What is SD-WAN? – Definition
Let’s consider a scenario. Think of your business as a bustling city, with information constantly flowing between offices, employees, and cloud applications like vehicles navigating through streets and highways. A traditional Wide Area Network (WAN) is like a network of main roads connecting these locations. But what happens when rush hour traffic or construction grinds everything to a halt? That’s where SD WAN comes in, acting as an intelligent traffic control system for your network.
SD-WAN stands for Software-Defined Wide Area Network. Unlike traditional WANs that rely solely on dedicated, inflexible routing hardware, Software-Defined Wide Area Network uses software to intelligently control and optimize traffic flow across multiple WAN links. Imagine having multiple lanes of traffic available – broadband internet, fiber optic cables, even 4G/5G cellular data connections – all feeding into and out of your business “city”.
An SD WAN system continuously monitors the quality and performance of each of these WAN links, analyzing the unique requirements of each application’s data stream. It then dynamically routes traffic across the most efficient and reliable connection(s) available at any given moment. This ensures that critical applications like video conferencing, Voice over IP, cloud file access, and backups run smoothly without interruptions, even during periods of peak usage or network congestion.
Here are the key benefits of Software-Defined Wide Area Network:
➣ Cost Savings – Leverage inexpensive internet/4G links to reduce MPLS spending
➣ Increased Bandwidth – Boost WAN capacity by bonding multiple connections
➣ Improved App Performance – Intelligently route apps over optimal paths
➣ Enhanced Reliability – WAN link redundancy and seamless failover
➣ Simplified Branch Deployments – Zero-touch provisioning and connectivity
➣ Cloud Acceleration – Direct cloud access from branches
➣ Centralized Management – Single-pane control over the entire WAN fabric
How Does SD-WAN Work?
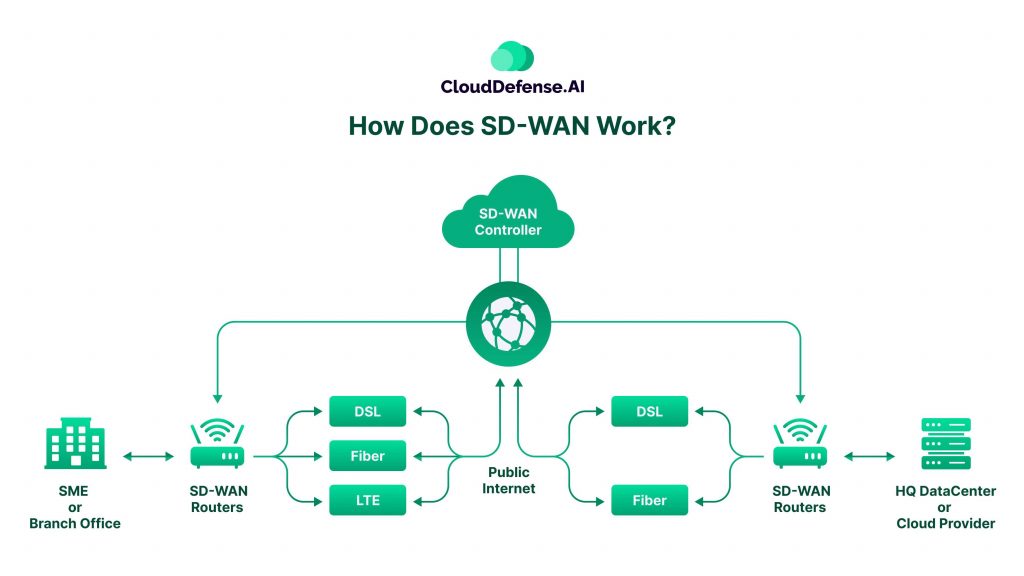
Traditional WANs rely on dedicated MPLS connections, which are like well-maintained highways, offering consistent performance but often at a high cost. SD WAN takes a different approach, utilizing multiple connections and acting like a smart traffic management system for your data flow. Let’s break it down:
Multiple Internet Connections: SD WAN doesn’t rely on just one internet service provider or a single dedicated line. Instead, it allows you to mix and match different types of connections from various providers – maybe some fiber optic lines, some cable broadband, and even 4G or 5G cellular links. It’s like having multiple routes to get from point A to point B.
