Definition – What is a Virtual Data Center?
A Virtual Data Center is basically a data center in the cloud. Instead of buying all the physical servers, storage, networking gear, and whatnot, you rent computing resources from a cloud provider. It’s all virtual, but it functions just like an on-premises data center.
The big upside is that you don’t have the huge capital costs of building out a traditional data center. You just pay for what you use in the cloud when you need it. Need more storage or computing power? Easy, just provision more virtual resources. Less demand? Scale back down. VDCs give you that top-notch flexibility and scalability that on-premises data centers can’t match. All while the cloud vendor handles the underlying infrastructure.
Key Components of Virtual Data Center
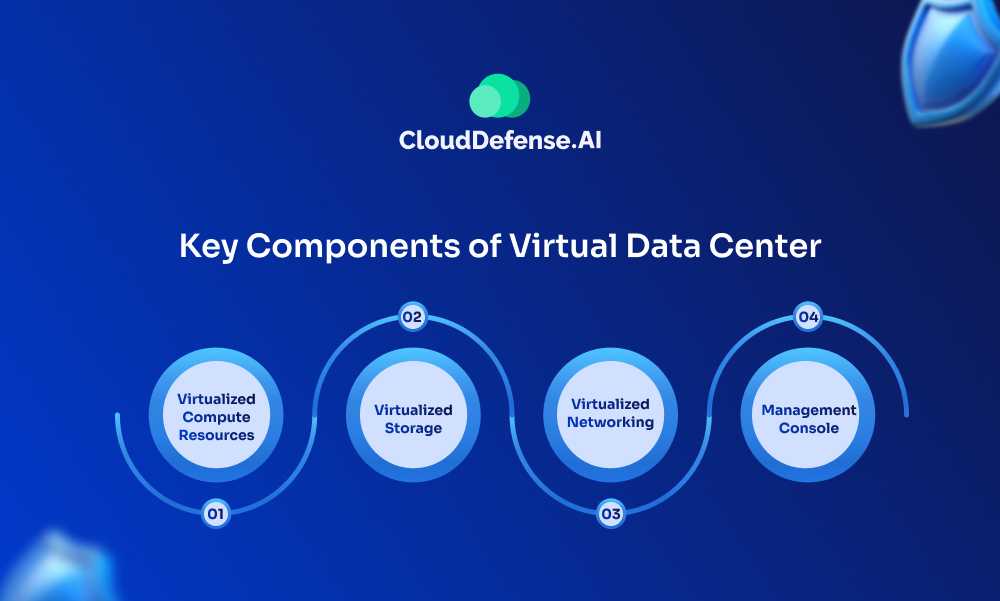
A typical virtual data center consists of the following key components:
- Virtualized Compute Resources: Virtual machines (VMs) or instances that provide the processing power for running applications and workloads.
- Virtualized Storage: Virtual storage arrays or volumes that offer storage capacity for data and applications.
- Virtualized Networking: Virtual switches, routers, firewalls, and load balancers that enable secure network connectivity and traffic management.
- Management Console: A web-based interface or control panel that allows customers to provision, configure, and manage their virtual data center resources.
Traditional Data Center VS. Virtual Data Center
Let’s say you’re running a small e-commerce business that’s rapidly growing. Your IT needs constantly change as you onboard new employees, add more online offerings, and deal with traffic spikes during sales.
With a traditional data center, you’d have to invest millions upfront in physical servers, storage arrays, networking gear, and facilities to house it all. Not only is that capital expense ridiculously high, but scaling that infrastructure up or down is a nightmare of procurement cycles and tech refreshes.
A virtual data center, on the other hand, lets you rent computing resources from a cloud provider like AWS, Microsoft or Google on-demand. Need more virtual servers or storage for that hot new product line? A few clicks and you’ve got it. Slow season coming up? Easily scale back down and only pay for what you’re using.
The differences really come down to cost, flexibility, and who manages the underlying infrastructure. Let’s look at some of the key differences in a table:
| Feature | Traditional Data Center | Virtual Data Center |
| Computing Resources | Physical servers/hardware you purchase | Virtual machines/instances rented from cloud |
| Storage | Your own disk arrays/SANs | Cloud storage services like EBS, blob storage |
| Network | Physical routers/switches/firewalls | Virtual cloud networking |
| Scalability | Limited by physical capacity | Scale virtualized resources up/down easily |
| Capital Costs | Very high upfront expenditure | Pay-as-you-go, no big upfront investment |
| Responsibility | You maintain/upgrade all hardware | Cloud vendor manages underlying infrastructure |
So in a nutshell, VDCs trade capital expenditure for operating expenditure, giving you way more agility and flexibility to respond to changing business needs. The cloud vendor handles maintenance and hardware refreshes for you.
