What is Secure Web Gateway?
A Secure Web Gateway is a cybersecurity solution that protects users from web-based threats by monitoring and filtering internet traffic.
It enforces security policies, blocks malicious websites, prevents data leaks, and defends against malware, phishing, and other cyber threats. SWGs typically include URL filtering, antivirus scanning, application control, and data loss prevention features.
They ensure secure internet access by inspecting web traffic in real time, whether users are on-premises or remote. SWGs can be deployed as cloud-based, on-premises, or hybrid solutions, helping organizations maintain compliance, enhance security, and protect sensitive data from cyber risks.
How Does an SWG Work?
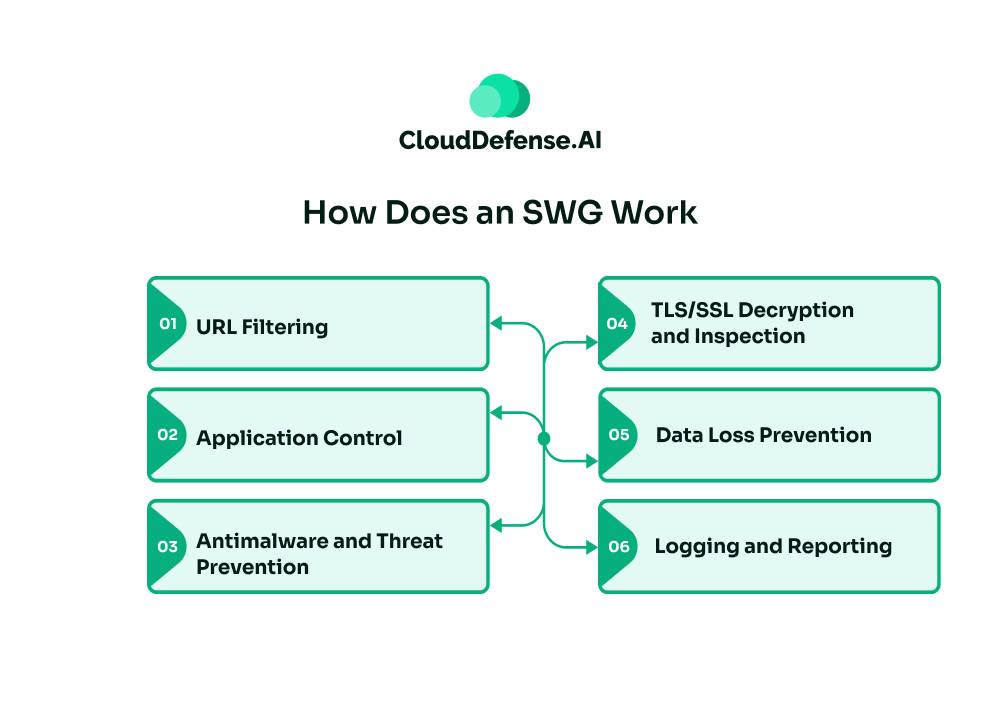
A Secure Web Gateway(SWG) serves as a protective barrier between an organization’s internal network and the internet, ensuring security and enforcing web usage policies. When a user attempts to access web content, the SWG undertakes several key functions:
- URL Filtering: The SWG checks the requested URL against a database of categorized URLs and predefined policies. It allows access if the URL is deemed safe and compliant with policies, blocking it otherwise.
- Application Control: It manages access to web-based applications, offering granular controls to restrict certain functions based on policy requirements.
- Antimalware and Threat Prevention: The SWG scans downloadable files and scripts for malicious content using known malware signatures. If malware is detected, it blocks the download to prevent infection.
- TLS/SSL Decryption and Inspection: It decrypts and inspects encrypted data for hidden threats, re-encrypting it for secure transmission if no threats are found.
- Data Loss Prevention: The SWG parses content for sensitive data, such as payment card numbers or proprietary information, blocking or alerting on discoveries based on company policy.
- Logging and Reporting: It logs user activity, threats, and policy violations for administrative monitoring, reporting, and forensic analysis purposes.
Why Are SWGs Important?
SWGs are essential in today’s cybersecurity landscape due to their pivotal role in protecting organizations against concealed cyberthreats within encrypted web traffic. By filtering and inspecting internet traffic, SWGs mimimize the risk of operational disruption and data breaches posed by sophisticated cyberattacks.
They address the threats that by adapting their threat detection capabilities, ensuring proactive defense mechanisms against emerging risks. Moreover, SWGs enable secure remote work by extending security controls beyond the traditional corporate perimeter, facilitating access to data and applications from any location without compromising security.
With the prevalence of encrypted traffic, SWGs play a critical role in decrypting and inspecting HTTPS traffic for hidden threats, thereby maintaining comprehensive security posture and regulatory compliance.
