Firewalls work on inspecting traffic to a system and block any activity that it identifies as a threat. Generic firewalls identify malicious traffic based on pre-defined policies. Next-generation firewalls, on the other hand, are a notch higher by providing additional security to the system.
So, what is a next-generation firewall?
A Next-Generation Firewall, or NGFW, is the third generation of firewalls. It offers additional features in comparison to additional firewalls that allow it to counter threats more effectively.
A rise in cybercrime has resulted in traditional firewalls being ineffective against most modern cyber threats. This has resulted in it evolving into NGFW, which is better, faster, and more secure. Read on as we discuss Next-gen firewall and its advanced capabilities.
Let’s dive right in!
What is a Next-Generation Firewall?
As mentioned earlier, a next-generation firewall is an update to legacy firewalls, offering more sophisticated capabilities. It helps to effectively counter threats at the application level of the TCP/IPS stack to implement an intrusion prevention System, malware protection, and other required security features.
NGFW and Firewalls can be compared to security checks at airports where passengers are required to go through two processes of vetting. The first security check just verifies the flight tickets, whereas the second security check inspects the possessions of the passengers.
Firewalls are the first security check, which only checks if the data is going to a legitimate location. On the other hand, NGFW is the second security check, which not only verifies the location of the data but also helps in identifying any malicious content that might affect the system.
Next-generation Firewall Features
Next-gen firewalls are known to offer much more sophisticated features compared to traditional firewalls. We have laid down some of the features of next-generation firewalls below that can help you differentiate between these two.
Deep Packet Inspection:
Traditional network firewalls analyze data at different levels of the TCP/IP communication model, starting from the lowest layer (hardware/data link) and moving up to the application layer.
However, next-generation firewalls go beyond this by also examining traffic at higher layers, especially the application layer.
In simpler terms, next-gen firewalls not only look at basic network data but also understand the specific applications in use, making it easier to spot any unusual or suspicious activities based on what’s considered normal.
Intrusion Prevention System:
By examining data at higher levels in the TCP/IP framework, next-generation firewalls become more effective at spotting and stopping threats. They can keep an eye out for potentially harmful actions by looking at patterns of behavior or anything out of the ordinary.
If something seems fishy, these firewalls can put a stop to it by blocking the suspicious data from entering the network.
High Performance:
The ability to handle a lot of network traffic without slowing down is a crucial aspect of next-generation firewalls. These advanced firewalls come with various security features that require high processing power, so having high performance is essential to ensure that business operations continue smoothly without interruptions.
DDoS protection:
Denial of service (DoS) attacks are essentially attempts to harm a service by overwhelming it with fake requests, causing it to become unresponsive to genuine user requests. Distributed DoS (DDoS) attacks take this a step further by using multiple computers to flood the service with these malicious requests.
Next-generation firewalls have an edge over traditional ones in dealing with these attacks because they are “stateful.” Being stateful allows these firewalls to examine various aspects of incoming connection requests in comparison to the characteristics of established connections.
This capability helps in spotting fake requests, even when they might look different or originate from different computers.
Benefits of Next-Generation Firewalls
Compared to traditional firewalls, next-generation firewalls offer significantly improved and more robust security. Traditional firewalls are somewhat limited in their capabilities. They can block traffic through specific ports, but they cannot enforce rules tailored to specific applications, safeguard against malware, or detect and stop unusual activities effectively.
This limitation can allow attackers to sneak in through unconventional ports, which a next-generation firewall would swiftly thwart.
Thanks to their contextual awareness and the ability to receive updates from external threat intelligence networks, next-gen firewalls excel in protecting against a wide range of advanced threats that are constantly evolving.
Moreover, they often employ intelligent automation to stay relevant to security policies, reducing the need for frequent manual configuration from the security team.
To sum it up for you, next-gen firewalls are like super-smart security guards that adapt and learn, making them a formidable defense against an ever-changing landscape of cyber threats. The advantages of next-generation firewalls outweigh traditional firewalls, explaining the increasing adoption in companies.
How does a Next-Generation Firewall Work?
Next-Generation Firewall provides more enhanced protection from application and internet traffic. The infographic below shows us how data packets go through an NGFW firewall.
