Cyber threats are growing fast, putting individuals, businesses, and even governments at risk. Among the most dangerous are malware and ransomware, two cyber weapons hackers use to steal data, disrupt systems, and extort money. But what’s the difference?
Malware is an umbrella term for malicious software, while ransomware is a more ruthless variant that locks files, allowing hackers to demand payment for their release. With high-profile ransomware attacks crippling major companies and costing millions, understanding these threats is a top priority at the moment.
In this article, we’ll compare malware and ransomware, explain how they spread, and, most importantly, explain how to stay protected.
What Is Malware?
Malware, short for malicious software, is any program or code designed to infiltrate, damage, or exploit computer systems, networks, or devices.
Cybercriminals use malware to steal sensitive information, disrupt operations, or gain unauthorized access to personal and corporate data. Malware can spread through email attachments, malicious websites, infected software downloads, and even USB drives, making it a persistent threat in the digital world.
Common Types of Malware
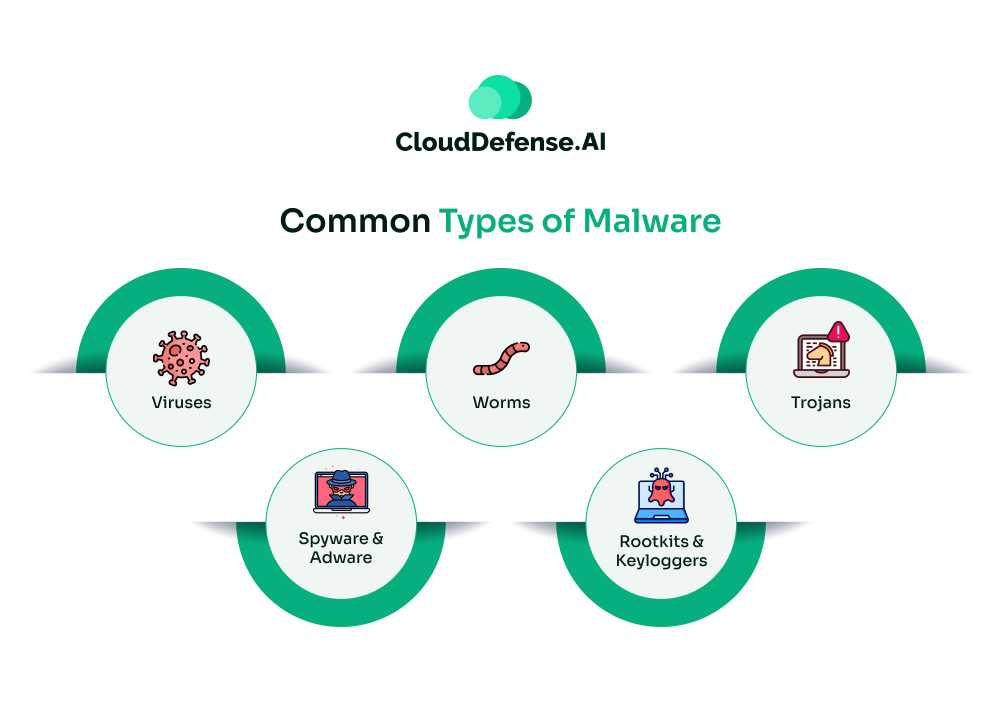
Malware comes in various forms, each with different methods of attack and damage potential. Here are some of the most common types:
- Viruses – Like a biological virus, this type of malware attaches itself to files or programs and spreads when executed. Once active, it can corrupt data, slow down systems, or even render devices unusable.
- Worms – Unlike viruses, worms don’t require user interaction to spread. They replicate themselves across networks, exploiting vulnerabilities to infect multiple systems quickly. Worms are notorious for causing widespread disruptions, such as slowing down entire networks or consuming system resources.
- Trojans – Named after the infamous Trojan Horse, trojans disguise themselves as legitimate software to trick users into installing them. Once inside a system, trojans create backdoors for attackers, allowing them to steal data, install more malware, or take control of the device.