Benefits of SWGs
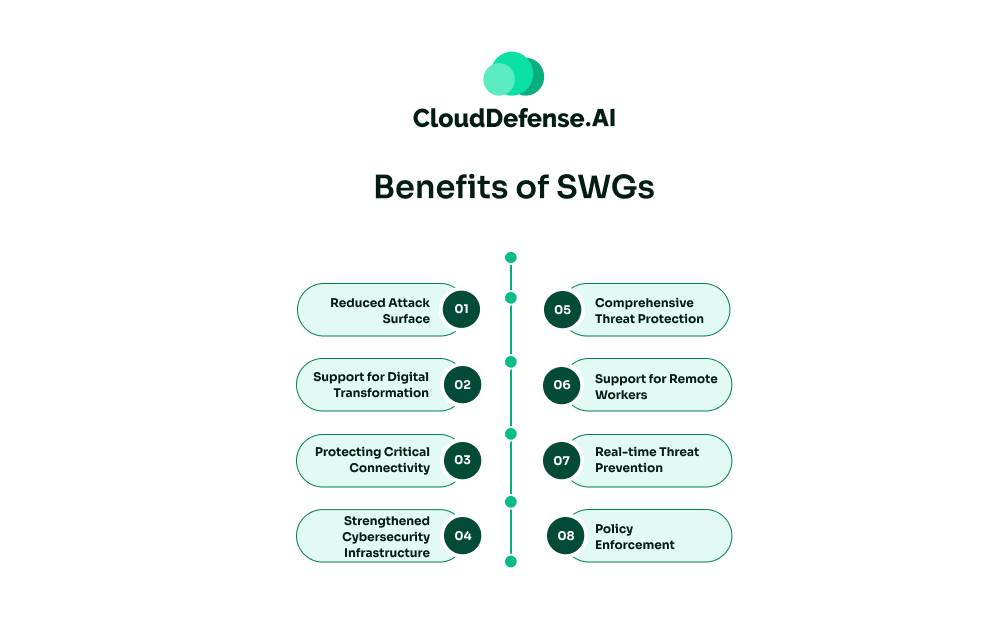
A SWG offers a wide range of benefits for organizations:
- Reduced Attack Surface: By minimizing potential attack vectors exploited by threat actors, SWGs help decrease the external attack surface, enhancing overall cybersecurity posture.
- Support for Digital Transformation: SWGs support businesses in digital, cloud, and workforce transformations by providing secure access to internet resources, SaaS applications, and facilitating remote work.
- Protecting Critical Connectivity: SWGs protect internet connectivity critical for IT operations, ensuring the security of servers and headless devices.
- Strengthened Cybersecurity Infrastructure: By protecting critical data and operations connected to the web, SWGs strengthen the cybersecurity infrastructure of organizations.
- Comprehensive Threat Protection: SWGs block access to high-risk and malicious websites and applications, enforce compliance policies and regulations, and prevent malware infections with a multi-layered security architecture.
- Support for Remote Workers: SWGs enable remote workers to securely access the internet and necessary resources while enforcing company security policies, thereby supporting flexible work models.
- Real-time Threat Prevention: SWGs protect against ransomware, malware, and phishing attacks in real-time, ensuring proactive threat mitigation and incident response.
- Policy Enforcement: SWGs enforce compliance with company, industry, or government regulatory policies, helping organizations maintain regulatory compliance and data integrity.
