Agent-based and agentless approaches represent two core methods for monitoring and securing systems. To briefly explain the differences between these two approaches:
- Agent-based security involves deploying software agents on each device to perform tasks such as scanning, patching, and monitoring.
- Agentless security uses APIs to interact directly with systems, bypassing the need for software installation.
Understanding both approaches can help create a security strategy that balances performance, scalability, and operational efficiency.
Read on to understand the differences between them and decide which approach would be the best for your company.
What Is Agent-Based Security?
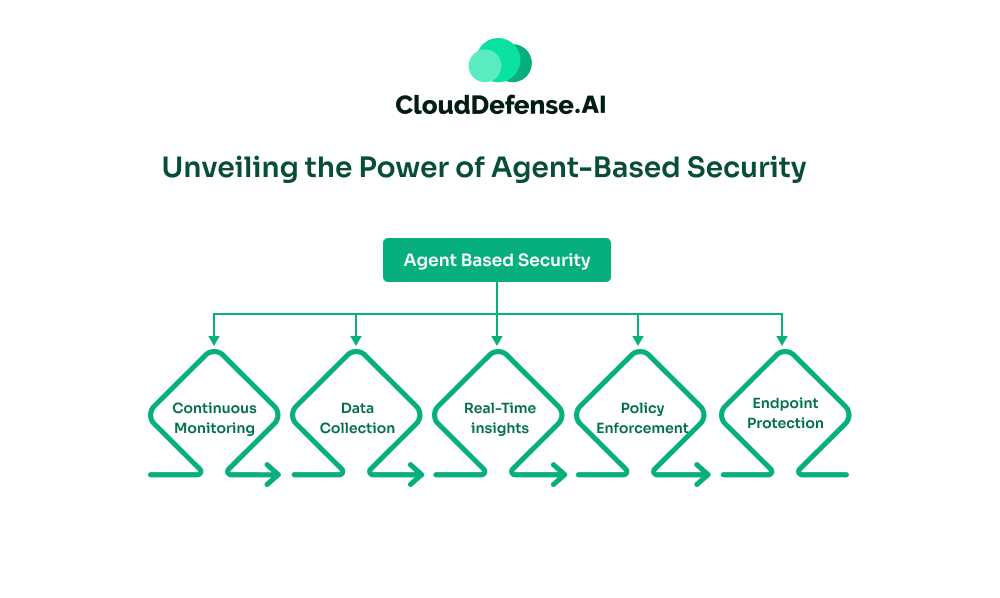
Agent-based security involves deploying specialized software components, known as agents, onto individual endpoints within a network. These agents continuously monitor their host devices, collecting data related to security, patch status, and vulnerabilities. This data is then transmitted, either automatically or on demand, to a centralized management system for analysis and action.
Because agents operate directly on the devices, they provide real-time insights and can independently enforce security policies, such as applying patches, managing configurations, restarting systems, or even acting as firewalls to manage network connections. This approach ensures in-depth, device-specific protection for endpoints across an organization.
Advantages of Agent-Based Security
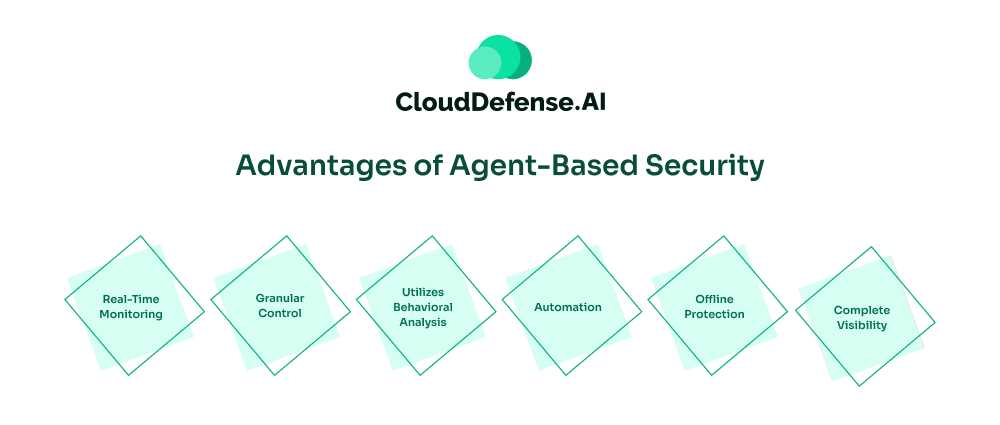
Agent-based security has several advantages that make it entirely suitable for a modern organization operating in the cloud;
- Real-Time Monitoring: Agent-based security solutions can continuously monitor a network’s endpoints and respond to threats when they detect them. With agent-based vulnerability scanners, organizations can detect and remediate threats proactively.