Key Benefits of A Virtual Data Center
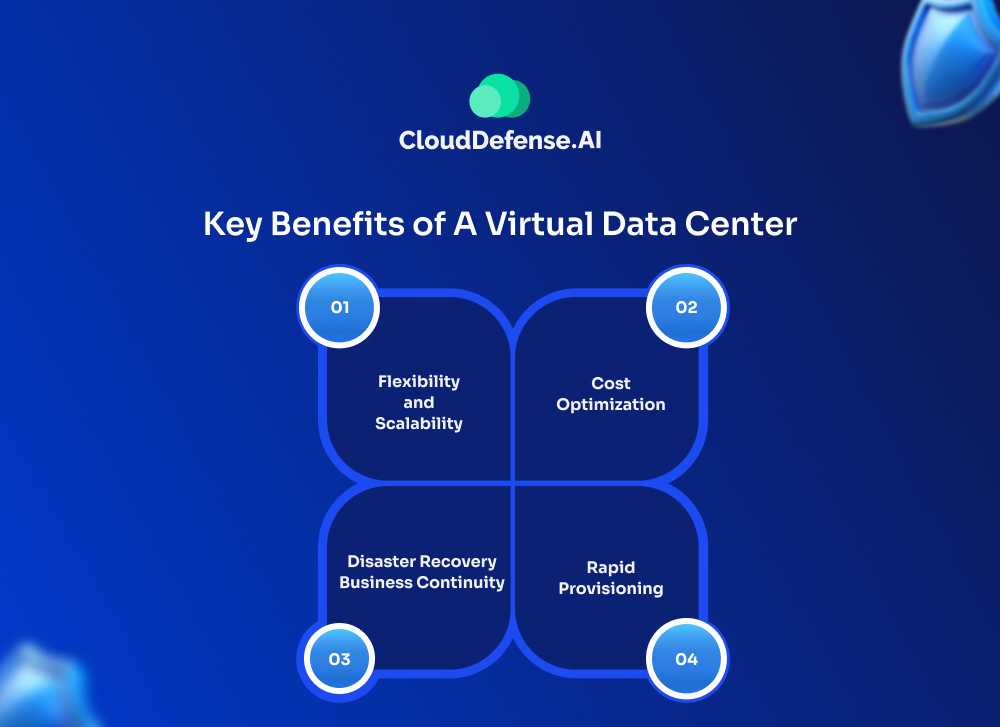
Flexibility and Scalability
One of the biggest draws of VDCs is how flexible and scalable they are compared to traditional data centers. Need more computing power for a new project? Just provision some new virtual machines or containers with a few clicks. Massive traffic spike coming? Scale up cloud resources temporarily to handle the load. When demand dies down, scale back down easily. This elasticity lets you align your IT capacity precisely with demand at any given time.
Cost Optimization
With a traditional data center, you’re paying massive upfront costs for servers, storage, networking gear, plus ongoing expenses for power, cooling, maintenance, etc. With VDCs, those heavy capital expenditures go out the window. You just pay for the cloud resources you consume on a usage-based model. No more overprovisioning assets you may not fully utilize. This pay-as-you-go pricing is a game-changer for optimizing IT costs.
Rapid Provisioning
In an on-prem data center, procuring and deploying new hardware is a lengthy process of supply chain issues, installation projects, etc. With VDCs, you can literally spin up new virtualized infrastructure in minutes through self-service portals and APIs. This agility translates directly to faster delivery of new apps and services.
Disaster Recovery/Business Continuity
Let’s face it, datacenter outages are an ugly reality. With a VDC, you can design robust backup, replication, and recovery solutions leveraging geographic distribution and redundancy across multiple cloud regions and availability zones. Way simpler than having to rebuild a whole new physical site.
Anyway, you get the idea – virtual data centers bring some killer advantages in terms of agility, cost optimization, and reliability compared to the old-school on-prem model.
The Synergy Between Virtual Data Centers and Cloud Computing
Virtual data centers (VDCs) and cloud computing are like two sides of the same coin. VDCs provide the underlying infrastructure, while cloud computing offers the services that leverage that infrastructure.