- Spyware & Adware – Spyware operates silently in the background, collecting sensitive information such as login credentials, browsing habits, and financial data. Adware, on the other hand, bombards users with intrusive ads, slowing down systems and potentially exposing users to more malware infections.
- Rootkits & Keyloggers – Rootkits are designed to hide deep within a system, giving hackers ongoing, stealthy access to a device. Keyloggers record every keystroke, capturing sensitive information such as passwords and credit card numbers without the user’s knowledge.
Malware is constantly evolving, with cybercriminals finding new ways to bypass security defenses. Understanding its different forms and how it spreads is the first step in preventing infections. By staying vigilant, using strong cybersecurity tools, and avoiding suspicious links or downloads, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce the risk of malware attacks.
Read our blog on ‘What is Malware?’ to get detailed insight on Malware.
What Is Ransomware?
Ransomware is one of the most dangerous types of malware, designed to encrypt files or lock users out of their devices, making them inaccessible until a ransom is paid.
Cybercriminals use ransomware to target individuals, businesses, and even government institutions, often demanding payments in cryptocurrency to make tracking difficult. These attacks can cripple entire organizations, disrupt critical services, and cause significant financial and data losses.
Notable Ransomware Attacks
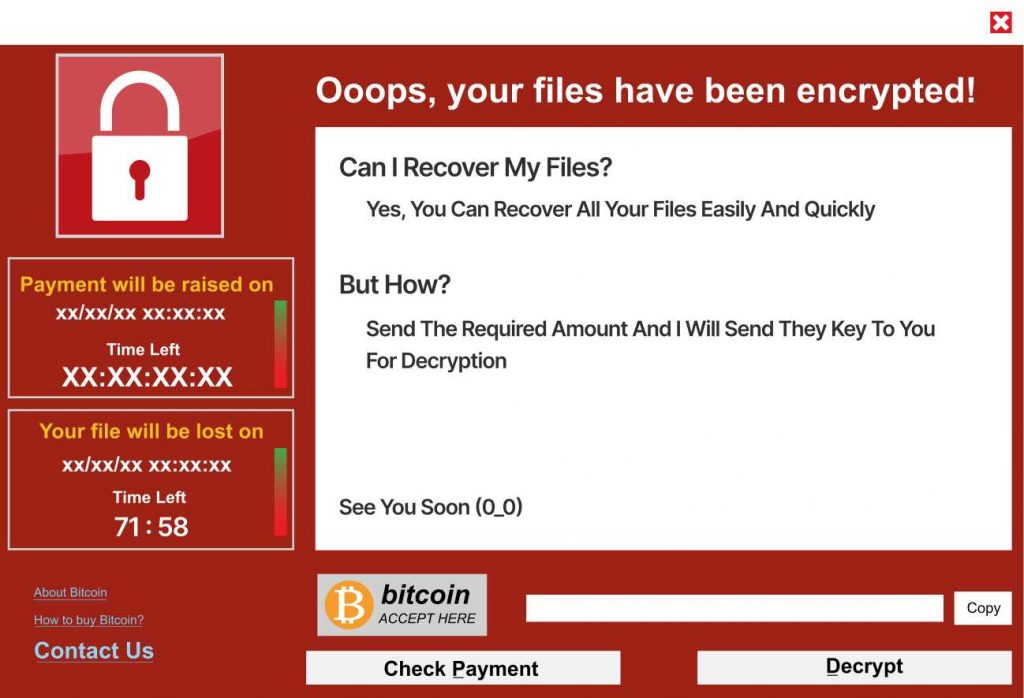
Over the years, several high-profile ransomware attacks have caused widespread damage, highlighting the severity of this cyber threat:
- WannaCry (2017) – Exploited a Windows vulnerability to infect hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide, disrupting businesses, hospitals, and governments.
- REvil (Sodinokibi) – A notorious ransomware group that targeted major corporations, demanding millions in ransom payments.
- LockBit – One of the most active ransomware strains, continuously evolving with self-spreading capabilities and double extortion tactics.