Edge Devices: To make all this magic happen, SD WAN uses special devices or appliances installed at each of your branch offices or data centers. These edge devices are responsible for establishing secure connections and intelligently routing your data traffic across the available internet links.
Central Management: There’s a central control system, often hosted in the cloud, that acts as the brain of your SD-WAN setup. From this central location, you can define rules and policies for how your network traffic should be handled, like which applications get priority or how to route data securely.
Intelligent Path Selection: Here’s where things get really cool. The SD-WAN edge devices constantly monitor the performance of each internet connection, checking for things like speed, congestion, and reliability. Based on your predefined policies and real-time conditions, SD WAN can automatically choose the best path (or combination of paths) for different types of data and applications.
Application Awareness: SD-WAN doesn’t treat all network traffic the same. It can identify and classify different types of applications and data flows, allowing you to prioritize mission-critical stuff like video conferencing or cloud-based applications over less important internet browsing or software updates.
Dynamic Adaptation: If one of your internet connections starts to experience issues or gets overloaded, SD-WAN can dynamically reroute your traffic to alternative paths without interrupting your applications or user sessions. It’s like having a personal traffic assistant that knows exactly which roads to take to avoid rush hour and construction zones.
WAN Optimization: Many SD-WAN solutions also incorporate techniques to optimize and reduce the amount of data traversing your internet connections. This could include compressing data, eliminating redundant transmissions, or caching frequently accessed information closer to your branch offices.
Security and VPNs: SD-WAN typically includes built-in security features like firewalls and VPN functionality, ensuring your data stays protected and compliant with industry regulations as it travels across various internet connections.
So in a nutshell, SD WAN gives you a smarter, more flexible, and more reliable way to connect all your business locations while potentially saving you money on those expensive dedicated lines. It’s like having a team of network traffic controllers working around the clock to keep your company’s data flowing smoothly, no matter what internet hiccups may occur.
Real-World Applications: Where Does SD-WAN Shine?
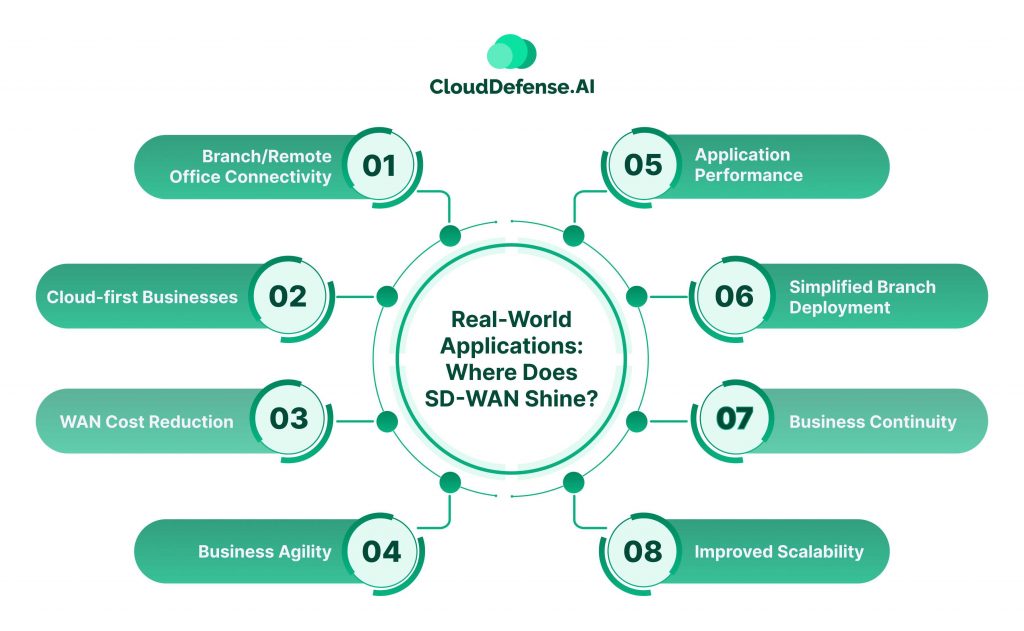
Branch/Remote Office Connectivity: Ditch those expensive MPLS leased line headaches. SD WAN allows you to connect branch offices using whatever affordable links are available – broadband internet, 4G/LTE, you name it. Yet you get enterprise-grade connectivity with better performance than traditional WAN approaches.