VDCs as the Engine Room:
Imagine a traditional data center – a massive warehouse filled with rows of servers. A VDC takes this concept and virtualizes it. Instead of physical servers, a VDC utilizes a pool of shared computing resources like processing power, storage, and networking. These resources are managed by hypervisor software, which acts like a conductor, allocating them efficiently.
Cloud Computing – Delivering on Demand:
Cloud computing uses the basic strength of VDCs and changes it into services people can use. These services might be on-demand storage, virtual machines, or even advanced analytics tools. Consider it this way: a power plant makes electricity, but businesses and homes need devices to use it well. Cloud services are like those devices using the energy from VDCs effectively.
The Synergy:
Here is where the magic takes place. VDCs give scalability and flexibility that cloud computing loves to use. Cloud providers can simply give resources as users need them, so businesses do not have to manage their own physical equipment. This means:
- Cost-efficiency: Businesses only pay for the resources they use.
- Scalability: Resources can be easily scaled up or down as needed.
- Agility: Businesses can quickly deploy and access new applications.
- Reliability: Cloud providers offer robust infrastructure with redundancy measures.
How Does a Virtual Data Center Work?
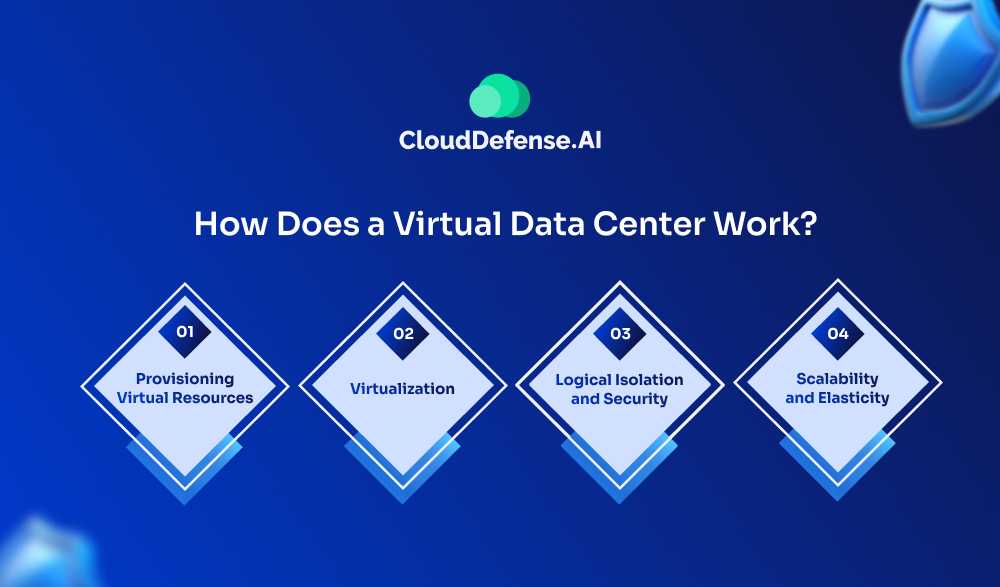
The virtual data center is hosted and managed by a cloud service provider, who owns and maintains the underlying physical infrastructure, including servers, storage arrays, and networking equipment. Here’s how it typically works:
Provisioning Virtual Resources
First, you must hit up that slick web-based console or control panel the provider hooks you up with. From there, you can pick and choose the virtual components you need, like virtual machines (VMs), storage volumes, and all the networking goodies like virtual switches, routers, and firewalls. It’s a piece of cake, even for the non-techie homies out there. Just a few clicks, and you can spec out your virtual resources with the CPU power, RAM, storage space, and network configs you’re looking for.
Virtualization
Now, behind the scenes, the service provider’s physical infrastructure is virtualized using some serious hypervisor tech. This virtualization layer is like the secret sauce that separates the physical hardware from the virtual machines, allowing multiple VMs to run simultaneously on a single physical server while keeping everything nice and isolated.
Logical Isolation and Security
Security is very important in the virtual data center business, so providers take it seriously. Even if many virtual data centers are using the same physical hardware, they keep each customer’s environment logically separate and secure to make sure privacy is safe and no uninvited guests can get in.
They use methods like virtual private networks (VPNs), firewalls, and access control lists (ACLs) for making this separation. Every virtual data center receives its own exclusive network part, with information moving safely between the virtual parts inside that section.
Scalability and Elasticity
One great thing about virtual data centers is how easily you can adjust resources up or down based on what your workload needs. In traditional physical data centers, scaling usually means a lot of work to get new hardware, set it up, and configure everything. But with virtual data centers, you can add or take away virtual resources quickly and without trouble.
