What is CDR?
Content Disarm and Reconstruction also referred to as Threat Extraction, is an innovative security technology that aims to protect against both known and unknown threats concealed within documents.
Unlike traditional security solutions that rely on detection methods, CDR takes a proactive approach by systematically removing any executable content present in documents, regardless of whether it has been identified as a potential threat.
This distinctive feature allows CDR to provide genuine zero-day prevention, offering unparalleled protection against emerging threats. By sanitizing files and ensuring their safe delivery, CDR effectively minimizes the risk of file-based cyber security threats infiltrating an organization’s network.
Who is Content Disarm and Reconstruction Technology Meant for?
CDR technology is designed to cater to a wide range of organizations spanning various industries. It primarily targets those seeking strong network protection and proactive defense against file-borne cyber threats.
CDR serves as a valuable asset for sectors such as financial services, telecom, information technology, manufacturing, construction, chemicals, hospitality, public sector, and healthcare, among others. With its ability to sanitize files and ensure the safe delivery of content, it offers a versatile solution adaptable to the security needs of diverse businesses and institutions.
How does CDR work?
CDR technology operates through a four-step process designed to strengthen organizational cybersecurity defenses by warding off potential threats embedded within files. Initially, CDR extracts the contents of incoming files, segmenting them into fundamental components like text, images, and code for thorough analysis.
Scanning the Files
Subsequently, the system verifies the file’s type and attributes to determine the appropriate handling strategy, focusing on common file types susceptible to malicious code. The core of CDR lies in its Content Disarm and Reconstruction stage, where files undergo disassembly into constituent components, each subjected to rigorous threat scanning.
Reconstructing the Files
This process scrutinizes text, images, embedded code, macros, and other objects for potential threats, ensuring comprehensive protection. Following thorough scanning, the Content Disarm and Reconstruction system reconstructs the file, eliminating any identified malicious code while preserving the integrity of the file’s content.
File Delivery
Finally, sanitized files are delivered back to users via email servers or direct downloads, allowing for safe access without compromising system security. By neutralizing potential threats embedded within files, Content Disarm and Reconstruction enhances organizational cybersecurity posture, reducing the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches.
Benefits of Content Disarm and Reconstruction
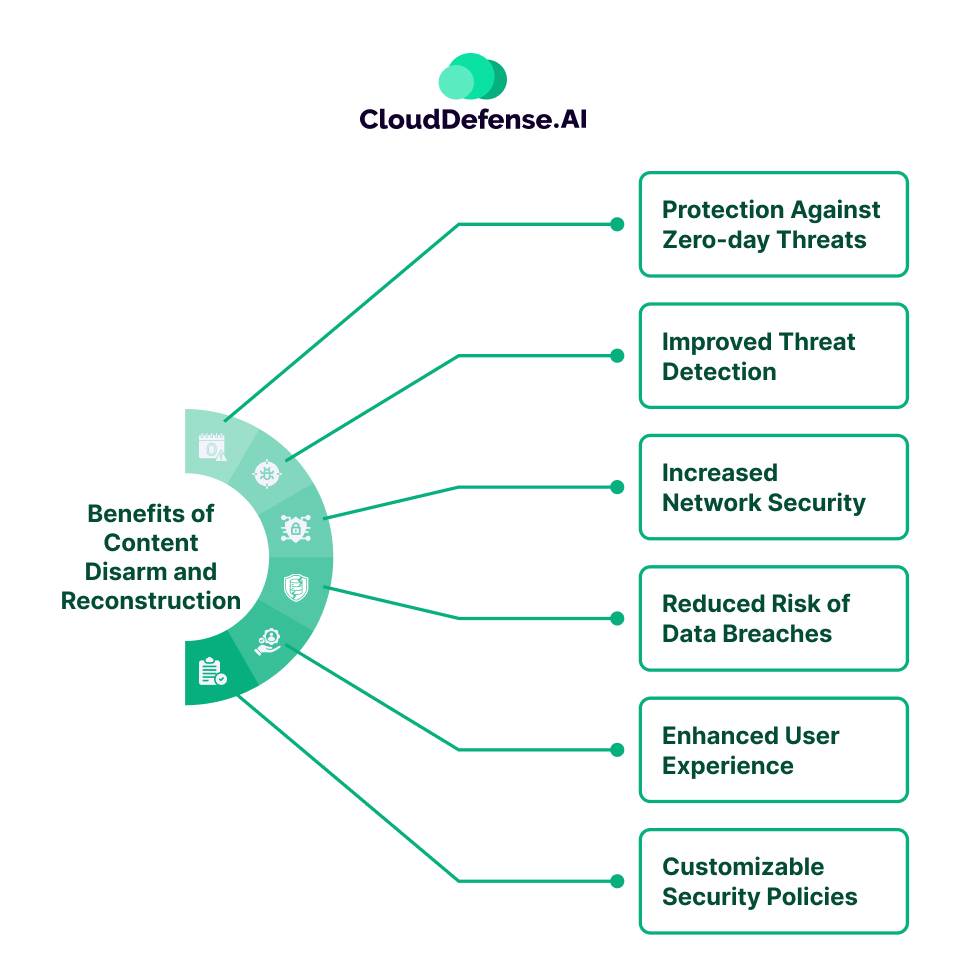
Implementing Content Disarm and Reconstruction technology offers numerous advantages for organizations seeking to enhance cybersecurity resilience and employee productivity. Here are some key benefits of integrating CDR into your organization’s security framework:
Protection Against Zero-day Threats
Content Disarm and Reconstruction technology effectively detects and removes zero-day threats, protecting against previously unknown vulnerabilities in software and providing proactive defense against emerging malware.
