As more people opt for cloud-native infrastructure, concerns rise about the security challenges companies face while ensuring data security and the safety of other resources. Cybersecurity ventures have predicted that the world will store 200 zettabytes of its data in the cloud over the next two years.
Looking at the current state of companies struggling to secure their infrastructure, one can only imagine the amount of damage threat actors could cause in the future. The majority of data can remain unprotected if necessary steps are not taken. Safeguarding your digital assets should be a priority. That is where Cloud Infrastructure Security comes in.
A quick read through this comprehensive guide will help you understand cloud infrastructure security in cloud computing, providing insights, best practices, and essential considerations to empower your business to fortify its virtual landscape against potential vulnerabilities.
What is Cloud Infrastructure Security?
Cloud Infrastructure Security (CIS) refers to the set of practices, technologies, and policies implemented to protect the underlying components and data within cloud computing environments. As businesses increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud for enhanced scalability, cost-effectiveness, and better performance, securing their virtual infrastructure becomes necessary.
Cloud infrastructure services include the hardware, software, networks, and storage that collectively form the foundation of cloud services. Security for this aspect involves protecting these elements from potential threats, unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber risks. Critical considerations in cloud infrastructure security include data encryption, identity and access management, network security, and compliance with industry regulations.
How Does Cloud Infrastructure Security Work?
Cloud infrastructure security operates through a layered defense strategy. Data is protected through strong encryption, ensuring confidentiality during transmission and storage. Advanced identity and access management controls regulate user permissions, preventing unauthorized access.
Continuous monitoring employs sophisticated tools to detect anomalies and potential threats in real time, enabling swift response. Automated security updates and patch management further bolster defenses, ensuring that vulnerabilities are promptly addressed.
Cloud security follows a shared responsibility model, with cloud providers securing the underlying infrastructure while users are responsible for safeguarding their data. This collaborative approach leverages the expertise of both parties, creating a comprehensive defense against unauthorized access, data breaches, and evolving cyber threats in the dynamic scope of cloud computing.
Types of Cloud and How to Secure Them
Three primary cloud infrastructure models are available to companies. Each requires a different set of approaches to cloud security. Let’s explore them in detail:
Public Cloud
The public cloud is hosted by a service provider that controls the underlying cloud infrastructure. Cloud service providers require their customers to follow a shared responsibility model. This condition has the service provider ensuring the security of the underlying infrastructure, and the customer is required to protect the resources hosted on the cloud.
Organizations using public clouds need to worry about securing their data through data encryption methods, their workload through other security tools, and staying compliant with industry standards. Cloud misconfigurations must also be averted, which can be maintained by securing services from Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) vendors.
Private Cloud
Private clouds are hosted on-premise and are considered much more secure than public clouds. By using private clouds, organizations maintain a higher level of control over all the underlying stacks of a cloud. Since private clouds are kept off the internet, this also makes it much easier to secure them.
However, private clouds still need some protection, with unauthorized access attempts being a probable threat. Security measures such as access controls, isolation of virtual machines (VMs) and other components, and cloud-native solid monitoring tools for increased visibility can effectively reduce any vulnerabilities that might be hiding.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid clouds use a mix of both private and public cloud infrastructure. Using different cloud models requires different approaches to secure each one, which we have already discussed. However, the best security approach for hybrid clouds is to create a single cloud security framework to protect your models. This will greatly reduce inefficiencies in your system.