Types of Ransomware
Ransomware comes in different forms, each with unique attack methods:
- Crypto Ransomware – This type encrypts files, making them completely inaccessible. Victims must pay for a decryption key, though paying doesn’t guarantee data recovery.
- Locker Ransomware – Instead of encrypting files, this variant locks users out of their entire system, displaying a ransom message on the screen.
- Double Extortion Ransomware – Cybercriminals steal sensitive data before encrypting files, threatening to leak it online if the ransom isn’t paid, increasing pressure on victims.
Read our blog on ‘What is a Ransomware Attack?’ to get more insight on Ransomware attacks.
Key Differences Between Malware and Ransomware
Grasping the differences between malware and ransomware is essential for developing effective cybersecurity strategies. While both are forms of malicious software designed to compromise systems, they diverge notably in their objectives, attack methodologies, and the severity of their impacts on victims.
The table below will help you understand the key differences that come out in Malware vs Ransomware:
| Aspect | Malware | Ransomware |
| Definition | Broad category of malicious software designed to harm or exploit devices and networks. | Specific type of malware that encrypts data and demands ransom for decryption. |
| Purpose | Varies: can steal data, disrupt operations, spy on users, or corrupt data. | Financial extortion: demands payment for data decryption or system access. |
| Impact | Can lead to data theft, system damage, unauthorized access, or operational disruption. | Locks or encrypts data, rendering it inaccessible until ransom is paid. |
| Delivery Methods | Delivered through phishing emails, malicious downloads, infected websites, or software vulnerabilities. | Often spread via phishing emails, malicious links, or exploiting software vulnerabilities. |
| Recovery | Involves identifying and removing the malicious software, then restoring from backups. | Recovery can be complex; may involve paying the ransom or restoring from backups if available. |
| Threat Awareness | Often operates covertly, causing damage over time without user knowledge. | Immediately announces its presence with a ransom note, creating urgency. |
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for implementing effective cybersecurity measures to protect against both malware and ransomware threats.
Is Ransomware Worse Than Malware?
Yes, ransomware is often worse than malware due to its ability to encrypt critical files and demand payment for decryption, causing severe financial and operational damage. Unlike typical malware, which may slow systems or steal data, ransomware actively cripples businesses, hospitals, and governments.
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, global ransomware damages are expected to reach $265 billion by 2031, with attacks occurring every two seconds. The rise of double extortion—where hackers steal data before encrypting it—further increases the threat.
Ransomware is considered one of the most severe cyber threats today because it can halt operations, incur massive ransom demands, and lead to data breaches. Therefore, prevention through strong cybersecurity measures and backups is critical.
How To Prevent Malware and Ransomware?
Protecting your systems against malware and ransomware requires an all-in-one strategy that merges fundamental cyber hygiene with sophisticated security protocols. Here are ways to strengthen your defenses:
Basic Cyber Hygiene
- Keep Operating Systems and Software Updated: Regularly update your operating systems, applications, and antivirus software to patch vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malware and ransomware.
- Use Strong Passwords and Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Employ complex, unique passwords for all accounts and activate MFA to add an extra layer of security, making unauthorized access more difficult.
- Download Software from Trusted Sources Only: Avoid downloading software from unverified sources, as they may contain malicious code. Always obtain software from reputable vendors.
- Avoid Clicking on Suspicious Email Links or Attachments: Be cautious with unsolicited emails, especially those containing links or attachments. Phishing attacks often use these methods to deliver malware.
Advanced Protection
- Deploy Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Solutions: Implement EDR tools to monitor, detect, and respond to suspicious activities on endpoints, providing real-time protection against threats.
- Use Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): For organizations utilizing cloud services, CSPM tools help ensure that cloud configurations are secure and compliant, reducing the risk of exploitation.
- Implement Zero Trust Architecture: Adopt a Zero Trust model that requires strict verification for every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of their location, to minimize potential attack surfaces.