Cloud-first Businesses: With more apps and data living in the cloud these days, SD-WAN provides the perfect on-ramp. Your branches can connect directly to cloud services with optimized performance and security, rather than backhauling traffic through the data center.
WAN Cost Reduction: This one’s a no-brainer. By leveraging inexpensive broadband internet and wireless links where possible, businesses can drastically reduce their spending on overpriced MPLS circuits and save big on WAN costs.
Business Agility: Need to make network changes, update policies or add a new branch office? No problem! The centralized SD-WAN management console lets IT handle it all seamlessly through software versus complex box-by-box configurations.
Application Performance: SD-WAN is application-aware, allowing you to prioritize mission-critical traffic like video conferencing over less important stuff. It routes high priority apps over the fastest available links for uncompromised performance.
Simplified Branch Deployment: Deploying a new branch office is now simple. Just plug in some SD WAN devices, flip a switch and they automatically connect back to the central controller, extending the corporate WAN.
Business Continuity: With multiple links between locations, SD-WAN provides awesome resiliency. If one circuit craps out, it automatically fails over to the other links so employees stay productive.
Improved Scalability: SD-WAN easily adapts to changing network demands. Businesses can add or remove connections as needed, making it a scalable solution for growth.
How SD-WAN Empowers Today’s IoT Revolution
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming industries, with billions of devices collecting and exchanging data. But managing this ever-growing network of devices can be a complex challenge. Here’s where SD-WAN steps in as a game-changer for today’s IoT deployments.
Traditional networks struggle with IoT demands:
- Limited bandwidth: Traditional WANs might not be equipped to handle the surge in data traffic generated by numerous IoT devices.
- Security vulnerabilities: The sheer number of connected devices creates a wider attack surface for potential security breaches.
- Management complexity: Manually configuring and managing individual IoT devices can be a time-consuming and error-prone process.
SD-WAN solves these challenges by offering several key benefits for IoT:
- Optimized Connectivity: SD-WAN intelligently routes IoT traffic based on specific needs. Critical sensor data can be prioritized over less urgent device communication, ensuring smooth operation.
- Enhanced Security: SD-WAN can segment the network, isolating IoT devices from other traffic and critical business data. This minimizes the potential impact of security breaches.
- Simplified Management: SD-WAN allows for centralized configuration and management of a large number of IoT devices. Templates and policies can be applied, streamlining deployment and ongoing maintenance.
- Scalability for Growth: As your IoT network expands, SD-WAN can easily adapt. New devices can be added quickly, ensuring your network infrastructure scales seamlessly with your growing needs.
- Cost-Effective Connectivity: SD-WAN allows you to leverage a mix of connections for IoT traffic. Cost-effective options like broadband internet can be used for non-critical data, reducing reliance on expensive MPLS circuits.
- Improved Reliability: With redundant connections offered by SD-WAN, even if a primary link fails, data from your IoT devices can be rerouted, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous operation.
Real-world examples of SD-WAN and IoT:
- Manufacturing: SD-WAN can optimize communication between factory floor sensors and cloud-based analytics platforms, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- Smart Cities: SD-WAN can manage traffic from connected sensors in traffic lights, parking meters, and environmental monitoring systems, optimizing city operations and resource allocation.
- Retail: SD-WAN can ensure reliable data flow from inventory tracking tags and smart shelves, improving stock management and customer experience.