7 Key Components of Cloud Infrastructure You Need to Secure
Several components in a cloud infrastructure make up the entirety of it. We’ll explain some of the cloud infrastructure components briefly below:
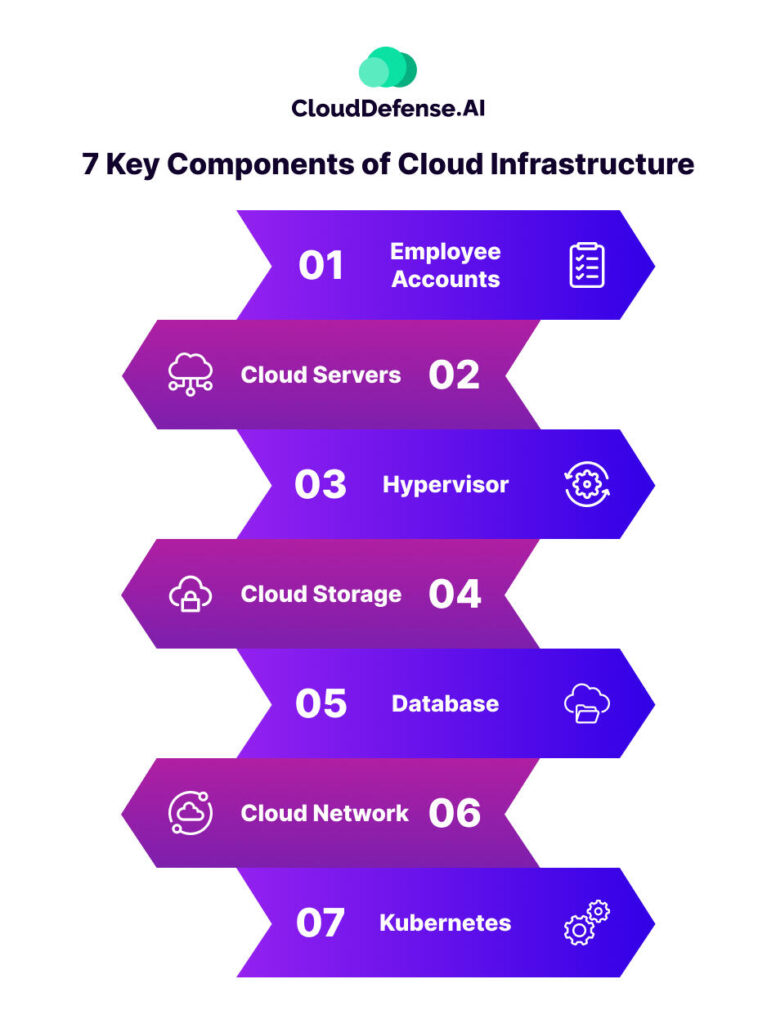
Employee Accounts
Accounts are created on a cloud to assist with a company’s services. Employee accounts often have privileges that determine how much infrastructure they can access. A compromised account can provide access to a cyber attacker, creating mayhem for a company.
Cloud Servers
The cloud may seem like a digitally constructed piece of technology. However, there are physical servers in the background that help to host these cloud services. A vulnerability in these servers can potentially lead to all companies employing cloud services being affected. Regular security audits and quick application of security patches are instrumental in fortifying cloud servers against cyber threats.
Hypervisor
A hypervisor is software that enables multiple operating systems to run on a single physical machine by managing VMs. Cloud systems run on hypervisors, which makes it essential to secure them. To secure a hypervisor, regularly update and patch the hypervisor software and implement network segmentation to isolate VMs. Utilise hardware-assisted virtualization and ensure secure boot processes.
Cloud Storage
Data on a cloud is stored in distributed physical servers. Virtualization is applied through containers to help segregate storage from the physical servers. This allows companies to use the storage options from any location with a good internet connection. Looking at the easy accessibility of cloud storage options, it is essential to maintain strong data protection methods to preserve its security.
Database
Cloud infrastructures contain databases for storing data, just like physical infrastructures. A compromised database can result in a major data breach. Implementing strong data encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments are essential to shield these databases from malicious exploits, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of critical business data.
Cloud Network
Different cloud components are linked together using virtual private networks. It is critical to secure private networks to ward off any potential breaches. This includes network segmentation, intrusion detection systems, and continuous monitoring to swiftly identify and neutralize any unauthorized access attempts, guaranteeing the confidentiality and integrity of data traversing the cloud network.
Kubernetes
Kubernetes are open-source components that help deploy, manage, and scale containerized applications. However, on the cloud, separating Kubernetes clusters from other layers can be a challenge. Each layer is built on top of another layer. Each needs to be secured to have a safe cloud infrastructure for your company.
