Imagine waking up one day to find a cryptic message in your system demanding you pay a ransom to regain your data. All that sensitive information is in jeopardy. Data that determines the fate of your business.
Does this description sound familiar? You may recognize this ransomware attack scenario — a rampant cybercrime that can be devastating for any company. Most enterprises do not know how to recover and prevent ransomware attacks. This usually results in the threat actors successfully extorting money and moving on to yet another hapless victim.
A thorough read of this article should empower you with an understanding of ransomware attacks and how to prevent and recover from such without succumbing to extortion
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software, commonly known as malware, designed to block access to a computer system or files until money is paid. It is a form of cyber extortion where the attacker encrypts the victim’s files or locks them out of their system and then demands payment.
Payments are often required to be made with cryptocurrency for anonymity, untraceable transactions, and to evade traditional financial systems. In exchange, the threat actors provide the decryption key to the victim so that they can secure their system or data.
How Big of a Threat Is Ransomware?
Ransomware has become a significant problem in the cyber world. Its impact has substantially affected individuals, businesses, and even critical infrastructure. The financial motivation behind ransomware makes it more appealing for cybercriminals to use this method of hijacking data for easy money. The tactic of double extortion, where attackers encrypt files and threaten to release sensitive data, has become more common.
Merely mentioning supply chain attacks and the ability of ransomware to cripple entire networks downplays its potential for widespread disruption of business. Despite increased awareness and cybersecurity efforts, new, more adapted ransomware continues to challenge defenses. Mitigating this threat requires a well-practiced approach, including strong cybersecurity measures, regular training to enhance user awareness, and proactive strategies for preventing and responding to attacks.
