What is Multi-Cloud?
Multi-cloud refers to the use of services from multiple public cloud providers simultaneously. In this setup, an organization integrates several public clouds from different providers, rather than relying on a single vendor for all cloud services. This approach enables a company to utilize various IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS offerings according to their specific needs.
Multi-cloud deployments can serve various purposes, such as enhancing redundancy and system backup, ensuring that services remain available even if one provider experiences an outage. Additionally, businesses may choose different cloud vendors for distinct services to use the best capabilities each provider offers.
What is Multi-Cloud Security?
Multi-cloud security refers to the strategies and technologies implemented to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in a multi-cloud environment, where organizations use services from multiple cloud providers. This approach ensures consistent security across public, private, and hybrid clouds while addressing challenges like diverse configurations, varying compliance requirements, and increased attack surfaces.
Effective multi-cloud security focuses on unifying security policies, monitoring tools, and threat detection mechanisms to mitigate risks. It simplifies the complexity of managing security across multiple platforms and reduces the likelihood of misconfigurations that can lead to vulnerabilities.
The rise of multi-cloud adoption has shifted the focus from securing isolated environments to building comprehensive, interoperable defenses that safeguard resources across providers. These solutions leverage automation, advanced analytics, and centralized controls to maintain visibility and respond to threats effectively.
Benefits of Multi-Cloud Security
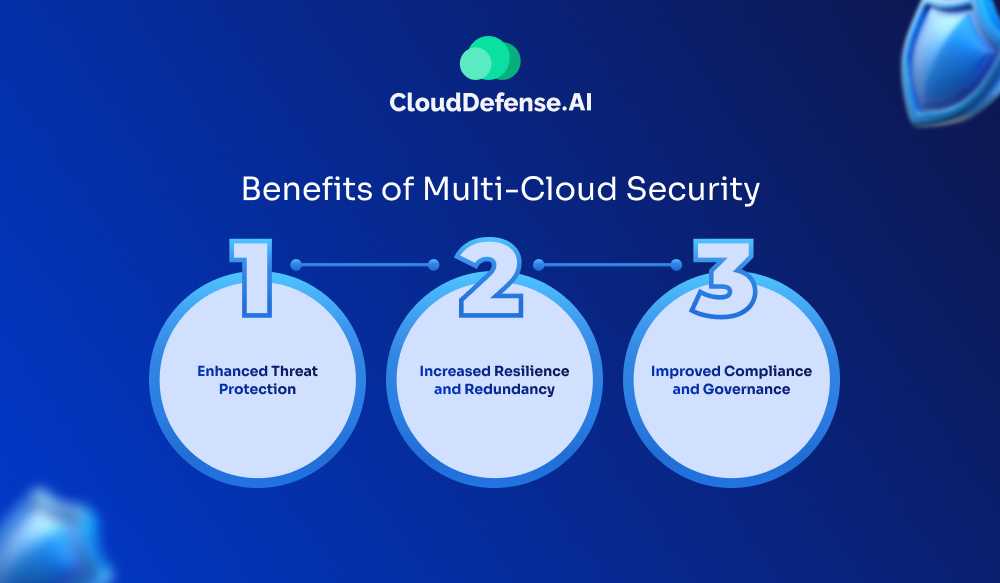
Adopting a multi-cloud security strategy offers several advantages that empower businesses to strengthen their operations and reduce vulnerabilities. Here are the key benefits of Multi-cloud security.
- Avoiding Vendor Lock-In: Multi-cloud security prevents reliance on a single provider, giving businesses the flexibility to choose the best solutions and avoid being tied to one vendor’s limitations or price structures.
- Boosting Performance: By using multiple cloud providers, businesses can optimize workloads for better performance, reducing latency and ensuring that resources are used efficiently across diverse platforms.
- Lowering Risk: A multi-cloud environment diversifies risk. If one cloud provider experiences downtime or a security breach, operations can continue with minimal disruption through other platforms.
- Meeting Compliance Requirements: Organizations can choose cloud services that align with specific regulatory requirements, ensuring adherence to data protection laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or others across different jurisdictions.
- Saving Costs with Multi-Cloud: With a competitive multi-cloud strategy, businesses can negotiate better pricing or optimize cloud usage to achieve significant cost savings.
Multi-Cloud Security Challenges

While multi-cloud security offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges that organizations must address. These challenges include management complexity, skills shortages, increased costs, compliance issues, interoperability problems, and heightened risks of data loss and breaches.
1. Complexity and Management Difficulties
Managing multiple cloud environments introduces significant complexity, primarily due to the need for more standardization and visibility across platforms. This complexity makes it challenging to monitor and manage security, compliance, and governance effectively. The diverse and often incompatible nature of different cloud providers’ services requires specialized skills and knowledge, which can be difficult to acquire and maintain.