- Granular Control: Security agents are present at each endpoint in a network, allowing the security team to customize security controls and policies and provide tailored protection according to requirements. Thus, the organization will have granular control over all the endpoints.
- Utilizes Behavioral Analysis: Agent-based solutions are also known to leverage behavioral analysis paired with machine learning to help organizations identify issues in endpoint behavior. This is beneficial for detecting advanced persistent threats and zero-day threats.
- Automation: Agent-based solutions allow you to enforce security policies and controls at each endpoint and automate them. You can easily automate the process directly on the devices. Automation also ensures that all network endpoints adhere to regulatory standards and configurations.
- Offline Protection: An agent-based solution’s unique benefit is that it can provide offline protection when the endpoint isn’t connected to the Internet. This is incredibly beneficial for networks with devices that frequently operate in offline mode.
- Complete Visibility: When an organization utilizes an agent-based solution, it is likely to have greater visibility into the security posture of each endpoint. Security teams can quickly learn about each endpoint’s patch status, identify vulnerabilities, and analyze malicious behaviors.
Challenges of Agent-Based Security
Here are some disadvantages of agent-based security;
- Resource Intensive: Agent-based security is highly resource-intensive and consumes a lot of resources for performing routine tasks. Less powerful devices often face low-end point performance due to this issue.
- Requires Individual Installation: Organizations have to install agent-based security at every endpoint of each network, which can be a daunting task. For complex networks, it can also be time-consuming and less efficient.
- Costly: Agent-based security is slightly expensive to deploy as organizations have to pay a subscription fee for each security agent. Moreover, the deployment and management of security agents also add to the operational cost.
- Scalability Challenge: It is not easy to scale agent-based security as the organization grows and starts to have more complex networks. It will be highly resource-intensive and costly for organizations to add and manage agents for new devices and offices.
What Is Agentless Security?
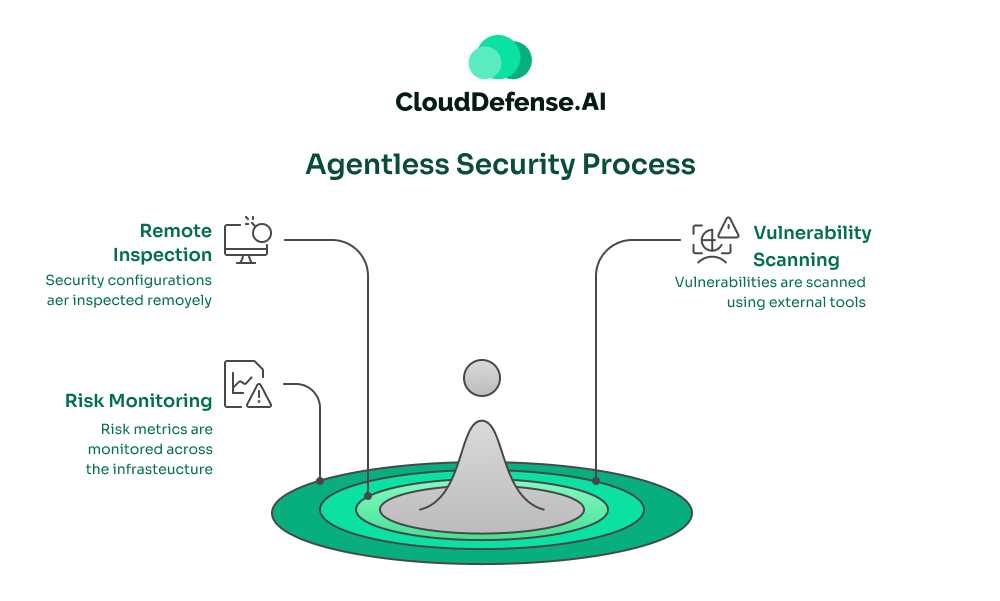
Agentless security eliminates the need to install agents on individual devices, offering a streamlined approach to monitoring and protecting systems. Instead of relying on endpoint software, agentless systems use external tools or APIs to remotely inspect security configurations, perform vulnerability scans, and monitor risk metrics across the infrastructure.
