Cloud computing has enabled companies to function much more effectively than ever before. The cloud has many advantages, including its cost-effectiveness, accessibility, scalability, efficiency, and high performance. However, it has also introduced an array of cyber threats that can be hard to tackle in the complex environment of the cloud.
Ransomware attacks have emerged as one of the most pervasive and damaging cyber threats in recent years, causing significant financial losses and disruptions across various sectors. According to a report by Comparitech, the toll on US government organizations was particularly staggering, with costs of $70 billion incurred during the period spanning from 2018 to 2020.
Cloud forensics and data visualization have evolved as necessary parts of cloud environments to tackle this epidemic. These tools help investigate and analyze a ransomware attack to understand its origins and identify the perpetrators. This process is crucial for recovery. Businesses face an escalating threat, underscoring the urgency for organizations to prioritize cloud forensics and data visualization, even with isolated networks.
Keep reading to learn more about these two essential methods and how they can assist you during a ransomware attack.
What Is Cloud Forensics?
Cloud forensics is a branch of digital forensics that focuses on investigating and analyzing digital evidence in cloud computing environments. As organizations increasingly adopt cloud services to store, process, and manage their data, the need for effective forensic techniques in the cloud has grown.
Cloud forensics involves the application of traditional digital forensics principles to cloud environments, but it also addresses the unique challenges and characteristics of cloud computing.
What Are the Benefits of Cloud Forensics?
Cloud forensics investigations offer several benefits in digital investigations and the cybersecurity sector. It enables investigators to analyze and gather evidence from cloud-based environments, where traditional forensic methods may fall short. Here are some benefits of cloud-based digital forensics.
Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud digital forensics allows investigators to handle large volumes of digital evidence efficiently, which is crucial for cloud-based environments’ vast and dynamic nature.
Real-time Monitoring and Logging: Enhanced capabilities for real-time monitoring enable rapid detection and response to security incidents, improving overall cybersecurity posture.
Event Reconstruction: Cloud forensics facilitates the reconstruction of events leading to a security breach, aiding in understanding the scope and impact of incidents.
Centralized Data: Centralizing data in the cloud simplifies evidence preservation and ensures data integrity, providing a unified and accessible repository for investigative purposes.
Collaborative Investigations: Cloud forensics supports collaborative investigations by enabling multiple stakeholders to access the same set of evidence, cementing transparency and coordination among teams.
Adaptability to Cloud Environments: Tailored tools and techniques address the challenges specific to cloud environments, where traditional forensic methods may be insufficient.
Efficient Retrieval and Analysis: Specialized techniques allow for the efficient retrieval and analysis of evidence in redundant and distributed cloud storage systems.
Mitigation of Cyber Threats: The capabilities of cloud forensics contribute to effective cyber threat mitigation, making it an irreplaceable tool for organizations relying on cloud services.
How to Monitor Ransomware Patterns?
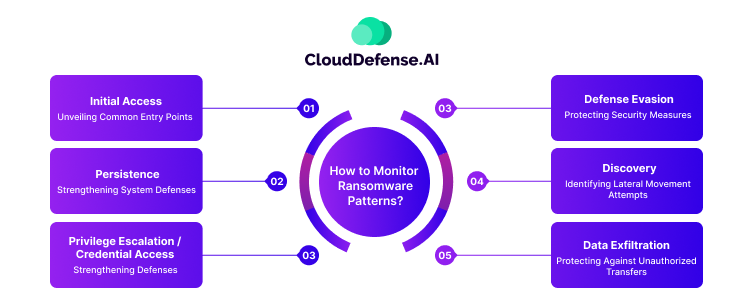
Ransomware attacks often follow a pattern, progressing through various stages. Monitoring these stages is crucial for early detection and prevention. Here’s a breakdown of tactics at each stage and how to detect them.
Initial Access: Unveiling Common Entry Points
Reports of Suspicious Emails: Despite lacking the notoriety of zero-day vulnerabilities, commonplace malicious emails remain a prevalent initial attack vector.
Detection: Organizations should prioritize security awareness training. Cultivating a culture encourages employees to report suspicious emails and mistakes without fear of punishment.
Suspicious RDP Connections: Exposed RDP, often dismissed, remains a leading point of compromise.
Detection: Refer to NCCGroup’s guide for capturing low-noise log events related to attempted and successful RDP sessions. Utilize PowerShell expert Kelvin Tegelaar’s script to document and log various installed remote access tools, enhancing detection capabilities.
Persistence: Strengthening System Defenses
Suspicious Scheduled Task Creation: Attackers commonly establish persistence through scheduled tasks.