Benefits of Cloud Infrastructure Security
Cloud Infrastructure Security brings you tons of benefits. We have listed some of them below:
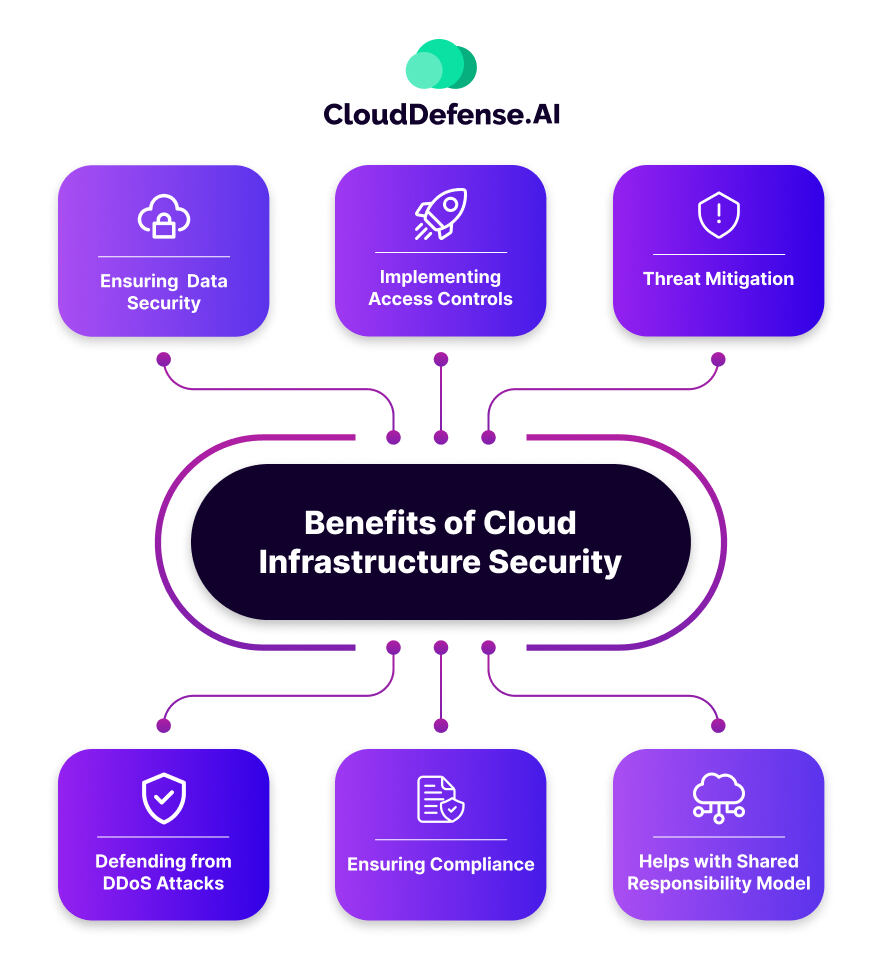
Ensuring Data Security
CIS contributes to data security by implementing strong encryption methods for data in transit and at rest. This solution protects sensitive information and prohibits intruders from using the data even if they manage to access it.
Implementing Access Controls
Cloud security solutions provide Identity Access Management (IAM) features, allowing organizations to control and monitor resource access. This ensures that only authorized individuals or systems can interact with sensitive data and applications.
Threat Mitigation
Identifying threats and mitigating them is essential to protect your cloud infrastructure. Most cloud security services have advanced threat detection tools. These systems continuously monitor for suspicious activities, potential vulnerabilities, and known threats, enabling timely response and mitigation.
Defending from DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are carried out to bring the system to a standstill and make it more vulnerable. DDoS protection measures are available in CIS to prevent malicious attempts from overwhelming systems or networks. This ensures the availability and performance of cloud-based applications.
Ensuring Compliance
Compliance frameworks such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, etc., lay down many regulatory requirements to ensure data security in organizations. Cloud infrastructure security solutions assist organizations in achieving and maintaining compliance with relevant regulations, reducing the risk of legal and financial consequences in the future.