Unlike agent-based security, which relies on a pull communication model, agentless security operates using a push communication style. Here, data is sent periodically from the monitored systems to a central management system for analysis and action. This flexibility makes agentless security particularly effective for baseline monitoring and centralized management.
Agentless systems often use tools installed on other layers, such as the network layer, to capture risk metrics and identify vulnerabilities. These systems allow for seamless scanning and protection without direct access to the host, making them suitable for environments where installing agents is impractical or undesirable.
Advantages of Agentless Security
Agentless security has become a popular approach that many modern organizations take, and it is mainly due to the benefits it has on offer;
- Easy Deployment: One of the primary reasons agentless security is widely preferred by many is its easy deployment without the installation of security agents. This helps save a lot of time and reduces the complexity of deployment.
- Lightweight Solution: Agentless security doesn’t run on endpoints, which prevents them from accessing significant amounts of resources, thus making it a lightweight solution for cloud networks. They depend upon the infrastructure and hardware of the device so they run seamlessly without affecting productivity.
- Highly Compatible: Agentless security is widely compatible with a lot of devices and operating systems so that it can be used in all kinds of cloud environments. Since it doesn’t need agents on endpoints, this solution can be something other than specifically compatible.
- Lower Cost: With easy management, no agent deployment at endpoints, and minimal resource requirements, agentless security solutions have lower operation costs. Moreover, the licensing cost is also lower than that of agent-based security.
- High Scalability: High scalability is one of the vital benefits that make it a go-to choice for most modern organizations, as the solution can scale with growing networks and devices. As the solution can be managed through a central platform, it eases the scalability.
- Centralized Control: Agentless security solution offers centralized management and control through which the security team can enforce, configure, and manage security policies. It helps simplify the security and allows teams to have better visibility into the security posture.
Disadvantages of Agentless Security
Like agent-based security, Agentless security also has some cons, and they are;
- Lacks Real-Time Security: One of the most significant drawbacks of agentless endpoint security is that it doesn’t provide real-time protection like agent-based security, as it mainly relies on APIs and log files for risk identification. When it comes to agent vs agentless monitoring, agentless lacks in proactively securing the network.
- Lower Granularity: Agentless endpoint security focuses more on offering precise control over security settings rather than fine-grained control and policy deployment on endpoints. This limitation in the granularity reduces the level of details an agentless security can collect.
- Dependency on Network: It is highly dependent on the availability of network connectivity on the device, and if not connected to the internet or existing network of the organization, it would leave the network vulnerable to attack. This also leads to the risk of high downtime when it is not connected.
- Less Effective Against Network-Based Attack: Agentless device security relies on the network when it comes to protection, so it might not be effective for addressing risks originating within the network.
What Is the Difference Between Agent-Based and Agentless Security?
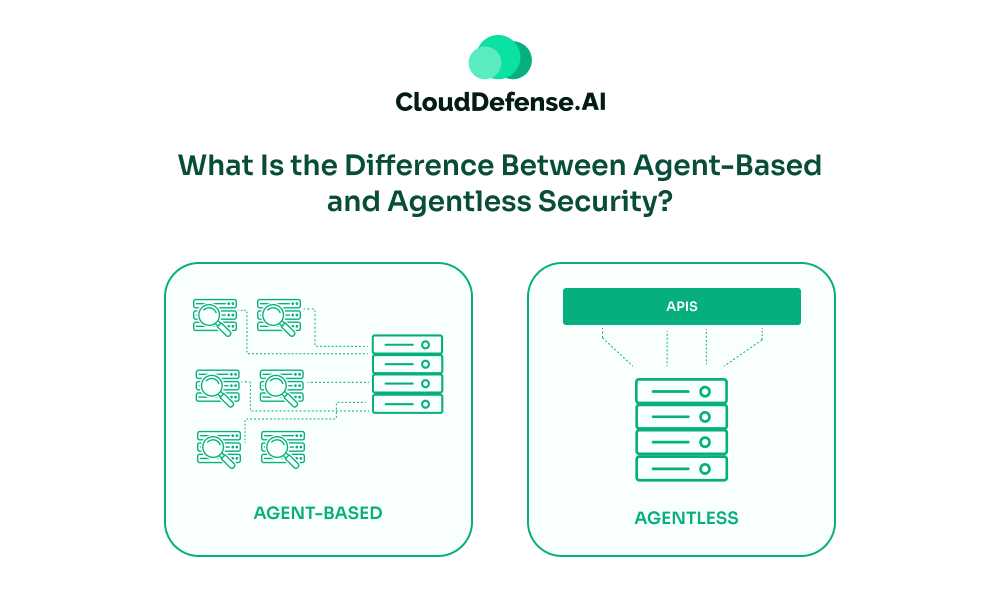
Agent-based and agentless security are two distinctive security approaches that both have the same aim but with a different focus. They are pretty different from each other in various aspects and have their own set of benefits and limitations.