Ransomware Statistics
All cyber attackers prefer ransomware to earn some quick cash, as most companies affected by it end up paying the threat actors. According to Sophos, in 2023, the average ransom asked by threat actors is $1.54 Million. This is almost double the average of last year, which was $800K. In the past 5 years, ransomware attacks have grown at a rate of 13%, with the average cost of each incident being $1.85 million.
The most shocking data of all is the fact that there were about half a billion ransomware attacks back in 2022. Statistics like these are alarming and demand more attention to mitigate this epidemic.
The alarming surge in ransomware incidents, as evidenced by the FBI’s reported cases in 2022, highlights the escalating threat to businesses. The projection from Cybersecurity Ventures foretelling a ransomware attack every other second by 2031 underscores the urgency for robust cybersecurity measures.
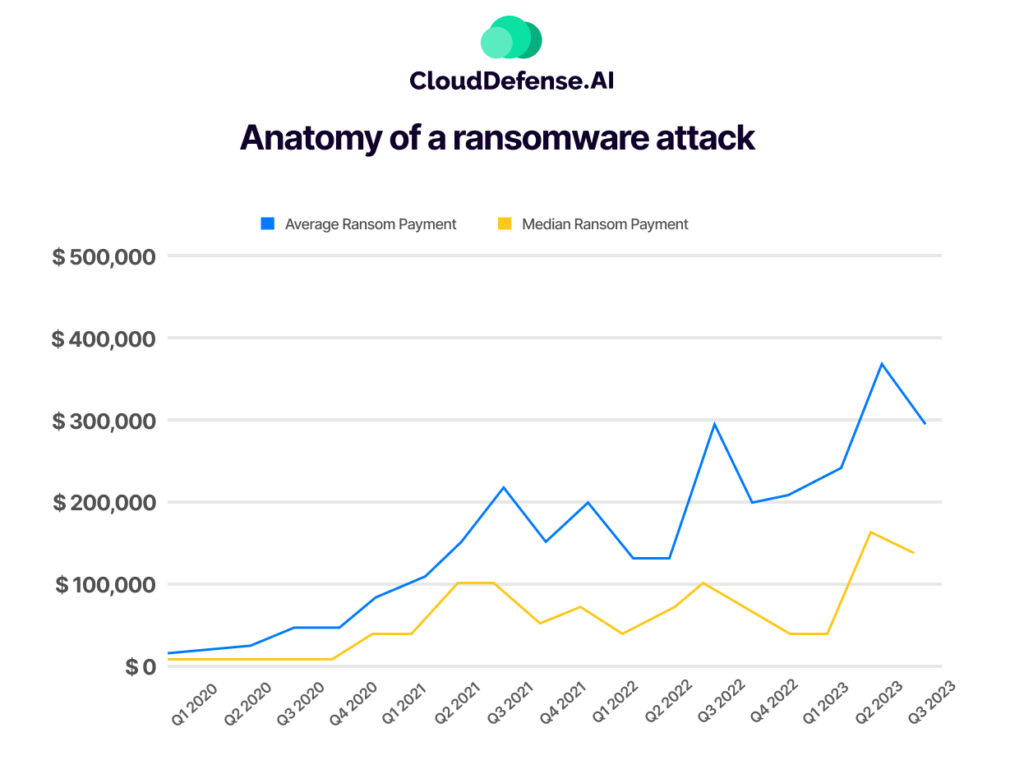
With an anticipated $265 billion in damages, the financial toll of these attacks is staggering. Equally concerning is the rising scale of ransom payments, with the average amount reaching $327,883 in Q1 2023, reflecting a 55% increase from the previous year. Disturbingly, almost half of these attacks now carry initial demands exceeding $1 million.
How Does a Ransomware Work?
As previously stated, ransomware is a type of malicious software designed to block access to a computer system or files until a sum of money is paid. Here’s a general overview of how ransomware typically works, though it’s important to note that the specifics can vary between different types of ransomware:
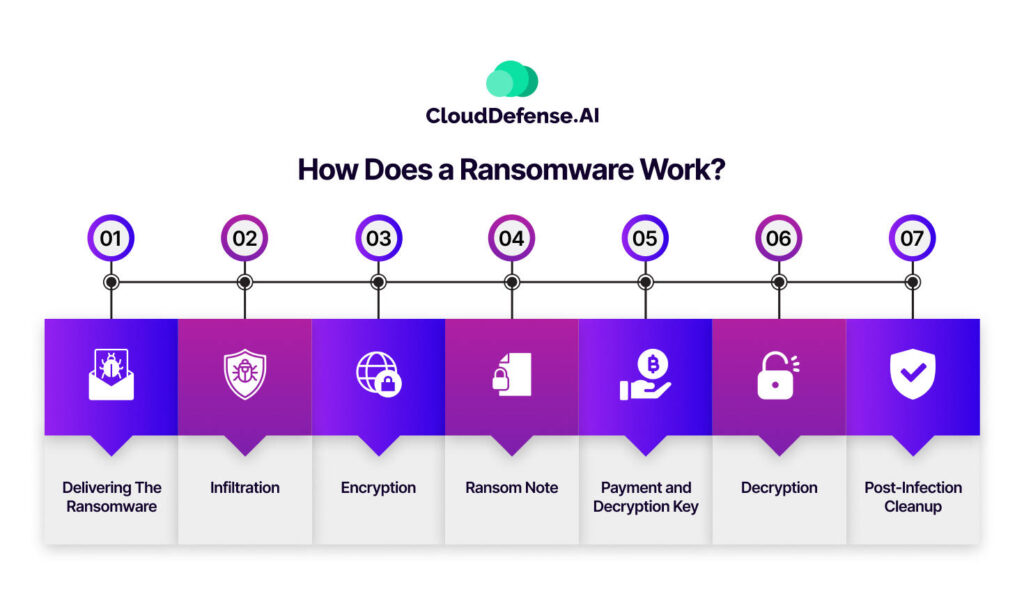
Delivering Ransomware
Ransomware is often delivered through phishing emails, malicious websites, or infected attachments. The goal is to trick the user into executing the malware unknowingly.
Infiltration
Once the malware is executed, it begins to infiltrate the system. Some ransomware strains use vulnerabilities in software to gain access, while others rely on social engineering to trick users into granting them access.