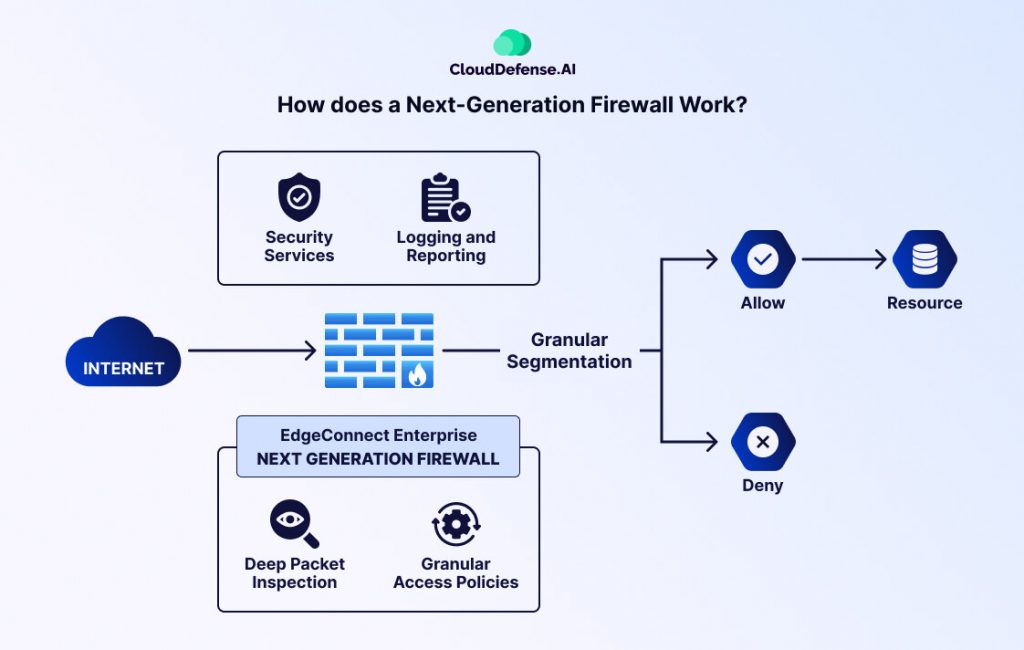
Next-generation Firewall vs. Traditional Firewall:
Let’s check out this chart to receive a detailed comparison of Next-generation firewalls and traditional firewalls:
| Traditional Firewall | Next-generation Firewall | |
| How Secure Is It? | Limited protection capabilities. Doesn’t provide all-around security. | Next-generation firewall protection is top-tier. It is more secure compared to Traditional Firewalls. |
| Does It Offer Visibility? | Provides less visibility as it covers only lower TCP/IP layers. | Provides complete visibility as it covers all TCP/IP layers. |
| How Do They Provide Protection? | They inspect ports. They can only work with applications that are developed with OSI model layers 2 and 4. | They can help to filter application packets that are based on layer 7 of the OSI model. |
| What Other Services Do They Provide? | Limited services provided. | Provides more advanced services such as anti-malware, IDS/IPS, and content filtering. |
What is Application Awareness and Control?
Application control is a security measure crucial for managing and regulating application usage within organizational networks. By accurately identifying and classifying applications regardless of ports or protocols, it enhances security by enabling the enforcement of tailored policies.
These policies govern application access, features, and bandwidth usage, effectively mitigating security risks such as malware propagation and unauthorized access.
Additionally, application control optimizes network performance by prioritizing critical applications and allocating bandwidth resources accordingly, ensuring efficient operation. Its adaptability with applications that may utilize standard protocols over non-standard ports, highlights its importance in modern cybersecurity strategies.
Difference Between Next-Gen firewalls and Unified Threat Management
What is UTM?
Unified Threat Management, or UTM, is a complete cybersecurity solution that integrates multiple security functionalities into a single, unified platform. This approach aims to simplify the management and deployment of various security measures, offering businesses a holistic defense strategy against a wide range of cyber threats.