- Conduct Regular Cybersecurity Training for Employees: Educate employees about cybersecurity best practices, phishing threats, and safe browsing habits to reduce human error, which is often a significant factor in security breaches.
By integrating these practices into your cybersecurity strategy, you can significantly reduce the risk of malware and ransomware attacks and enhance your organization’s overall security posture.
Defend Against Ransomware and Malware Using CloudDefense.AI
CloudDefense.AI offers a comprehensive security platform designed to protect your critical assets through advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
Advanced Threat Detection and Response
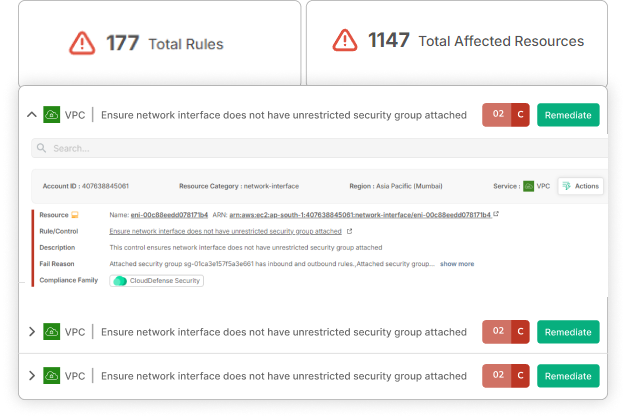
CloudDefense.AI employs cutting-edge AI and machine learning technologies to identify and mitigate evolving cyber threats swiftly. By continuously monitoring your digital infrastructure, it ensures rapid detection and response to potential vulnerabilities, keeping your systems secure.
Unified Threat Visibility and Rapid Investigation
The platform provides unified threat visibility, allowing for quick identification and assessment of security incidents. This comprehensive view enables efficient incident response, ensuring that threats are addressed promptly to minimize potential damage.
Risk-Based Prioritization and End-to-End Visibility
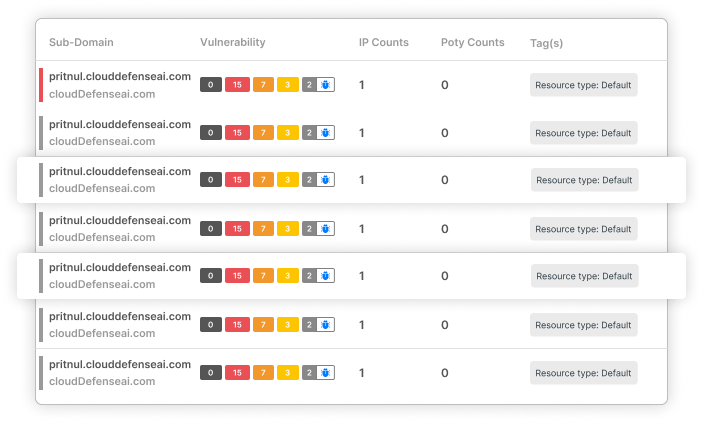
With risk-based prioritization, CloudDefense.AI helps you focus on the most critical threats, optimizing your security efforts. End-to-end visibility across your IT infrastructure ensures that no potential vulnerabilities are overlooked, providing a robust defense against ransomware and malware attacks.
Advanced Attack Simulation and API Configuration Auditing
To strengthen your defenses, CloudDefense.AI offers advanced attack simulation features, allowing you to proactively identify and address potential weaknesses. Additionally, API configuration auditing ensures that your integrations are secure, reducing the risk of exploitation through misconfigurations.
Comprehensive Security Measures
Beyond threat detection and response, CloudDefense.AI provides a suite of security measures, including secret management, IaC scanning, and container vulnerability management. These features work together to prevent loopholes and expose secrets that could be exploited by crypto-malware, ensuring a fortified security posture.
By integrating CloudDefense.AI into your cybersecurity strategy, you can effectively defend against ransomware and malware threats, ensuring the safety and integrity of your organisation’s data and infrastructure.
Book a free demo now and witness the power of AI-powered cloud security!