2. Skills and Knowledge Gaps
The effective management of multi-cloud security necessitates a workforce with specialized expertise in various cloud platforms. However, there is often a need for more skilled personnel, which increases operational risks. With adequately trained staff, organizations may be able to implement and maintain strong security measures, leaving their cloud environments vulnerable to threats.
3. Increased Costs
Implementing a multi-cloud security strategy can be expensive. Organizations may need to invest in new tools, processes, and personnel to manage their multi-cloud environments effectively. These additional costs can be substantial, particularly for businesses that need to build out their security capabilities from scratch.
4. Compliance and Regulatory Challenges
Different cloud providers are subject to varying compliance and regulatory requirements, complicating efforts to maintain consistent compliance across all cloud environments. Ensuring that all data and applications adhere to relevant standards can be difficult, requiring continuous monitoring and adaptation to changing regulations.
4. Interoperability Issues
Using multiple cloud providers can lead to interoperability issues, especially when trying to move workloads and data between different environments. Different clouds may use various protocols and standards, creating challenges in ensuring seamless integration and communication between platforms. This can hinder operational efficiency and flexibility.
5. Risk of Data Loss or Corruption
The risk of data loss or corruption is heightened in multi-cloud environments, particularly if adequate backup and recovery processes are not in place. Organizations must ensure strong data protection measures to protect against potential data breaches or failures that could compromise critical information.
6. Increased Risk of Data Breaches
Storing sensitive data across multiple cloud environments can amplify the risk of data breaches and theft. If an attacker gains access to one cloud environment, they could potentially use it as a starting point for further attacks, moving laterally across interconnected systems to access and exfiltrate sensitive data. strong security measures and monitoring are essential to mitigate this risk.
Multi-Cloud Security Architecture
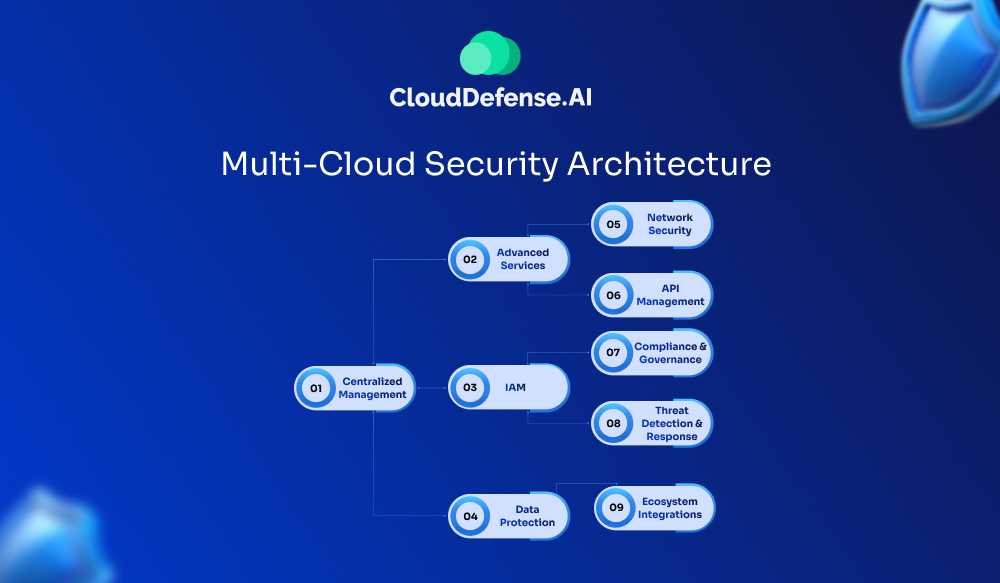
Multi-cloud security architecture is a structured approach designed to protect data and applications across diverse cloud environments. Let’s check out some of the key components below:
1. Centralized Management
Includes dashboards, reporting, and logging to assist with governance and troubleshooting across disparate environments.
2. Advanced Services
Includes load balancing, content delivery networks, firewalls, WAF, and ZTNA.
3. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Controls user and application access to cloud resources, ensuring consistent security practices across all cloud providers.
4. Data Protection
Includes encryption of data at rest and in transit, along with backup and disaster recovery plans to ensure data availability during outages.
5. Network Security
Involves implementing secure network connections and protocols to protect data in transit across different cloud providers.
6. API Management
Secures applications and APIs spread across multiple cloud architectures to deliver responsive and reliable user experiences.
7. Compliance and Governance
Ensures implementation of policies across all cloud services to meet regulatory requirements and industry standards.