Encryption
The ransomware then starts encrypting files on the infected system, making them inaccessible to the user. Encryption is the process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. The victim typically receives a ransom note explaining that their files will only be decrypted if they pay a specified amount of money, usually in cryptocurrency.
Ransom Note
The ransomware displays the ransom note on the victim’s screen. This note contains instructions on how to pay the ransom, usually in Bitcoin or another cryptocurrency that is difficult to trace. It may also include a threat to permanently delete the files if the ransom is not paid within a certain timeframe.
Payment and Decryption Key
If the victim decides to pay the ransom, they follow the instructions provided in the ransom note to make the payment. Once the payment is received, the cybercriminals are expected to send the decryption key to the victim, allowing them to unlock their files.
Decryption
With the decryption key, the victim can unlock their files and regain access to their system. However, paying the ransom does not guarantee that the cybercriminals will provide the decryption key, and it encourages further criminal activity.
Post-Infection Cleanup
After the files are decrypted, the victim must clean their system thoroughly to remove the ransomware and any other malware that might have been installed. This may involve running antivirus and anti-malware tools and ensuring that the system is fully patched and updated.
It’s crucial to note that paying the ransom is generally discouraged, as it does not guarantee the recovery of files, and it condones criminal activities. Prevention through regular backups, keeping software updated, using robust security practices, and being cautious with email and internet usage are key measures to protect against ransomware attacks.
What Are the 10 Steps You Should Follow After a Ransomware Attack Occurs?
Experiencing a ransomware attack can be a stressful and challenging situation. Here are ten steps you should consider taking after a ransomware attack occurs:
1. Do Not Panic
We know this can be difficult, especially when you wake up and find all your sensitive files encrypted. However, to tackle the situation more effectively, it is crucial that you keep your calm.
Most victims feel they should pay the ransom to help end the nightmare. However, there are potential options to deal with the situation without having to pay the ransom at all
2. Document the Ransomware Note
Document the whole scenario. This can help you take legal action later and also identify the ransomware strain. Take pictures of the ransom note or any other interaction with the hacker. You can use a secondary device or even take a screenshot with the affected device. Keeping evidence helps expedite the process.
3. Isolate All Affected Systems
You should immediately isolate the device the moment you notice your system has been compromised. Ransomware spreads itself throughout the network to all devices connected to it. Isolation helps reduce the affected surface.
4. Identify The Ransomware
Identifying the ransomware can help you to deal with it more efficiently. You must know the strain of the ransomware to find the relevant decryption key that you can employ to unlock your files. Some free services that you can use from the internet are ID Ransomware and Emsisoft’s ransomware detection tool.
These sites will require you to upload a sample of the encrypted file, a copy of the ransomware note, and any contact information of the attacker. The ID site will analyze this data to deduce the ransomware strain.
5. Search for Decryption Tools
We have good news. Multiple decryption tools on the internet can help crack ransomware. Once you have identified the ransomware variant, you can plug it into one of the decryption sites. A popular option is No More Ransom, a decryption site that adds new keys regularly. Decryption tools are your best bet to avoid paying a ransom.
6. Disable All Maintenance Operations
Switch off any automated maintenance operations you might have running on the system. Automated maintenance eliminates any temporary logs and files that can be used for forensic attack analysis.
7. Disable Backups
Powerful ransomware can also affect your backups if the storage location is connected to the system. Immediately disconnect backups from the network to safeguard them. Keep the backups isolated until you have rectified the entire situation.
8. Reset All Your Credentials
Credentials are often saved on a system statically. If your system is affected by ransomware, consider resetting all your account credentials using a secondary device. Once you have dealt with the ransomware, change your credentials again. Stolen credentials can be much more harmful than ransomware attacks.
9. Report To Authorities
Ransomware attacks are a criminal offense and must be reported to law enforcement agencies. Every country has computer incidents and cybercrime units that might help decrypt your compromised files. Even if they aren’t successful, they can still help to protect others from getting attacked.
