What Is OpenStack?
OpenStack is an open-source cloud platform designed to manage and orchestrate distributed computing, network, and storage resources. It aggregates these resources into pools and allows for their on-demand provisioning through a self-service portal, making it a powerful tool for creating and managing private and public clouds.
Originally launched in 2010 by Rackspace and NASA, OpenStack has grown into a robust framework that enables organizations to build and manage cloud infrastructure that is competitive with commercial cloud offerings like AWS or Microsoft Azure.
OpenStack is more than just a virtualization platform – it’s a fully functional cloud environment. Unlike traditional virtualization management platforms like VMware vSphere, OpenStack provides users with a cloud-native experience, allowing them to request and manage resources programmatically through APIs.
This capability makes OpenStack a popular choice for organizations looking to implement a hybrid or multi-cloud strategy, optimize cloud costs, or avoid vendor lock-in associated with proprietary solutions.
How Does OpenStack Work?
At its core, OpenStack is a modular cloud platform. It consists of several components, each responsible for a specific function within the cloud environment. These components work together to provide a comprehensive cloud infrastructure that can scale horizontally across a data center.
Nova
Nova is OpenStack’s compute engine, responsible for managing instances (virtual machines). It supports a variety of hypervisors, including KVM, VMware ESXi, and Hyper-V, making it highly versatile and compatible with different environments.
Neutron
Neutron provides networking-as-a-service, enabling connectivity between instances. It supports a range of networking technologies, including software-defined networking tools like Open vSwitch and Cisco ACI, ensuring robust and scalable network management.
Cinder
Cinder handles block storage, providing persistent storage that can be attached to instances. This is crucial for applications that require durable storage beyond the lifespan of a single instance.
Swift
Swift is OpenStack’s object storage service, similar to AWS S3. It allows for the storage and retrieval of unstructured data using a RESTful API, providing scalable and highly available storage.
Glance
Glance manages disk images, enabling users to create, register, and retrieve images for use in instances. This makes it easy to deploy instances with pre-configured operating systems and applications.
Keystone
Keystone is the identity service in OpenStack, handling authentication and authorization for users and services. It supports integration with external identity providers like LDAP and Active Directory, making it easier to manage access in large organizations.
Together, these components form the backbone of an OpenStack cloud environment. They are orchestrated through a unified dashboard (Horizon) or via APIs, giving users flexibility in how they interact with the cloud. OpenStack also supports additional services like orchestration (Heat), telemetry (Ceilometer), and database management (Trove), making it a comprehensive solution for cloud management.
Who Uses OpenStack?
OpenStack has a broad user base, ranging from small startups to large enterprises and service providers. It is particularly popular in industries that require significant control over their cloud infrastructure, such as telecommunications, finance, and government. These sectors often deal with sensitive data and stringent compliance requirements, making OpenStack’s flexibility and transparency appealing.
Notable companies using OpenStack include:
- AT&T: One of the largest telecommunications companies globally, AT&T uses OpenStack to manage its vast network infrastructure and provides cloud services to its customers.
- NASA: As one of the original developers, NASA uses OpenStack to manage its scientific data and support its research initiatives.
- Walmart: The retail giant leverages OpenStack to power its e-commerce platform, ensuring scalability and reliability during peak shopping periods.
- CERN: The European Organization for Nuclear Research uses OpenStack to manage the massive amounts of data generated by its particle accelerators.
Service providers also use OpenStack to build public and private cloud offerings, providing their customers with cloud services that can compete with those of hyper scalers like AWS and Google Cloud.
Advantages of OpenStack
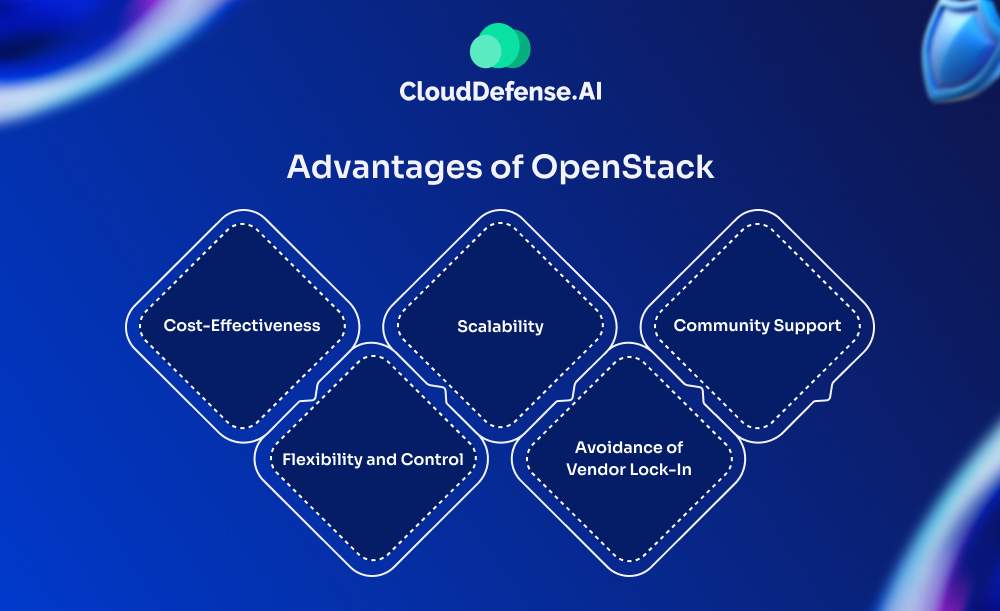
Here are a few advantages that companies can avail from OpenStack
- Cost-Effectiveness: OpenStack is open-source, which means it’s free to use and modify. This can lead to significant cost savings, especially for organizations that want to avoid the licensing fees associated with proprietary platforms. Additionally, by reducing operational expenses over time, OpenStack offers a lower total cost of ownership compared to traditional virtualization solutions.
