Organizations continue to face security challenges in the cyber world. With the rapid escalation of cybercrime to the complexities of securing expansive IT environments. Amidst these challenges, two prominent solutions stand out: Managed Detection and Response, MDR, and Security Information and Event Management, SIEM. While both are effective in protecting organizational assets, they operate differently in scope, functionality, and approach.
In this blog, we’ll explore the differences of MDR vs. SIEM, learning more about their unique advantages and disadvantages. By understanding the distinctions between these cybersecurity solutions, organizations can make informed decisions to plan out their defense strategies effectively.
What is MDR?
MDR, or Managed Detection and Response, is a proactive outsourced cybersecurity service. It offers 24/7 monitoring of an organization’s IT environment by a team of security analysts. These analysts detect and respond to potential threats in real time, using a combination of technology and human expertise.
MDR is distinct from managed SIEM services as it includes continuous monitoring, incident response, vulnerability assessments, compliance management, and regular security posture reports. Its rising popularity is evident from predictions by Gartner, with 50% of organizations expected to adopt MDR by 2025 and 40% of mid-sized organizations relying solely on MDR by 2024.
How Does MDR Work?
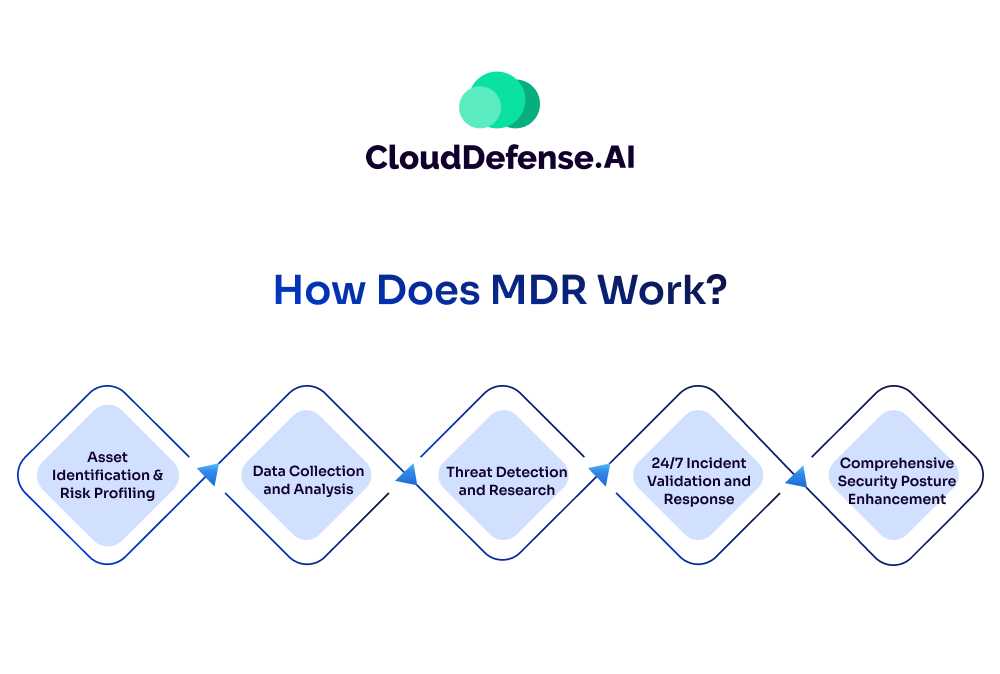
MDR operates by integrating advanced software, analytics, and expert-led services to safeguard organizations against evolving cyber threats. Here’s how it works:
1. Asset Identification and Risk Profiling
MDR begins by identifying all assets within an organization’s IT environment and profiling their associated risks. This includes assets across cloud, hybrid, and on-premises environments.
2. Data Collection and Analysis
Activity information from various sources such as logs, events, networks, endpoints, and user behavior is collected and analyzed comprehensively. This data collection helps in detecting anomalies and potential threats.
3. Threat Detection and Research
MDR providers continuously research and codify threats and vulnerabilities discovered in the wild. By leveraging this intelligence, they can quickly recognize and respond to similar threats within their clients’ environments.
4. 24/7 Incident Validation and Response
MDR analysts validate security incidents round the clock. They prioritize critical events and provide recommended response actions to mitigate threats effectively. This ensures that threats are promptly identified and remediated.
5. Comprehensive Security Posture Enhancement
MDR goes beyond incident response. It assists organizations in enhancing their overall security posture by offering services such as threat hunting, investigation, guided response, and remediation. These services aim to not only address existing threats but also prevent future incidents.
What is SIEM?
SIEM, or Security Information and Event Management, integrates security event management and security information management. SEM analyzes real-time log and event data for immediate threat detection, while SIM provides a historical view of security logs and trends. Acting as the cornerstone of a SOC, SIEM ingests and correlates vast amounts of data from IT systems and security devices.
It enables rule configuration for alert generation based on specific data patterns and integrates threat intelligence for enhanced detection. SIEM aggregates and normalizes data from various security solutions to provide a unified view of an organization’s security posture. Through continuous monitoring, analysis, and reporting, SIEM helps organizations proactively respond to security incidents and threats.
How Does SIEM Work?