Detection: Monitor and set alerts for Windows Event IDs 4698 and 4700. Make use of Kelvin Tegelaar’s PowerShell script for enhanced detection capabilities.
Unexpected Remote Access Software: Attackers increasingly deploy third-party software like AnyDesk, Atera, TeamViewer, and Splashtop.
Detection: Regularly monitor for the presence of these tools, especially if they aren’t part of standard usage. Employ Kelvin’s script, with modifications as suggested by Luke Whitlock for AnyDesk monitoring, to flag unexpected installations.
Privilege Escalation / Credential Access: Strengthening Defenses
Extracting Credentials from LSASS: Attackers commonly target the Windows Local Security Authority Subsystem (LSASS) for credential extraction.
Detection: Leverage Microsoft’s Attack Surface Reduction (ASR) rules, applicable on Windows 10 build 1709 or Windows Server build 1809 and higher. Utilize ASR rules for blocking various common malicious activities, as highlighted in Palantir’s security team post. Many Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools offer similar blocking and detection capabilities to safeguard against LSASS abuse.
Defense Evasion: Protecting Security Measures
Disabling / Uninstalling Antivirus: Attackers may attempt to evade detection by simply disabling or uninstalling antivirus and other security tools.
Detection: Utilize Kelvin Tegelaar’s script designed for detecting antivirus tampering. Leverage your Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) system to regularly alert you on the status of installed and running security tools, ensuring prompt identification of any tampering attempts.
Discovery: Identifying Lateral Movement Attempts
Unexpected Use of Port Scan and Network Discovery Tools: After establishing a beachhead, attackers explore the network for lateral movement opportunities, often utilizing built-in Windows utilities like nltest.exe, ipconfig, whoami, and ADFind. Port-scanning tools like Advanced IP Scanner are also common.
Detection: Set up monitoring and alerts if these tools aren’t part of regular operations. Implement automation rules to proactively block suspicious port scanners and reconnaissance tools, bolstering defenses against potential lateral movement.
Data Exfiltration: Protecting Against Unauthorized Transfers
Suspicious Outbound Connections and Traffic Spikes: To exert more control over victims, attackers increasingly exfiltrate data before encryption. Detecting data exfiltration involves monitoring indicators such as major spikes in outbound traffic, unexpected connections to public IP addresses, uncommonly used ports, high volumes of DNS queries, and suspicious file extensions (.rar, .7z, .zip, etc.).
Network monitoring and firewall rules are crucial, supported by insights from the “Exfiltration” section in MITRE ATT&CK.
Abuse of Built-in and Open Source File-Transfer Tools: Attackers exploit legitimate tools like Microsoft BITS, curl.exe, Rclone, and Mega for data exfiltration.
Detection: Block or monitor the use of these tools, considering their standard usage. For more nuanced detection, explore advanced methods such as detecting Rclone, Mega, and Rclone abuse and referencing MITRE ATT&CK ID T1197 for additional insights.
Cloud Forensic for Ransomware Investigation Checklist
Ransomware incidents demand a thorough investigation. The following checklist guides you through the crucial phases of using cloud forensics for ransomware investigation.
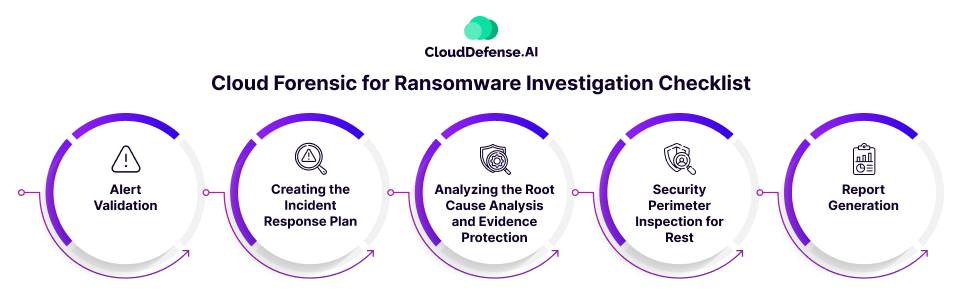
Alert Validation
Swiftly address SOC alerts, using accurate forensic tools for detailed analysis. Employ triage tools for simultaneous scans across endpoints and verify alerts from various sources, ensuring a comprehensive response to potential ransomware threats.
Creating the Incident Response Plan
Upon confirming a security breach through triage results, swiftly initiate the Incident Response Plan. Engage Cybersecurity service teams, encompassing Endpoint Security, Cloud, and Network. Isolate affected endpoints, devices, networks, and servers promptly.
Establish communication with the employee who triggered the attack. Collaborate with external teams, such as cybersecurity insurance providers and law enforcement, if necessary, to bolster the response to the ransomware incident.