8. Threat Detection and Response
Improves security response with controls across different cloud environments for efficient detection and remediation.
9. Ecosystem Integrations
Supports advanced application delivery, security capabilities, L7 gateways, and automation tools for software development and deployment
Multi-Cloud Security Best Practices
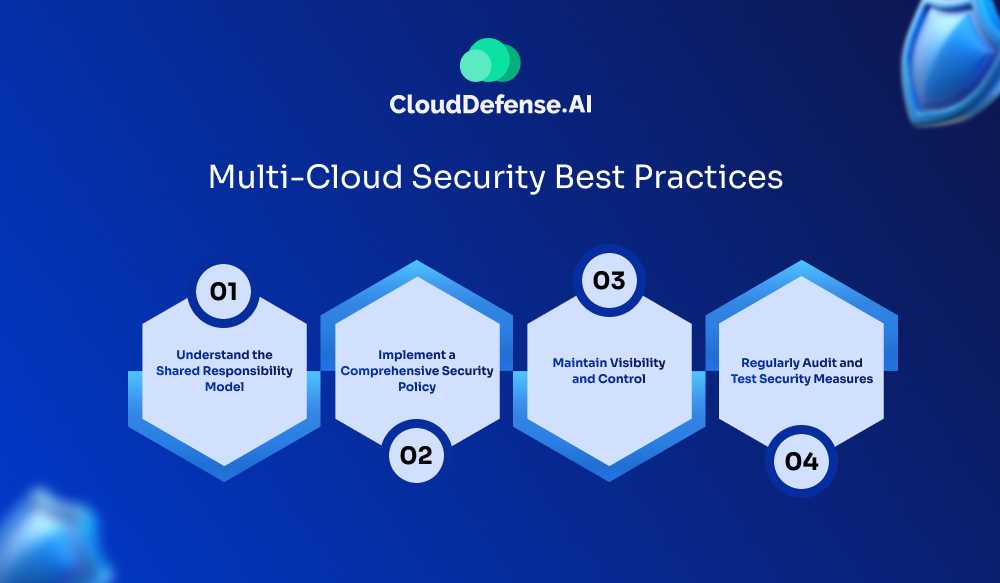
Implementing multi-cloud security effectively requires a strategic approach. These best practices can help organizations maximize security benefits while minimizing risks associated with managing multiple cloud environments.
1. Understand the Shared Responsibility Model
Recognizing the security responsibilities shared between cloud providers and customers is important. While providers secure their infrastructure, customers must secure their data and applications. This distinction ensures top security measures are in place, such as protecting against cyber threats at the application and API layers.
2. Implement a Comprehensive Security Policy
Create a strong, end-to-end security policy that covers data centers and all cloud environments. This policy should include encryption, access controls, and application-level security (L7). Regularly updating and reviewing the policy to align with best practices and compliance standards is important. Using automated protections with telemetry, behavioral analytics, and machine learning can enhance security effectiveness.
3. Maintain Visibility and Control
Centralized monitoring and management tools provide real-time visibility into cloud environments, enabling quick detection and response to security incidents. These tools are vital for maintaining control over a multi-cloud infrastructure and ensuring consistent security practices.
4. Regularly Audit and Test Security Measures
Regular audits and security tests are necessary to identify vulnerabilities and validate the effectiveness of security measures. Conducting vulnerability assessments, penetration tests, and security audits at both the infrastructure and application layers helps address potential security gaps proactively, enhancing overall security posture.
Future of Multi-Cloud Security
The future of multi-cloud security is increasingly critical as more organizations adopt multi-cloud strategies. With 89 percent of enterprises distributing applications and services across multiple clouds, and 80 percent combining private and public clouds, protecting data becomes a necessity. As security incidents are inevitable, industries handling sensitive data, like banking, healthcare, and government, face heightened risks.
The shift towards hybrid work and global operations introduces new vulnerabilities, making comprehensive security measures essential. Despite the prevalence of sensitive data transfers, the Ponemon Institute’s 2022 study reveals that 55 percent of organizations transfer this data to the cloud without encryption or masking. Future security efforts must focus on strong encryption, data masking, and tokenization to protect the data perimeter in complex multi-cloud environments.
Final Words
Multi-cloud adoption can help companies to maintain agility and competitive advantage. Understanding the challenges and requirements of multi-cloud environments is essential for navigating potential risks.
By adopting a cloud-first mentality and implementing security solutions such as the ones offered by CloudDefense.AI, organizations can maintain control and secure their data effectively. Multi-cloud security ensures strong protection and operational resilience in an ever-evolving digital world.