Here’s an in-depth look at what UTM includes:
Unified Security Services
At the core of UTM is the integration of diverse security services, including antivirus, intrusion detection/prevention (IDS/IPS), VPN, spam filtering, and URL filtering. By consolidating these security measures into a single device or platform, UTM smoothens the implementation and administration of security policies.
Broad Coverage
UTM solutions provide extensive protection against various cybersecurity threats, including malware, phishing attacks, data breaches, and other malicious activities. This broad coverage ensures that organizations have robust defenses in place to protect their networks, endpoints, and data assets from evolving threats.
Single Management Interface
One of the key benefits of UTM is its centralized management interface, which enables administrators to oversee and control all security services from a unified dashboard. This single-pane-of-glass approach enhances visibility and simplifies the task of configuring, monitoring, and managing security policies across the entire network infrastructure.
Scalability and Flexibility
UTM solutions are designed to be scalable and adaptable to meet the evolving security needs of businesses. Whether it’s expanding network infrastructure or adding new security functionalities, UTM platforms offer flexibility to accommodate changes without compromising security effectiveness.
This scalability makes UTM particularly well-suited for small to medium-sized businesses that require cost-effective and versatile security solutions.
Differences: NGFW vs. UTM
- Scope of Protection: NGFWs focus on advanced threat detection and prevention, with specialized capabilities for deep packet inspection and application-level security. UTM systems offer a broader range of security services encompassing antivirus, IDS/IPS, VPN, and content filtering.
- Target Audience: NGFWs are often deployed in large enterprises with high-intensity traffic environments, while UTM solutions are preferred by SMBs seeking an all-in-one security solution that is easy to manage and scale.
- Granularity vs. Integration: NGFWs provide granular control and visibility into individual applications and network traffic, whereas UTM platforms prioritize integration and simplicity, offering a unified approach to security management.
- The Sophistication of Threat Detection: NGFWs use advanced technologies like machine learning and behavioral analysis to detect and mitigate sophisticated threats, whereas UTM solutions focus on complete coverage and ease of use.
Challenges of Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW)
NGFWs are surely way ahead of legacy firewalls, but just like other advanced technologies, there are challenges associated with implementing them.
- Implementation Is Complex: Next-gen firewalls have many advanced features that require skilled IT professionals to handle them.
- Processor Overload: Filtering traffic through multiple security features can affect processor and network performance. This, in turn, can slow down other processes running on the system.
- False Alert: NGFWs inspect traffic very strictly, and there are instances when it mark legitimate data as a threat.
- Integration With Other Security Programs: It has been noticed that it is hard to integrate Next-generation firewalls with other threat identifier software. This is mainly due to proprietary issues and the complexity of these firewalls.
- Expensive: Next-generation firewalls come with many advanced features that regular firewalls do not possess. This results in NGFW being priced much higher.
FAQ:
Take a look at some of the queries that people have regarding NGFW.
Next-Generation Firewall works on which layer?
Next-generation firewalls work on layer 7 of the OSI model. This is an upgrade to regular firewalls that only work on layers 2 and 4. Working on layer 7 helps NGFW to inspect data deeply.
Why do you need a Next-Generation Firewall?
NGFWs are much smarter compared to generic firewalls. Their smart capabilities allow them to carry out deep analysis and inspection of packets on layer 7 of the application model. The comprehensive features offered by NGFW help to prevent threats more effectively.
Are Next-Gen Firewalls hardware-based or software-based?
They are both hardware-based and software-based. Some physical Next-generation firewall appliances are deployed to protect internal company networks. On the other hand, they are also deployed as software based on clouds to protect from threats coming from outside the company.
What Is the Difference Between a Firewall and an NGFW?
Firewalls are reliant on static inspection of applications. With more dynamic applications coming into the market, firewalls cannot identify threats coming from them. NGFW works on the seventh layer of the application model, providing more security than a traditional firewall.
Conclusion
By understanding “What Is a next-generation firewall,” we empower ourselves with the knowledge to safeguard our networks against a multitude of sophisticated threats. This intelligent, context-aware firewall offers us a powerful defense against an array of threats, ensuring that our digital environments remain secure and resilient.
As we move forward in the digital age, embracing the potential of next-gen firewalls is essential to fortify our defenses and protect our data and systems from the ever-rising threats in the industry.







