecurity best practices, data handling procedures, and incident response measures. Ensure policies are regularly updated to reflect evolving threats and compliance changes.
Step 6: Train Employees on Cybersecurity Best Practices
Employees are the first line of defense against cyber threats. Conduct regular training sessions on:
- Identifying phishing and social engineering attacks
- Secure password management
- Proper handling of sensitive data
- Incident reporting protocols
Step 7: Perform Regular Audits and Assessments
Cyber threats continuously evolve, making periodic audits and assessments crucial. Utilize penetration testing, risk analysis, and compliance reviews to detect weaknesses and refine security measures accordingly.
Step 8: Collaborate With Third-Party Vendors
Third-party vendors can introduce security risks. Ensure they adhere to the same compliance standards as your organization. Conduct due diligence and establish security agreements to mitigate potential threats.
Step 9: Monitor, Report, and Adapt
Continuous monitoring is vital for maintaining compliance. Implement real-time security analytics, threat detection systems, and incident reporting frameworks to quickly identify and mitigate risks. Regularly update security strategies to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Cybersecurity compliance is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance and adaptation. By following these nine steps, organizations can build a resilient security framework that not only meets regulatory requirements but also strengthens overall cybersecurity posture.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity compliance is a vital aspect of an organization’s security posture. It ensures that the organization is taking all the necessary measures to protect sensitive data and digital assets. When an organization complies with regulatory requirements, it ensures that the security measures are effective and adhere to industry standards.
Throughout this article, we have provided a complete guide to cybersecurity compliance to help every organization stay compliant. Vendors like CloudDefense.AI are also assisting organizations in adhering to compliance requirements without any complexities. Want to know how? Book a free demo with us now!