The following chart highlights the fundamental differences between these two approaches:
| Aspect | Agentless Security | Agent-Based Security |
| Deployment | Straightforward to deploy as it requires no installation or configuration on endpoints. | Requires installation of security agents on individual endpoints. |
| Resource Usage | Minimal, as it operates using network, device, and firewall resources without affecting endpoints. | High, as it relies on endpoint resources like CPU, RAM, and storage. |
| Compatibility | Broadly compatible across multiple devices and operating systems. | Compatible with various devices, but may require specific agents for certain endpoints. |
| Granularity | Limited endpoint control; manages security at the network level. | Fine-grained endpoint control with proactive security capabilities. |
| Visibility | Provides network-level visibility with centralized monitoring and scanning. | Offers endpoint-level visibility, with agents performing scans based on predefined policies. |
| Network Dependency | Fully dependent on network connectivity; downtime during outages can impact operations. | Can operate offline, making it suitable for distributed networks. |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Does not offer real-time monitoring; instead, uses APIs and log files for insights. | Provides real-time monitoring for immediate threat detection and response. |
| Environment Compatibility | Highly effective for cloud environments, particularly multi-cloud setups. | Compatible with hybrid, on-premise, and cloud environments, but can be challenging to deploy in complex systems. |
| Usage | Primarily used for patch management and asset monitoring in networks. | Commonly used for Linux-based patch management and application control at endpoints. |
| Mitigating Network Attacks | Less effective for mitigating network-based attacks; focuses on external threats. | Highly effective in addressing both network-based and insider threats. |
| Complexity in Setup | Requires complex configurations across networks. | Configuration complexity depends on the number of endpoints and network architecture. |
Both agent-based and agentless security have their unique strengths and limitations. Agentless solutions are ideal for organizations seeking simplicity and scalability in cloud environments, while agent-based solutions excel in environments requiring detailed endpoint control and real-time monitoring.
Choosing the right approach depends on your organization’s specific security requirements, resources, and infrastructure.
Agent-Based or Agentless Security: Which Solution is Better?
Both agent-based and agentless security solutions are effective in modern IT environments, but the best choice depends on your organization’s infrastructure and specific requirements. Here’s a breakdown to help you decide:
Agent-Based Security
Agent-based security is ideal for networks with relatively standard configurations and systems with simple workloads. Its ability to enforce security policies, provide endpoint-level control, and perform real-time monitoring makes it a powerful option for organizations prioritizing security granularity and runtime protection.
However, it does require manual configuration for each endpoint, which can increase deployment time and effort.
Agentless Security
Agentless security shines in environments with complex and dynamic workloads, especially those relying on APIs. Its ease of deployment, lower cost of ownership, and minimal resource usage make it a practical choice for large-scale organizations with diverse infrastructures.
Agentless solutions are particularly effective in cloud-centric environments where scalability and rapid deployment are essential.
Conclusion: Go Agentless with CloudDefense.AI
If your organization values robust endpoint protection, offline functionality, and granular control, agent-based security is the way to go. On the other hand, if scalability, easy deployment, and seamless integration across complex systems are priorities, agentless security might be a better fit.
For organizations adopting agentless solutions, CloudDefense.AI is a leading agentless provider offering top-tier protection with minimal setup and maximum efficiency. However, agent-based security continues to play a critical role in industries requiring deeper insights, advanced security controls, and real-time threat mitigation.
Ultimately, the right solution will depend on your organization’s existing network infrastructure, scalability requirements, deployment timelines, and data collection needs. Both approaches have their merits, and a hybrid strategy could even leverage the strengths of both to achieve optimal security.







