What is POS Security?
POS security involves implementing protective measures to secure point-of-sale systems and environments where transactions occur.
These measures are designed to prevent unauthorized access, protect sensitive data, and defend against various cyber attacks. POS security is crucial for safeguarding credit card information, personally identifiable information, and other sensitive customer data from theft or misuse.
How POS Security Works?
POS security operates through a combination of technological safeguards and best practices. It begins with securing the physical and digital components of POS systems. This includes installing anti-virus software, using end-to-end encryption, and regularly updating systems to mitigate vulnerabilities.
An attack on a POS system typically starts with a hacker exploiting a weakness or using social engineering to gain access. Once inside, the hacker installs malware to capture card details as they pass through the POS system’s memory. The stolen data is then transferred to an external location for malicious use. Organizations can counter these threats by deploying measures such as whitelisting, code signing, and using chip readers to enhance security.
Examples of Data Breaches Involving POS Security Compromises
Several high-profile data breaches have highlighted the vulnerabilities of POS systems:
Target (2013)
One of the most significant breaches occurred when attackers infected Target’s POS systems with the Trojan. POSRAM malware compromising the personally identifiable information (PII) and payment card information of approximately 70 million customers.
This massive breach exposed sensitive data and caused widespread panic and a loss of consumer trust. As a result, Target faced substantial financial repercussions, including a $39 million class action settlement and additional legal costs amounting to $19.9 million. The incident underscored the critical need for robust POS security measures.
Home Depot (2014)
In 2014, hackers successfully breached Home Depot’s POS systems, affecting up to 56 million customers across 2,200 stores. This large-scale data breach allowed cybercriminals to access and misuse significant amounts of customer payment information.
The breach’s aftermath was costly for Home Depot, leading to a $19 million settlement for a class action lawsuit. The breach highlighted vulnerabilities within Home Depot’s POS systems and emphasized the importance of continuously monitoring and updating security protocols to prevent similar incidents.
Wendy’s (2020)
The fast food chain Wendy’s experienced a notable data breach in 2020 when it confirmed that 1,025 of its stores had been infected with POS malware. This breach compromised an undisclosed number of customer records, highlighting the ongoing risks associated with POS system vulnerabilities.
The data breach resulted in multiple class action lawsuits against Wendy’s, illustrating inadequate POS security’s potential legal and financial consequences. This incident served as a reminder of the need for vigilant security practices and the importance of staying ahead of cyber threats.
Best Practices for POS Security
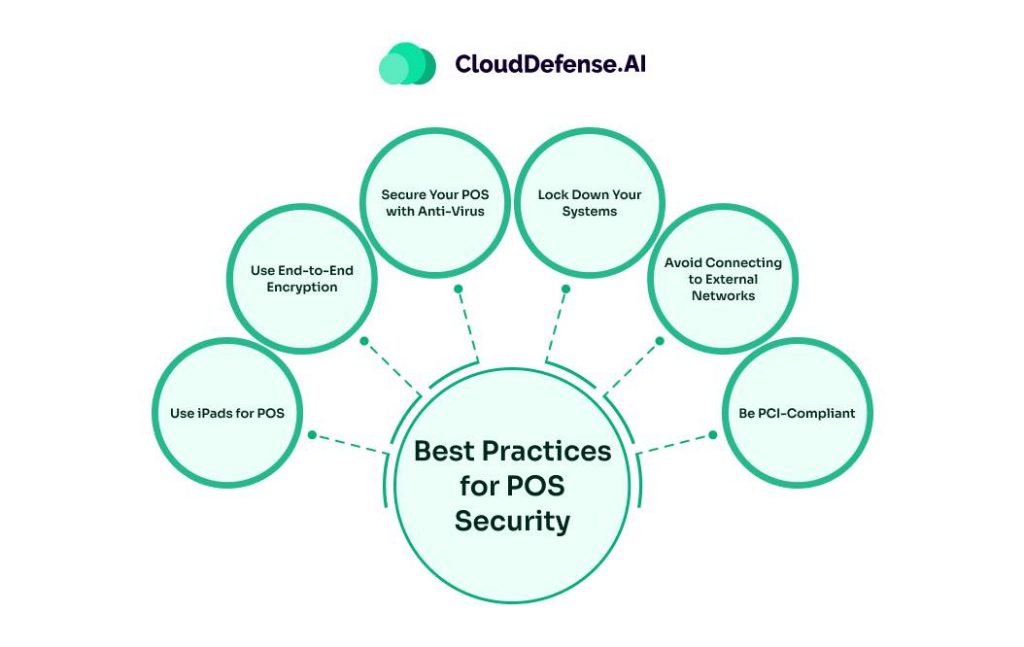
Organizations can adopt several best practices to enhance the security of their POS systems. These practices address various vulnerabilities and threats, ensuring the protection of sensitive customer information and the integrity of the transaction process.
Use iPads for POS
Using iPads for POS systems leverages the security features of Apple’s iOS, which only allows one application to run at a time. This reduces the risk of malware infiltrations that typically require multiple applications running simultaneously, making it harder for malicious software to penetrate the system and steal data.
Use End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption protects data from the moment it is captured at the POS terminal until it reaches the POS software server. This method ensures that even if hackers intercept the data, they cannot read it without the encryption key. Implementing end-to-end encryption helps keep customer information secure throughout its lifecycle.
Secure Your POS with Anti-Virus
Anti-virus software is essential for detecting and blocking malware that can compromise POS systems. Regular scans and updates help identify and neutralize threats, ensuring that any detected issues are addressed promptly to prevent data loss or theft.
Lock Down Your Systems
Physical security measures are crucial for preventing unauthorized access to POS systems. Devices should be locked down at the end of each working day and tracked diligently. Limiting access to trusted individuals can minimize the risk of unauthorized use and data breaches.
Avoid Connecting to External Networks
Keeping POS systems on secure internal networks reduces the risk of remote attacks. Organizations can lower the chances of remote system compromises by avoiding connections to external networks and restricting business-critical tasks to secure corporate networks.
Be PCI-Compliant
Compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is essential for organizations handling credit card transactions. PCI DSS provides a comprehensive framework of best practices for data security and fraud prevention. Organizations must ensure they meet these standards to protect cardholder data and reduce the risk of fraud.
Final Words
Protecting your point-of-sale system is important today. Understanding potential threats and implementing robust security measures can protect your business and customers from financial loss and reputational damage. Remember, POS security is an ongoing process that requires vigilance and adaptation to evolving cyber threats.