Analyzing the Root Cause Analysis and Evidence Protection
Conduct a thorough root cause analysis to unveil the attack’s origin. Determine the extent of compromise and assess the type of data affected. Engage a forensics lab to address critical questions about the breach.
Preserve digital evidence meticulously with ransomware forensic tools, ensuring its security against tampering after a ransomware attack.
Security Perimeter Inspection for Rest
Swiftly restore networks to minimize downtime. Inspect malware attack traces to eliminate backdoors and Indicators of Compromise (IOCs). Thoroughly inspect and validate backups before initiating restoration. Update and secure all servers during the restoration process to fortify against potential ransomware threats.
Report Generation
Document the entire incident response process thoroughly. Create a comprehensive report outlining the attack, investigation steps, and outcomes. Utilize the report for debriefing sessions with the team, fostering a shared understanding.
Share the report across departments, ensuring clarity for all stakeholders. Conduct group meetings to explain the incident and reinforce prevention measures against future ransomware attacks.
What Is Data Visualization?
Data visualization in cloud security involves graphically representing detailed security data in cloud computing. Utilizing charts, graphs, dashboards, and maps, it offers a clear view of the security landscape. This helps in swift analysis, pattern recognition, and informed decision-making for security professionals and analysts.
The cloud is dynamic, with abundant data and threats always evolving. Visualization becomes essential to detail all security data on the cloud categorically. It empowers security teams to glean insights into network traffic, user behavior, vulnerabilities, and threat intelligence, facilitating anomaly detection and an understanding of the cloud security posture.
How Does Data Visualization in Cloud Forensics Help Prevent Ransomware Attacks?
Organizations collect a deluge of information daily, including IP data, server files, communication records, and more. Traditional cybersecurity methods struggle to keep up with evolving threats. Data visualization offers a solution, providing analysts with a holistic view of enterprise networks through graphs, charts, dashboards, or maps. Data visualization plays an important role in preventing cyber attacks by addressing key aspects of cloud security.
Strategic Data Organization
Data visualization offers a structured approach in the dynamic landscape of evolving data and cyber threats. Analysts benefit from organized reports and files, streamlining data interpretation and saving valuable time.
Advanced Threat Detection
Visualization tools, including comparative graphs, enable analysts to swiftly identify suspicious activity patterns. These tools enhance data readability, simplifying the analysis of complex information and aiding in detecting anomalies.
Expedited Decision-Making
Rapid threat detection translates into prompt decision-making. Data visualization allows security professionals to swiftly respond to potential breaches, such as unauthorized data sharing, mitigating risks effectively.
Synergy with Software Solutions
Data visualization complements cybersecurity solutions like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management). While automated tools detect recurring threats, visualization optimizes human analysis and decision-making, making data more accessible.
Collaborative Information Sharing
Visualizations democratize data access, fostering collaboration among analysts and integration into internal security systems. Interactive dashboards enable sharing with non-technical users and various company departments, promoting a holistic cybersecurity approach.
Accelerated Forensic Analysis
In the aftermath of a cyberattack, data visualization expedites in-house forensic analysis. Analysts can swiftly extract valuable insights, helping prevent future incidents, resolving vulnerability, and reinforcing threat management processes.
FAQ
Is the cloud safe from ransomware?
While no system is entirely immune, cloud platforms often have strong security measures, reducing ransomware risks. Regular updates, data encryption, and built-in security features enhance protection. However, users must implement best practices, including access controls and backups, to fortify cloud security.
How is cloud forensics done?
The cloud forensics process involves identifying, collecting, and preserving digital evidence in cloud environments. Using forensic analysis, investigators examine data sources, maintain a chain of custody, and document findings. The process ensures legal admissibility and helps respond to security incidents in cloud-based systems.
How can ransomware attacks be stopped?
Preventing ransomware requires strong cloud security measures: regular software updates, employment of strong security tools, backup of critical data, user education on phishing awareness, and implementation of network segmentation. A comprehensive approach minimizes vulnerabilities and strengthens defenses against ransomware attacks.
Conclusion
Cloud forensics and data visualization are integral components in the fight against ransomware attacks. Cloud forensics equips organizations to investigate and analyze incidents within cloud environments, while data visualization provides analysts with a strategic and efficient means to comprehend vast amounts of data.
Together, these tools enhance threat detection, speed up decision-making, and enable collaborative cloud security efforts. By adopting these practices and following a comprehensive ransomware investigation checklist, organizations can strengthen their defenses and respond effectively to evolving cyber threats.
Read more about ransomware attacks in our article, “How to Recover and Prevent Ransomware Attacks: Step By Step”.