Common SWG Deployment Challenges
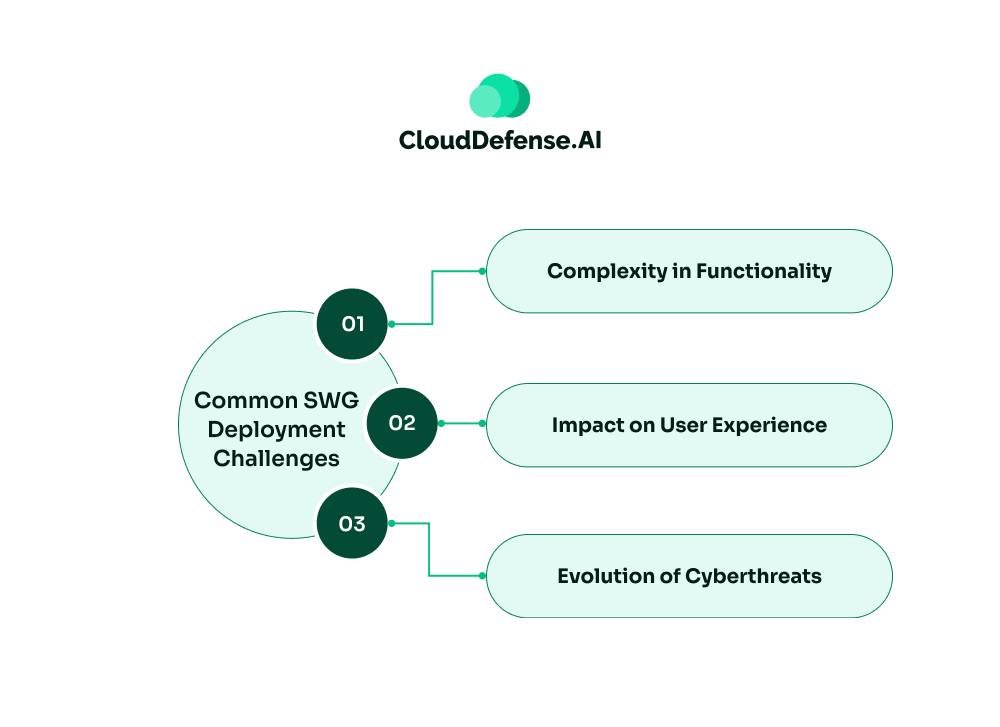
Common SWG deployment challenges stem from various factors:
Complexity in Functionality
Implementing SWGs separately can add to the complexity of security stacks, requiring ad hoc management and potentially leading to disjointed security measures. Integration with adjacent security technologies, such as within a SASE framework, can simplify management and enhance visibility.
Impact on User Experience
Traditional on-premises infrastructure for securing internet traffic may lead to poor user experiences due to latency and performance issues. Centralized data centers often result in traffic backhauling, causing delays and frustration among users, potentially leading them to bypass security measures.
Evolution of Cyberthreats
Modern cyberthreats continually evolve, challenging traditional SWG solutions. Adversaries now utilize legitimate SaaS platforms for malicious activities, employ phishing kits at scale, and execute meddler-in-the-middle attacks. Traditional SWGs relying on hashes, static signatures, and offline web content crawling struggle to keep pace with these threats.
How Do SWGs Enforce Acceptable Use Policies?
SWGs enforce acceptable use policies by authenticating users through methods like single sign-on or explicit usernames and passwords. Once authenticated, SWGs apply user-specific access rules to regulate internet usage.
For example, access to certain websites may be blocked for regular users but permitted for cybersecurity team members. SWGs enforce acceptable use policies defined by organizations, which may include blocking access to categories of websites like gambling or adult content.
Utilizing URL filtering and categorization databases, SWGs dynamically block or permit access to websites based on predefined policies. This approach ensures a secure and compliant online environment, promoting responsible internet usage while protecting against unauthorized access and potential security risks.
How Do SWGs Secure Remote Workers and Branch Offices?
Cloud-delived SWGs secure remote workers and branch offices by serving as intermediaries for internet traffic, eliminating the need for backhauling to distant data centers. They provide secure access to the internet, ensuring all web traffic undergoes inspection and enforcement of security policies.
Unlike traditional on-premises SWGs, cloud-delivered SWGs are designed to support distributed networks, offering scalability and flexibility. They enable efficient and scalable security solutions, particularly beneficial for branch offices without on-premises SWGs or data centers.
By routing internet traffic through a centralized security gateway, cloud-delivered SWGs ensure consistent security enforcement and compliance with organizational policies across all locations. This approach optimizes performance and enhances security for remote workers and branch offices, supporting the requirements of modern distributed networks.
SWGs vs. Firewalls
SWGs and firewalls play distinct yet complementary roles in network security. While firewalls focus on network layer inspections, SWGs provide deeper scrutiny at the application layer. Firewalls traditionally inspect IP addresses, ports, and router-based protocols, while next-generation firewalls extend their reach to application layer (Layer 7) inspections.
In contrast, SWGs primarily operate at Layer 7, scrutinizing applications, web traffic, and a broader array of ports and protocols. Modern cloud-delivered SWGs combine advanced functionalities like URL filtering, SSL decryption, and SaaS application control with firewall capabilities within SSE platforms.
SWGs supplement rather than replace firewalls, offering a more comprehensive approach to web security defense by addressing both network and application layer vulnerabilities.
SWGs vs. Proxies
SWGs and proxies serve different functions in network security. While both intercept and manage internet traffic, SWGs focus on security while proxies primarily handle networking tasks. Proxies act as intermediaries between clients and destinations, shielding client IP addresses and providing privacy.
They come in explicit and transparent types, with explicit proxies requiring client configuration and transparent proxies operating without user awareness. In contrast, SWGs offer comprehensive security solutions, inspecting traffic for threats and enforcing security policies.
They go beyond networking functions to include features like URL filtering, SSL decryption, and advanced threat prevention. While proxies offer privacy and basic security, SWGs provide a more strong Adefense against cyber threats and are essential components of modern security architectures.