Wide Area Networking Solutions: A Head-to-Head Comparison
SD-WAN, MPLS, and VPN are different networking technologies that address various connectivity and security requirements. Here’s a table that compares these technologies:
| Feature | SD-WAN | MPLS | VPN |
| Description | Software-defined Wide Area Network. Manages traffic across multiple connections (internet, MPLS, LTE) | Multiprotocol Label Switching. Dedicated, private network service offered by carriers. | Virtual Private Network. Encrypts data traveling over a public network. |
| Technology | Software-based | Hardware-based | Software-based |
| Connections | Multiple connections (internet, MPLS, LTE) | Single, dedicated MPLS circuit | Can be used over any connection (internet, MPLS) |
| Routing | Intelligent, dynamic routing based on application needs and real-time conditions | Pre-configured, static routing | Limited routing capabilities |
| Security | Can integrate with security solutions (firewalls, IDS) | No built-in security | Encrypts data, but overall security depends on underlying connection |
| Cost | Generally less expensive than MPLS | Most expensive option | Varies depending on connection type |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, easily add or remove connections | Limited scalability, requires provisioning from carrier | Limited scalability, depends on underlying connection |
| Management | Centralized management interface | Complex configuration and management | Requires configuration on both endpoints |
| Ideal for | Businesses with cloud-based applications, branch office connectivity, cost optimization needs | Businesses requiring high performance, guaranteed bandwidth, mission-critical applications | Securing communication over a public network |
The choice between SD-WAN, MPLS, and VPN depends on an organization’s specific requirements, such as application performance needs, security considerations, cost constraints, and the level of control and visibility required over the network infrastructure.
How to Deploy SD-WAN
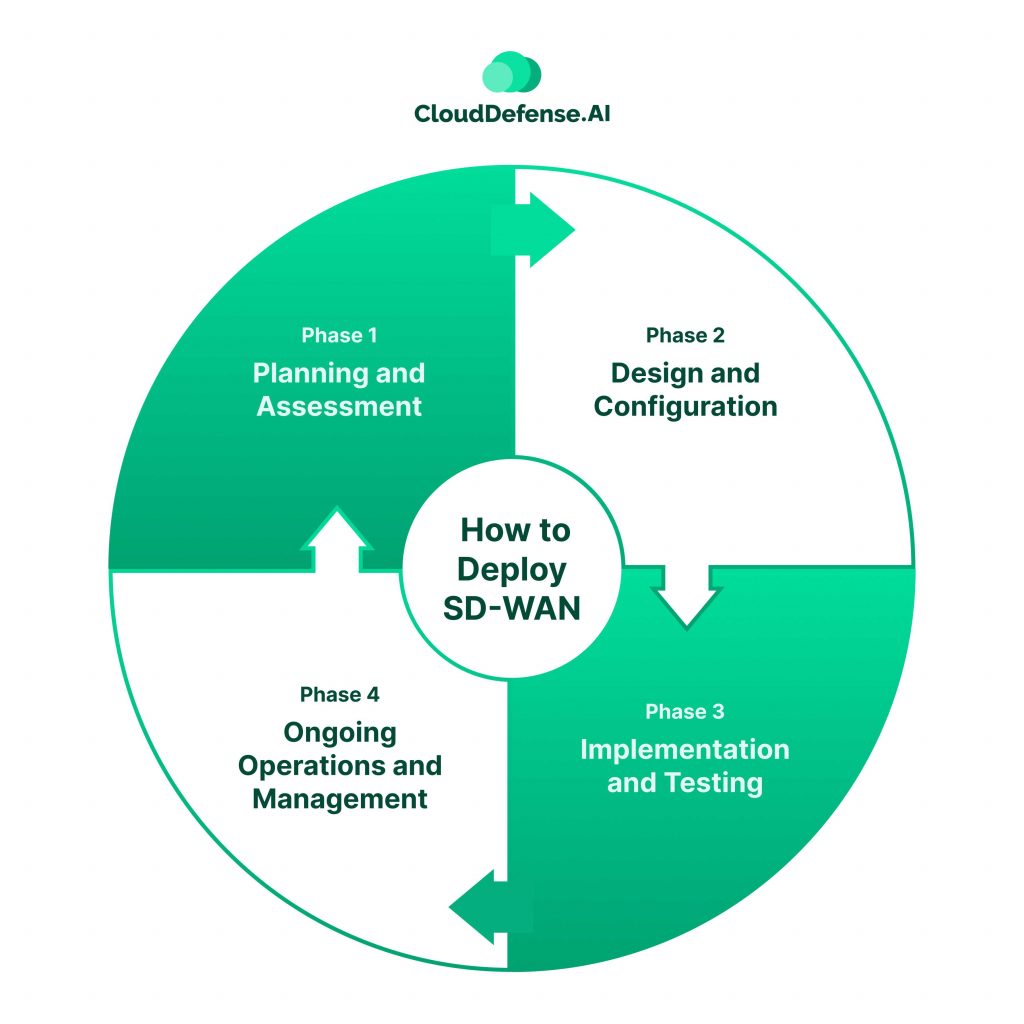
Deploying SD-WAN can be an exciting step towards a more efficient and reliable network. Here’s a roadmap to guide you through the process:
Phase 1: Planning and Assessment
- Evaluate Your Needs: Clearly define your business objectives for deploying SD-WAN. Are you looking to optimize cloud application performance, improve branch office connectivity, or reduce costs?
- Assess Your Network: Analyze your existing network infrastructure, including bandwidth requirements, application usage patterns, and geographic distribution of locations.
- Define Your Deployment Model: Choose between a Do-It-Yourself (DIY), managed SD-WAN, or co-managed service provider approach based on your internal expertise and resource availability.