Helps with Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud Service Providers (CSP) require their clients to follow a shared responsibility model where the latter is responsible for ensuring data security. Cloud infrastructure security excels in supporting that.
5 Major Security Threats to Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud Infrastructures have to face constant security threats. We have listed five of them below for you to understand:
- Insecure API: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are integral to cloud services, but insecure API implementations can expose vulnerabilities. According to Gartner, APIs are targeted the most to gain access to enterprise data in recent times. If APIs lack proper authentication, encryption, or validation mechanisms, they become potential entry points for attackers to manipulate or compromise the integrity of data and applications.
- Cloud Misconfigurations: Misconfigurations in cloud security settings can lead to serious vulnerabilities. This includes poorly configured storage permissions, network security group rules, or improperly set encryption protocols. Cybercriminals often exploit these misconfigurations to gain unauthorized access, steal data, or launch attacks within the cloud environment.
- Unauthorized Access: Unauthorized access is the act of using compromised credentials to gain entry to cloud resources without proper authorization. Unauthorized access often result in other threats to the system.
- Internal Threat: Internal threats to companies are present within an organization and may include malicious insiders, human error, and compromised accounts. In 2020, Goldstein stated that Insider threats cause 60% of data breaches. This type of threat might occur intentionally by employees with malicious intent or unintentionally due to employees’ negligence.
- Data Breach: Data breaches pose the highest threat to cloud infrastructures, where sensitive information may be exposed to cyber attackers. Most threats to a system have a common goal of stealing sensitive data from companies, as that is the most valuable asset for a company. In October, about 114 publicly disclosed data breaches worldwide amounted to a loss of 867,072,315 data records.
Best Practices for Protecting Cloud Infrastructure
Here are some cloud infrastructure security best practices to help you achieve top-notch security for your cloud infrastructure:
Understanding the Shared Responsibility Model
We have already mentioned how CSPs do not provide security for your resources and data on the cloud. Before deploying your security controls, it is best to evaluate your CSP. This will help you understand what measures you need to take to ensure complete cloud infrastructure security.
Training Employees
Mitigate internal threats by training employees. Emphasize best practices, like secure password management and recognition of phishing attempts. Provide education on data protection and regular security updates to reduce internal threats, fostering a culture of awareness and safeguarding against potential risks in cloud environments.
Enforcing Security Policies Across the Company
Create security policies that require strict adherence to security of best practices in your company. Guidelines like these help maintain a culture of responsibility toward the integrity of the cloud infrastructure.
Carry Out Routine Security Audits
Routine security audits and penetration testing help to ensure that your cloud infrastructure security measures are on par with industry standards. Consider carrying out these tests on your system, as they are a great way to determine where to upgrade to boost your defenses.
Consider Securing Services from a CNAPP Vendor
Ensuring cyber security around the clock can be stressful. You can always choose a Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) to reduce worry about security and allow you to concentrate on improving your services.
CNAPP solutions provide advanced threat detection, secure development, and runtime protection for cloud-native applications. Amidst numerous options, CloudDefense.AI stands out, leading the market with its distinctive trio of features: Hacker’s View™, Noise Reduction, and Code to Cloud.
FAQs
Here are a few queries that people have regarding cloud infrastructure security:
What is the primary goal of Cloud Infrastructure Security?
The primary goal of cloud infrastructure security is to minimize any threats it may face, allowing your company to function better and offer its services more efficiently.
What role does encryption play in cloud security?
Encryption helps prevent data from being accessed by any unauthorized individual. In cloud security, data can be encrypted at both rest and in transit.
How often should organizations conduct security audits in their cloud infrastructure?
On average, companies worldwide conduct biannual or annual security audits on their cloud infrastructure. However, for better results and improved security, it is best to conduct at least one security audit every quarter of the year.
Conclusion
As the world accelerates towards migration to the cloud, the importance of prioritizing Cloud Infrastructure Security cannot be overstated. Organizations can strengthen their cloud infrastructure by adopting various security measures, policies, and best practices available in the market. We hope this comprehensive guide has been insightful for you in your quest to build an efficient cloud infrastructure security system.