Improved Threat Detection
CDR goes beyond traditional antivirus solutions by detecting and neutralizing threats that may evade detection, such as fileless malware or encrypted threats, thereby enhancing threat detection capabilities.
Increased Network Security
By eliminating potentially harmful code from files, CDR helps prevent the spread of malware within the network, boosting overall network security posture and reducing the risk of widespread infections.
Reduced Risk of Data Breaches
Malware often serves as a gateway for cybercriminals to infiltrate systems and exfiltrate sensitive data. CDR minimizes this risk by sanitizing files of malicious content before they can be opened, thereby reducing the likelihood of data breaches.
Enhanced User Experience
CDR’s positive selection approach ensures that legitimate files pass through the inspection process swiftly, without causing delays or disruptions for users. This approach enhances user experience and productivity by allowing access to trusted files.
Customizable Security Policies
With CDR, organizations can customize security policies to align with their specific needs and preferences. This flexibility empowers users to define which file types are permitted through the CDR process, enabling customization of security protocols to suit unique organizational requirements.
What does Content Disarm and Reconstruction help protect against?
CDR technology is designed to protect organizational networks from a wide range of file-borne cyber threats. It prevents malware delivery through file attachments and eliminates active content, embedded objects, macros, and malicious code from files, making them safe for use. CDR effectively guards against viruses, worms, Trojans, rootkits, ransomware, and crypto-jacking attacks.
It neutralizes file-based threats originating from email, web browsers, file servers, FTP, the cloud, and endpoint devices. By intercepting and sanitizing files, CDR mitigates risks associated with file sharing and prevents exploits targeting vulnerabilities in applications.
Content Disarm and Reconstruction’s Evolution over Time
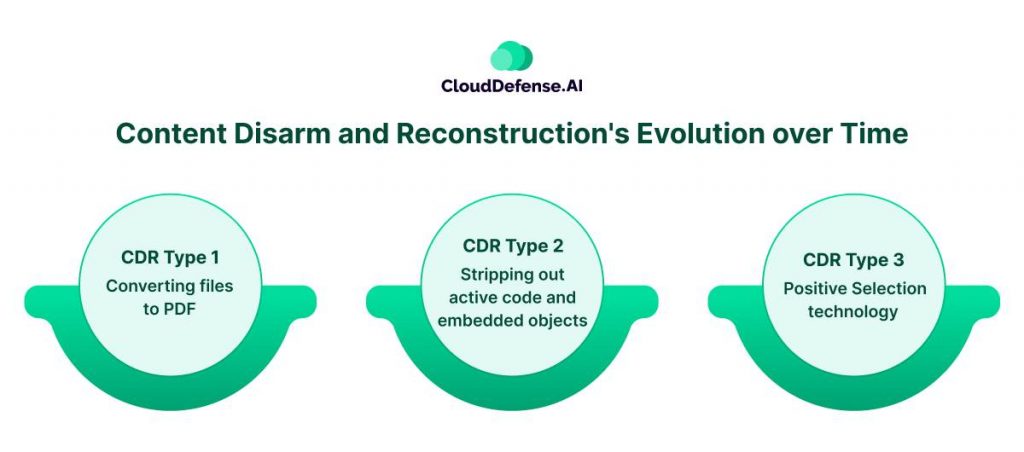
Over time, CDR technology has undergone significant evolution, enhancing its capabilities and addressing limitations to better protect against file-borne cyber threats. The evolution of CDR can be observed through different types of CDR that have been mentioned below:
- CDR Type 1: Converting files to PDF: Initially, CDR technology relied on converting files into PDF format to neutralize potential threats. While this approach effectively eliminated the risk of activating malicious code, it resulted in flattened and unusable documents, impacting organizational productivity.
- CDR Type 2: Stripping out active code and embedded objects: The next version of CDR technology aimed to improve file safety by selectively removing specific content, such as embedded objects and potentially active code. However, this approach often led to loss of functionality, such as essential macros and business logic, and overlooked security risks by allowing vulnerable templates to remain within the document.
- CDR Type 3 – Positive Selection technology: The latest advancement in CDR technology, Positive Selection, employs template-based reconstruction to preserve all features and functionality of the original file. This advanced form of CDR selectively copies known-good and safe content, ensuring that only secure template elements remain intact. By doing so, Positive Selection technology provides full protection while maintaining usability, representing the pinnacle of CDR evolution.
Final Words
The projected growth of the CDR market highlights its importance in enhancing cybersecurity. Its low maintenance and fast analysis make it an attractive option. However, for optimal protection, it’s best to integrate CDR with existing security measures. This ensures comprehensive defense against threats while minimizing disruptions to daily operations. Stay aware and prioritize cybersecurity to protect your business against rising risks.