How to Secure the Virtual Data Center
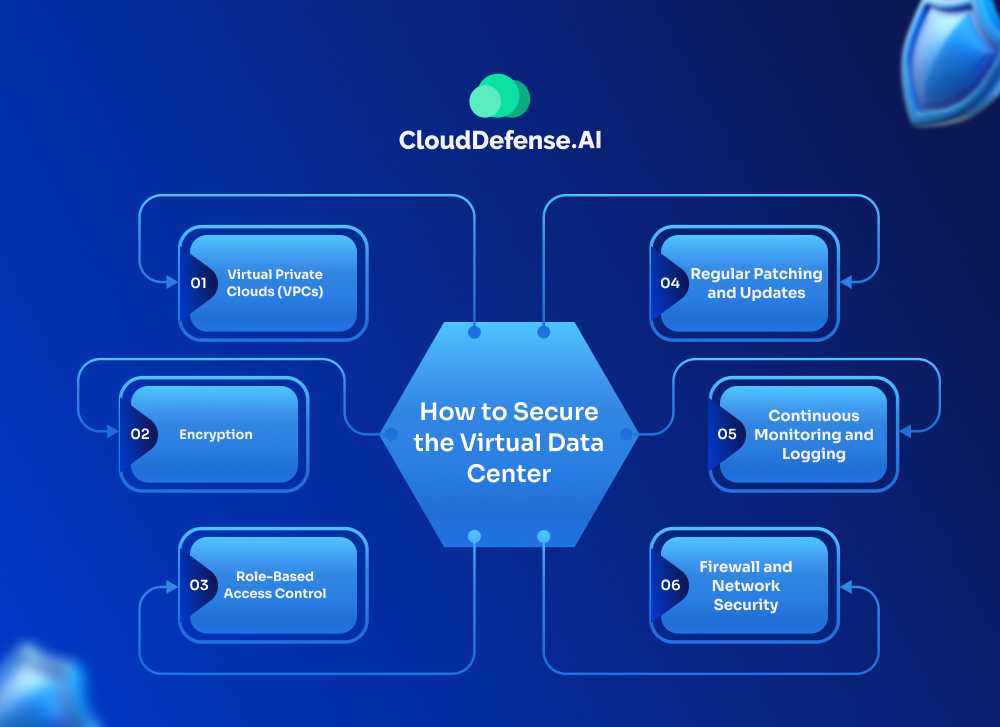
Security is very serious in this game, so it’s important to make sure that virtual data centers are protected more strongly. Here is how to do it:
Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs)
One of the most cool ways to keep your virtual data center safe is by creating a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). VPCs let you have full control over your virtual network, where you can make subnets, arrange routing tables and establish network gateways. You are also able to adjust security features like network ACLs and security groups that control the traffic coming in and out of your VPC.
Encryption
Encryption is the key to keeping your information safe and secure. Most of these service companies provide ways to lock data that is stored and that is being sent, using common encryption methods like AES-256. This makes sure that even if somebody gets your data, they can’t read it without the correct keys to decode it.
Role-Based Access Control
In a virtual data center, there are many users and teams that may access various resources. In this situation, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) becomes important. RBAC helps you set up particular roles and give rights, so only approved people can use and handle certain resources.
Firewall and Network Security
Firewalls are like a virtual data center’s first protection against unwanted access and harmful traffic. Many service providers give you managed firewall services that you can adjust to manage inbound and outbound traffic according to rules that have been determined beforehand. You can also put in extra steps for keeping your network safe, like using systems for checking and stopping any dangers. These include intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), which watch for bad activities and stop them where they can.
Continuous Monitoring and Logging
Keeping an eye on your virtual data center carefully is very important to finding and dealing with security troubles. Cloud security solutions usually give you tools to watch and record things, which help you keep track of what’s happening, how much resources are used, and look at system logs for signs of possible security problems.
Regular Patching and Updates
In the same way as in the real world, data centers that are virtual also need to be kept current with new security fixes and program updates. Usually, providers of these services take care of updating and patching the basic infrastructure, but you must pay attention to updating your virtual machines and software yourself.
Final Words
The future of data centers is surely virtual. Do not stay behind while your competitors move quickly with the flexibility and growth potential of VDCs. Virtual data centers give the opportunity to cut IT costs, make better use of resources, and quickly adjust to changing needs. It is time to leave behind the limits of physical hardware and welcome the cloud-based transformation. Make the switch today and get the true potential of your digital future!