The Future of SWGs
The future of SWGs is moving towards cloud-delivered models augmented with AI, emphasizing scalability and cyber resilience. Traditional on-premises web proxy appliances are being replaced by cloud-delivered proxies to accommodate remote work and the adoption of cloud-based applications.
AI-driven SWGs play an important role in threat detection and security operations, swiftly analyzing web traffic to counter dynamic threats effectively. Future SWG deployments should prioritize native integration, simplified management, and digital experience monitoring with AIOps capabilities.
Organizations need solutions offering dynamic capacity, elastic scalability, high availability, and uncompromised cyber resilience to ensure secure access to the internet and SaaS applications while addressing evolving web threats.
The market for cloud-hosted SWG services is expected to surpass appliance-based solutions as organizations increasingly move to the cloud, with significant growth projected in the coming years.
How to Choose a Secure Web Gateway
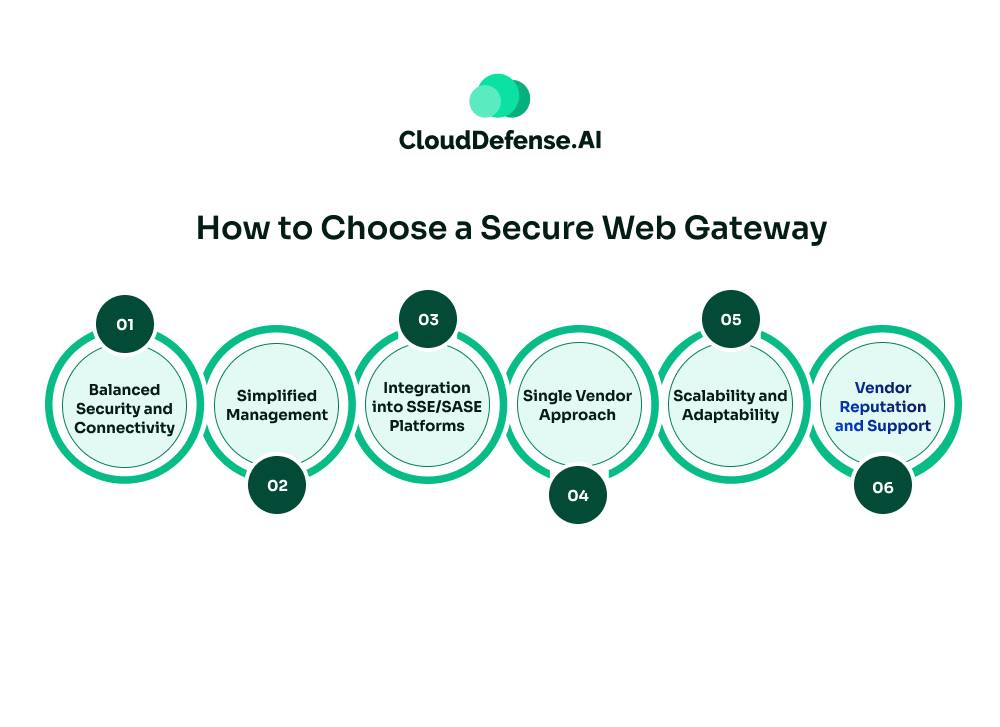
When selecting a SWG, organizations should consider several critical factors.
Balanced Security and Connectivity
Prioritize solutions that strike a balance between robust security measures and smooth user connectivity. Efficient, uninterrupted access to resources for users is essential.
Simplified Management
Choose an SWG that simplifies management by reducing operational complexity. Streamlining user interfaces, products, dashboards, and vendors can mitigate security risks and enhance efficiency.
Integration into SSE/SASE Platforms
View the SWG as a foundational component of a unified SSE/SASE platform. Consider vendors offering a consolidated solution encompassing various security services, enabling centralized policy management and streamlined operations.
Single Vendor Approach
Opt for vendors providing a single SASE solution covering multiple services like FWaaS, CASB, ZTNA, and SD-WAN. This approach eliminates the need for managing multiple interfaces and products, enhancing operational efficiency.
Scalability and Adaptability
Ensure the chosen SWG solution offers scalability and adaptability to evolving threats. Look for features enabling future expansion and integration with emerging technologies.
Vendor Reputation and Support
Assess the vendor’s track record, reputation, and level of customer support. Choose vendors known for reliability, innovation, and responsiveness.
Final Words
SWGs are essential for protecting organizations from online threats and ensuring policy compliance. With factors like balanced security, simplified management, and integration into comprehensive security platforms, organizations can choose the right SWG to meet their needs. The future of SWGs lies in cloud-delivered models with AI enhancements, promising continued advancements in web security.