Phase 2: Design and Configuration
- Design Your SD-WAN Architecture: This involves determining the number and location of SD-WAN appliances, identifying the connections you’ll use (MPLS, internet, LTE), and defining traffic routing policies.
- Select Your SD-WAN Solution: Research different SD-WAN vendors and choose a solution that aligns with your needs and budget.
- Configure Security Policies: Integrate your SD-WAN with firewalls and intrusion detection systems to ensure robust network security.
Phase 3: Implementation and Testing
- Stage and Deploy SD-WAN Appliances: Install the SD-WAN appliances at your branch offices and data center according to the designed architecture.
- Configure Network Settings: Set up connection parameters, traffic shaping rules, and security policies on the SD-WAN devices.
- Thorough Testing and Validation: Perform rigorous testing to ensure proper functionality, application performance, and failover mechanisms are working as intended.
Phase 4: Ongoing Operations and Management
- Monitor Network Performance: Continuously monitor network performance metrics like latency, packet loss, and application response times.
- Security Management: Regularly update security software and policies to stay ahead of evolving threats.
- Performance Optimization: Fine-tune traffic routing policies based on real-time network conditions and application demands.
- Scalability and Expansion: As your business grows, the SD-WAN architecture can be easily scaled by adding new connections or locations.
Following these steps and carefully considering your specific needs, you can successfully deploy an SD-WAN solution that empowers your business with a reliable, efficient, and cost-effective network foundation. Remember, consulting with SD-WAN experts can be valuable throughout the process, especially for complex deployments.
The Future of SD-WAN
The future of SD-WAN is poised for transformation, driven by emerging technologies like 5G, IoT, and edge computing. SD-WAN will evolve into an intelligent, self-optimizing platform, harnessing AI and machine learning for dynamic adaptation. It will seamlessly integrate with cloud services and security, blurring boundaries and enabling a holistic, software-defined networking approach.
However, this shift also heightens cybersecurity risks, necessitating robust security measures woven into SD-WAN’s fabric. Organizations must embrace this future, leveraging SD-WAN’s agility and intelligence to stay ahead in an increasingly complex digital front. Those who adapt will thrive, while those who resist change risk being left behind in this era of inevitable networking disruption.