10. Pay Ransom As a Last Resort
This is your last option and should only be considered when no other method works. You can potentially survive without paying the ransom if all tour-sensitive files have been backed up somewhere else. You can also decrypt the files with a decryption tool. Ultimately, you need to conduct a financial assessment of your options. Is it cheaper to pay the ransom or lose your files?
Read on as we help you uncover how you can recover and prevent ransomware attacks to protect yourself from future threats.
Recover from a Ransomware Attack
Once you have successfully dealt with the ransomware attack, it is time to forge ahead and recover.
Recover the Data
Keeping backups of your data is paramount to recovering from any ransomware attacks. Always ensure your backups are kept in a safe and secure storage location. If you were delayed in disconnecting your backups when the attack initiated, you should ensure your backup is ransomware-free before using it.
You can still recover the data even if the backup is affected by ransomware using professional help. Professional intervention can be expensive. You must compare the cost of the recovery with the financial damage you might incur if the data is lost.
Create a Report
Businesses should be transparent with their customers. Immediately after a ransomware attack, you should create an incident report. Reports can not only be used to inform to your customers but are also required by insurance companies to validate your claims.
Prevent Future Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks can be prevented by increasing vigilance and proactively approaching cybersecurity. To secure themselves against future ransomware attacks, organizations must adopt a well-planned cybersecurity strategy. Regular data backups, stored securely offline, act as a crucial line of defense, ensuring that recovery is possible without succumbing to ransom demands.
Consistent software updates, including operating systems and antivirus tools, are essential to patch known vulnerabilities that cybercriminals exploit. Deploying reputable antivirus and anti-ransomware software, updated in real-time, provides additional protection from ransomware attacks.
Employee education plays a pivotal role. Training staff to recognize phishing attempts and suspicious links minimizes the risk of a ransomware breach. Implementing network segmentation isolates critical systems, hindering the lateral movement of attackers. Stringent access controls, limiting user permissions to essential functions, further mitigate potential damage.
Advanced email security solutions filter out phishing attempts and malicious attachments while enabling multi-factor authentication bolsters user account security. A well-defined incident response plan guides organizations in the event of an attack, emphasizing clear communication and coordination with law enforcement.
Routine security audits, both internal and external, identify and address vulnerabilities, while robust patch management processes ensure that systems remain up to date. Collaboration and information-sharing within cybersecurity communities enhance threat intelligence, allowing organizations to stay abreast of evolving risks.
Recognizing the dynamic nature of cyber threats, this comprehensive approach, including technical defenses, employee training, and strategic planning, is essential for safeguarding against the persistent menace of ransomware.
FAQs
How does ransomware spread?
Ransomware typically spreads through phishing emails, malicious attachments, or compromised websites. Once a user interacts with infected content, the ransomware encrypts files and may propagate within networks, exploiting vulnerabilities to maximize its impact.
Should I pay the ransom?
The general advice from cybersecurity experts and law enforcement agencies is to not pay the ransom. Paying does not guarantee that you’ll regain access to your data, and it further incentivizes criminal activities. Instead, report the incident to law enforcement, isolate affected systems, and consider restoring data from backups.
Is there a way to defeat ransomware?
No foolproof method guarantees immunity from ransomware, but regular backups, software updates, robust security measures, user training, and a well-prepared incident response plan help minimize the risk and impact of attacks.
Can you survive a ransomware attack?
Surviving a ransomware attack involves proactive measures. Regular backups, offline storage, security software, user training, network segmentation, access controls, and an incident response plan can help minimize damage and facilitate recovery without succumbing to ransom demands.
Conclusion
Recovering from a ransomware attack demands a strategic approach. By following the outlined steps for recover and prevent ransomware attacks, including regular backups, employee training, and advanced security measures, organizations can boost their defenses.
Vigilance, adaptability, and a commitment to cybersecurity best practices are critical. As the internet evolves, navigating and mitigating the impact of recent ransomware attacks becomes a necessity and a cornerstone of resilient and secure operations in our cyber world.