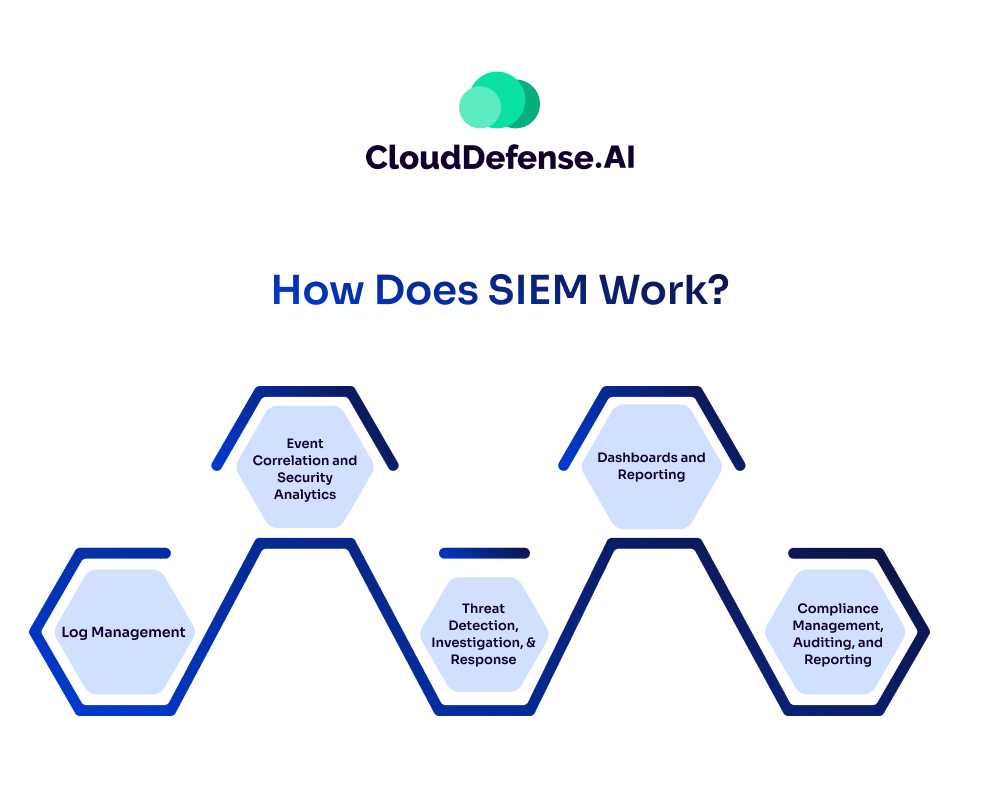
SIEM functions as a vital cybersecurity tool by collecting, aggregating, and analyzing data from diverse sources within an organization’s IT environment in real-time. It employs predetermined rules to detect and generate alerts for potential security threats. SIEM software tackles common security team challenges by managing logs comprehensively, facilitating threat detection, investigation, and response, and aiding compliance management. Key aspects of SIEM functionality include:
1. Log Management
SIEM consolidates log data from various sources, parsing and enriching it for easier analysis and long-term storage.
2. Event Correlation and Security Analytics
Utilizing rules and statistical correlations, SIEM provides actionable insights during forensic investigations, identifying and mitigating cyber threats swiftly.
3. Threat Detection, Investigation, and Response
SIEM streamlines incident management with features like SOAR, case management, and playbooks, enhancing response efficiency and effectiveness.
4. Dashboards and Reporting
SIEM presents real-time threat activity through intuitive dashboards, enabling security analysts to interpret context and drill down for further investigation. It also facilitates report generation and integration with other software for advanced insights.
5. Compliance Management, Auditing, and Reporting
SIEM aids organizations in meeting regulatory compliance requirements by automating compliance monitoring, analysis, and reporting.
MDR vs. SIEM
MDR and SIEM solutions serve to enhance organizational security, yet they diverge in several critical aspects which are mentioned below in the table.
| Aspect | MDR | SIEM |
| Focus | Detection and response to unknown threats, including zero-day attacks | Monitoring known threats and identifying anomalies |
| Technology vs. Human Expertise | Relies on a combination of technology, processes, and human expertise | Primarily relies on hardware and software for event detection and analysis |
| Reactive vs. Proactive | Proactive threat hunting and detection | Reactive approach, generates alerts based on collected data |
| Cost | Generally more cost-effective, suitable for organizations lacking complex environments or an in-house SOC | Often includes substantial expenses in terms of finances and time |
Choose the Right Solution for Your Business
Choosing between SIEM and MDR hinges on an organization’s security priorities and resources. SIEM suits those focusing on compliance, while MDR caters to advanced threat detection and response. Combining both enhances security comprehensively. Considerations include budget, team expertise, and the organization’s size and maturity. For teams aiming to scale, SIEM solutions like CloudDefense.AI provide focused threat detection. Careful assessment aligns the chosen solution with specific security needs, ensuring strong defense strategies.
Final Words
In conclusion, while the choice between SIEM and MDR may seem challenging, the optimal strategy often involves utilizing both solutions for comprehensive security coverage. Although replacing SIEM with MDR might not be advisable, integrating managed SIEM can provide excellent value.
MSSPs and SIEM tools are likely to incorporate elements of MDR, further blurring the lines between the two solutions. Understanding the differences between MDR and SIEM can help you in making informed decisions. With the right vendor and solution in place, businesses can confidently defend against a wide range of threats.
Consider going for CNAPPs such as CloudDefense.AI to get a complete security solution within one platform. Book a free demo now to get hands-on experience.