- Flexibility and Control: OpenStack’s open-source nature provides unparalleled flexibility. Organizations can customize the platform to fit their specific needs, whether it’s integrating with existing tools, developing custom features, or optimizing for particular workloads. This level of control is particularly beneficial for businesses with unique or complex requirements.
- Scalability: OpenStack is designed to scale horizontally, making it an ideal solution for large-scale deployments. It can handle thousands of nodes across multiple data centers, providing the capacity needed for enterprise-level applications.
- Avoidance of Vendor Lock-In: OpenStack’s open-source license allows organizations to avoid being locked into a single vendor’s ecosystem. This can provide greater freedom to choose the best technologies and vendors for their needs, as well as the ability to switch providers without significant migration challenges.
- Community Support: OpenStack has a vibrant and active community of developers and users. This community-driven approach ensures that the platform continuously evolves, with regular updates, new features, and security patches.
Disadvantages of OpenStack
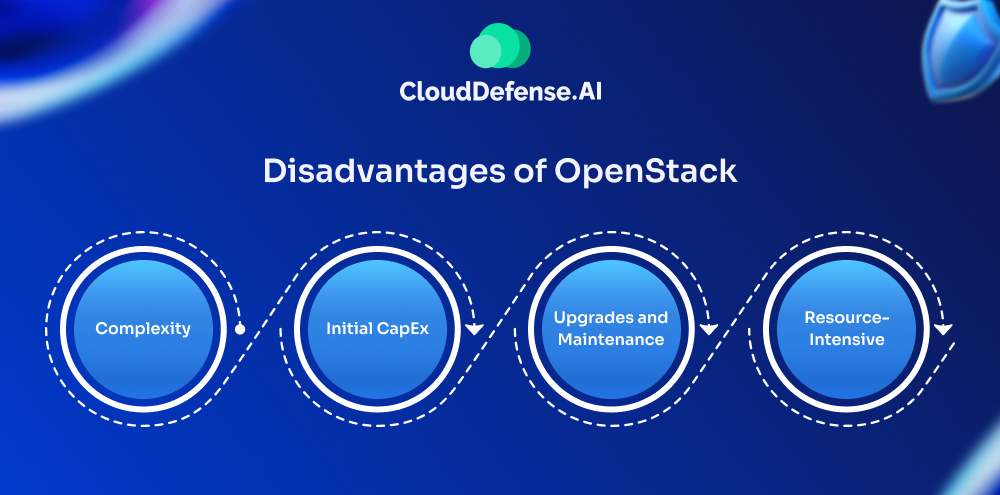
Other than the benefits, OpenStack has its own fair share of disadvantages.
- Complexity: Despite its many advantages, OpenStack is not without its challenges. The platform’s complexity can be overwhelming, particularly for organizations without significant in-house expertise in cloud infrastructure. Setting up and managing an OpenStack environment requires a deep understanding of its components and how they interact.
- Initial CapEx: While OpenStack can reduce operational expenses in the long run, the initial capital expenditure for setting up an OpenStack cloud can be high. This includes costs related to hardware, network infrastructure, and skilled personnel to manage the deployment.
- Upgrades and Maintenance: Maintaining an OpenStack environment requires ongoing effort. Upgrades can be particularly challenging, as they may involve significant changes to the underlying architecture. Organizations need to plan and execute these upgrades carefully to avoid disruptions.
- Resource-Intensive: Running OpenStack at scale requires substantial hardware resources. Allocating the necessary resources may be challenging for smaller organizations or those with limited budgets.
Final Words
OpenStack is a powerful and versatile cloud platform that offers numerous benefits to organizations seeking to build and manage their cloud infrastructure. Its open-source nature provides flexibility, cost savings, and control that are hard to match with proprietary solutions. However, it’s not without its challenges. The complexity of OpenStack and the need for skilled personnel can be a barrier to entry for some organizations.
That said, for businesses with the right expertise and resources, OpenStack can be a game-changer, enabling them to build a cloud environment that meets their unique needs, scales with their growth, and avoids the pitfalls of vendor lock-in. Whether you’re a large enterprise looking to optimize your cloud costs or a service provider aiming to offer competitive cloud services, OpenStack is a solution worth considering.







